©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Methodol. Nov 20, 2021; 11(6): 294-301
Published online Nov 20, 2021. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v11.i6.294
Published online Nov 20, 2021. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v11.i6.294
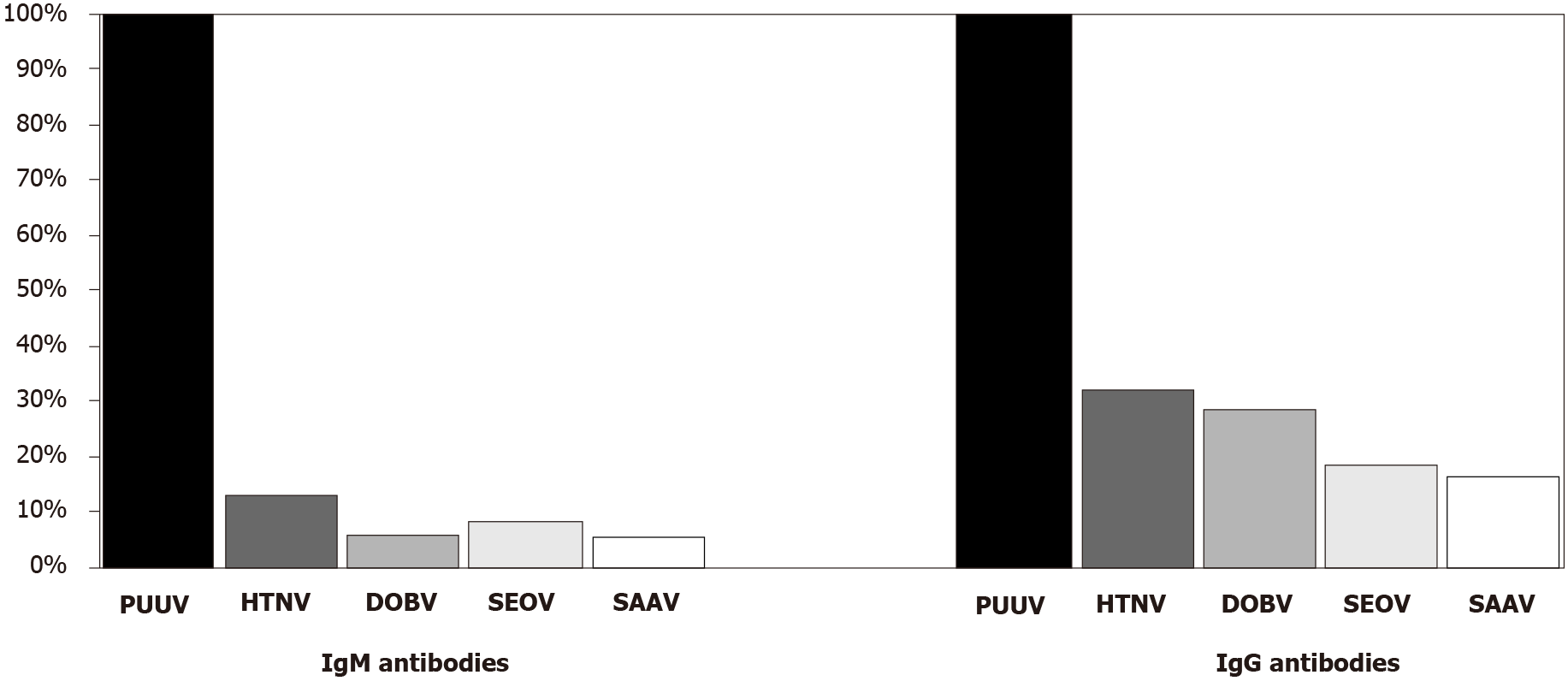
Figure 1 Cross-reactive patterns of hantavirus immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies in Puumala-infected patients by indirect immunofluorescence assay.
PUUV: Puumala; DOBV: Dobrava; HTNV: Hantaan; SEOV: Seoul; SAAV: Saaremaa; Ig: Immunoglobulin.
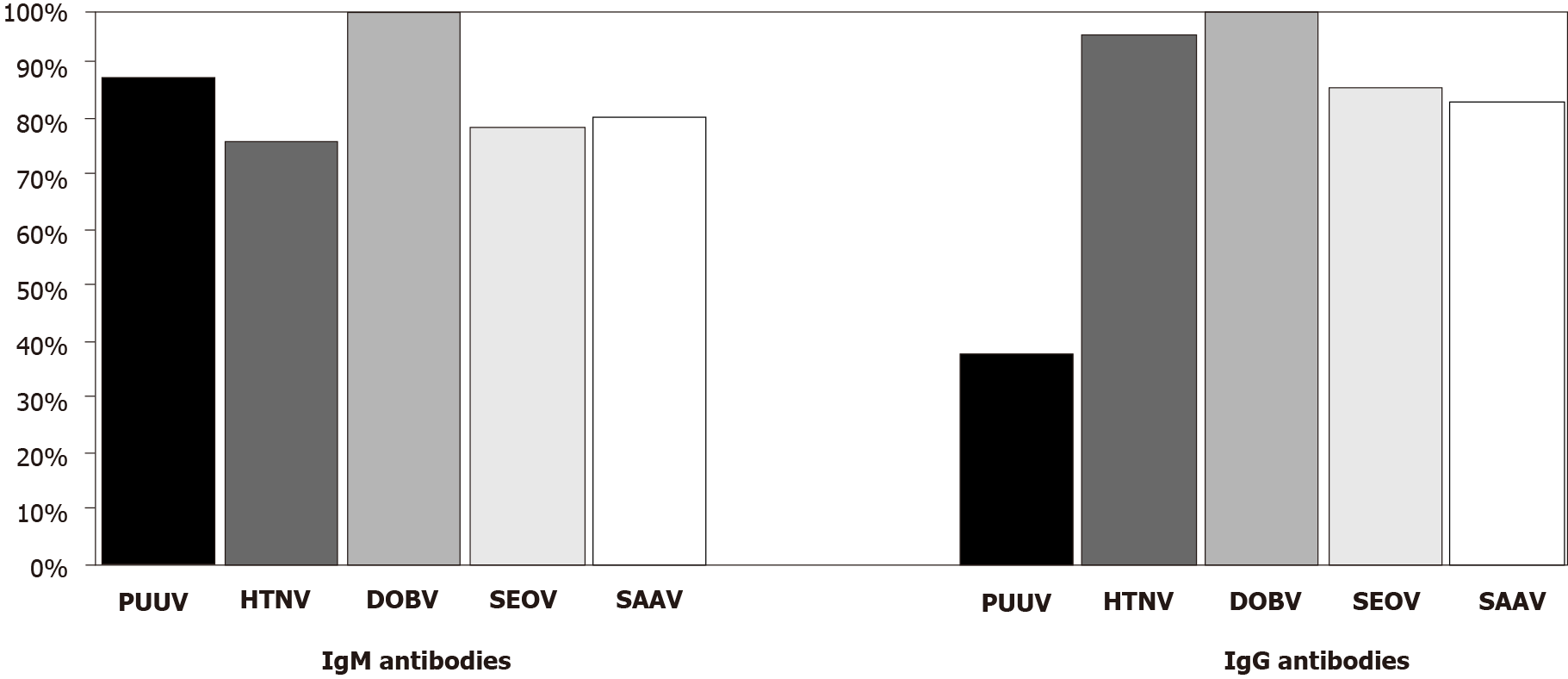
Figure 2 Cross-reactive patterns of hantavirus immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies in Dobrava-infected patients by indirect immunofluorescence assay.
PUUV: Puumala; DOBV: Dobrava; HTNV: Hantaan; SEOV: Seoul; SAAV: Saaremaa; Ig: Immunoglobulin.
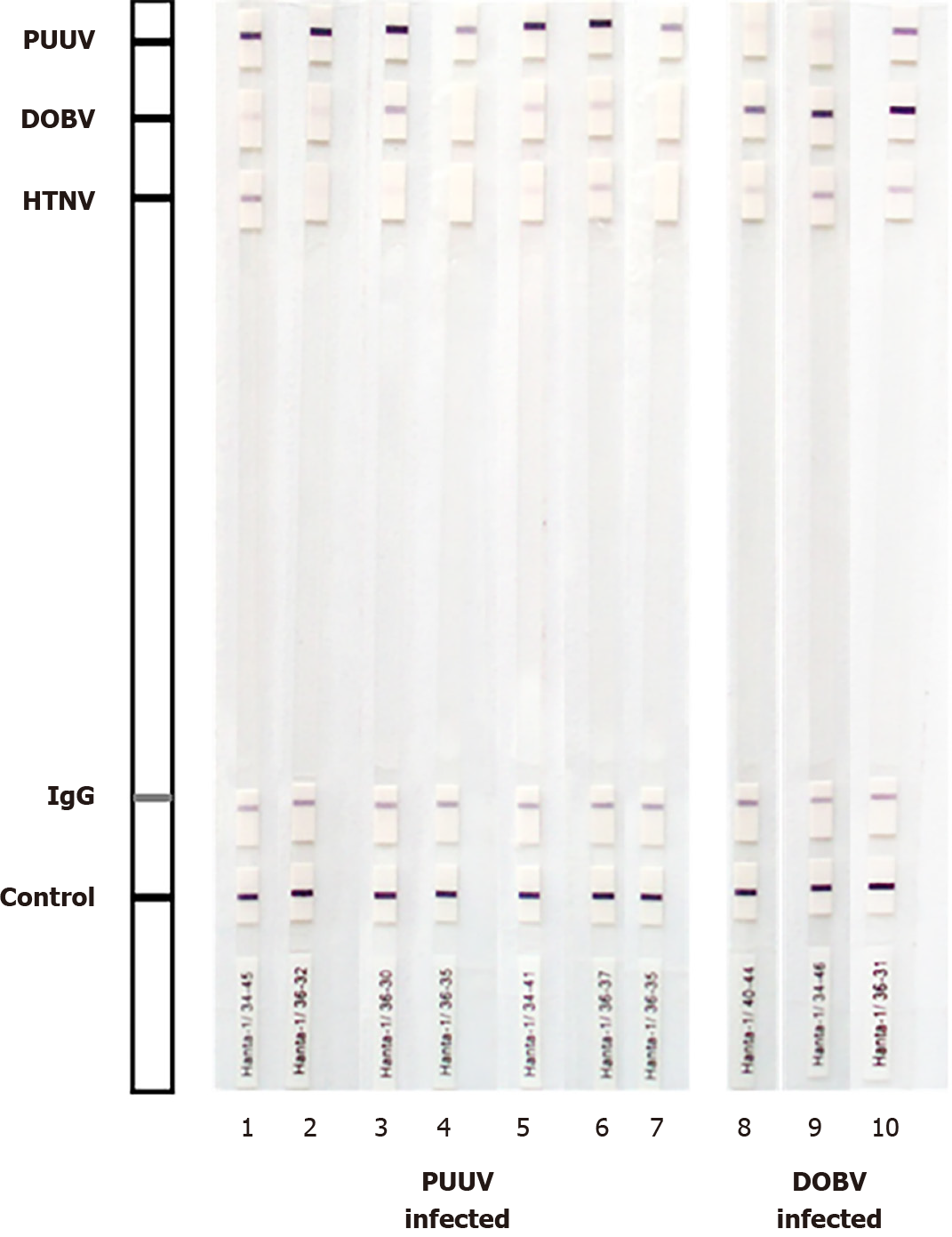
Figure 3 Western blot analysis of Puumala and Dobrava- infected patients.
The test strips were coated with the affinity purified nucleocapsid Puumala (PUUV); Dobrava (DOBV) and Hantaan (HTNV) antigen. A correctly performed test for immunoglobulin (Ig)G antibodies against hantavirus antigens is indicated by a positive reaction of the control band and the IgG band. Some samples (strips 1, 3, 5, 6, 8-10) cross-reacted with other hantaviruses, however, based on signal intensity, a very strong band to the homologous virus antigen was detected compared to a very weak/weak band of the related hantavirus antigens.
- Citation: Vilibic-Cavlek T, Barbic L, Stevanovic V, Savic V, Mrzljak A, Bogdanic M, Tabain I. Comparison of indirect immunofluorescence and western blot method in the diagnosis of hantavirus infections. World J Methodol 2021; 11(6): 294-301
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v11/i6/294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v11.i6.294