©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Transl Med. Apr 12, 2014; 3(1): 31-36
Published online Apr 12, 2014. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v3.i1.31
Published online Apr 12, 2014. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v3.i1.31
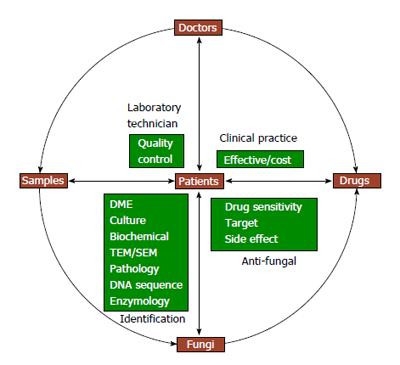
Figure 1 Essential factors for translational medical mycology.
DME: Direct microscopic examination; TEM: Transmission electron microscopy; SEM: Scanning electron microscopy.
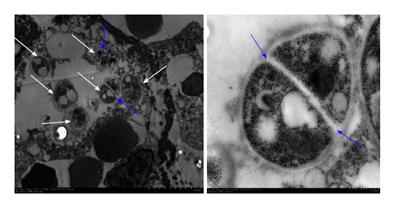
Figure 2 In transmission electron microscopic examination, there are 6 organisms with cell wall (white arrows), of which 2 have septated wall (blue arrows) within a macrophage.
This specific structure of Penicillium marneffei helped to clarify the pathogen as Penicillium marneffei.
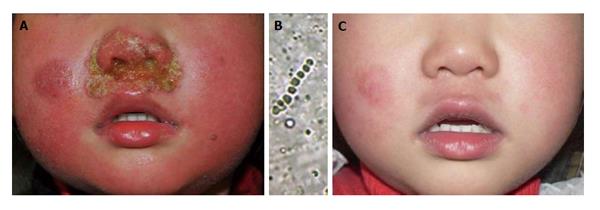
Figure 3 A 3-year-old girl was consulted with impetigo-like lesions around the nostrils.
A: Pustules and erythema around nostrils; B: Hyphae and clustered spores in the crust but the culture was negative. The pathogenic agent was identified as Arthroderma vanbreuseghemii (a teleomorph of Trichophyton interdigitale) using polymerase chain reaction-based sequencing of the crusts; C: The pustules and erythema disappeared after 35 d of antifungal treatment.
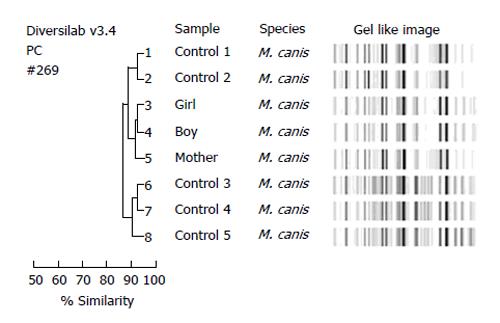
Figure 4 Molecular typing of eight Microsporum canis isolates showed distinct and similar fingerprint patterns visualized by the gel-like image and as indicated by a > 90% similarity coefficient in the dendrogram.
The three isolates from patients of a same family (number 3, 4, 5) were grouped together with a ≥ 98% similarity compared with the control isolates of M. canis. M. canis: Microsporum canis.
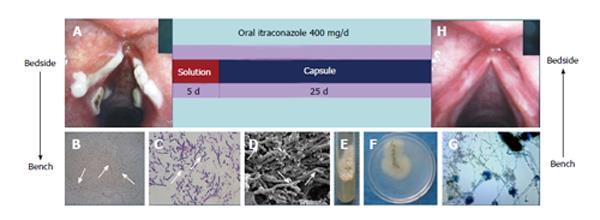
Figure 5 Treatment was successful with oral itraconazole solution the first five days followed by capsules, which completely cured the patient in 30 d.
A: A laryngoscopy was performed and revealed obvious white plaques on the swollen vocal cords and laryngeal ventricle. Samples were taken from the vocal cords; B: Numerous hyphae branching at 45° angles were detected by light microscopy; C: Pathology; D: Scanning electron microscopy; E and F: A velvety and powdery colony developed on Sabouraud Dextrose Agar at 28 °C; G: Microscopic examination of a slide culture revealed the morphologic features consistent with those of Aspergillus fumigatus. The patient was treated with oral itraconazole solution followed by capsules for 30 d; H: Laryngoscopy showed that the vocal cords were smooth without any white plaques.
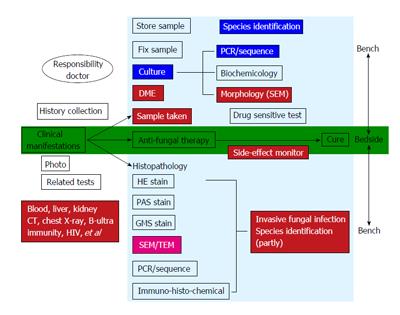
Figure 6 Translational medical mycology diagnosis and treatment pathway-from bedside to bench to bedside.
CT: Computed tomography; DME: Direct microscopic examination; TEM: Transmission electron microscopy; SEM: Scanning electron microscopy; HE stain: Haematoxylin and eosin stain; GMS stain: Gomort methenamine silver stain; PAS stain: Periodic Acid Schiff stain; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Lama J, Ran X, Ran YP. Translational medical mycology guides clinical and laboratory practice on fungal diseases. World J Transl Med 2014; 3(1): 31-36
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6132/full/v3/i1/31.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5528/wjtm.v3.i1.31