©The Author(s) 2016.
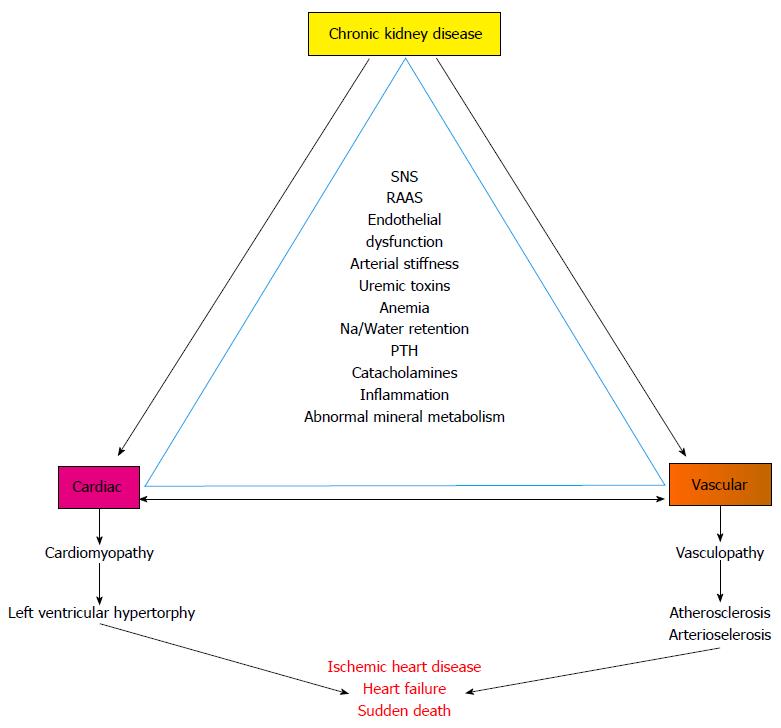
Figure 1 Cardiovascular abnormalities in chronic kidney disease.
Depicts the association of chronic kidney disease related risk factors and cardiac and vascular abnormalities and outcomes in chronic kidney disease. SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; RAAS: Renin angiotensin aldosterone system; Na: Sodium; PTH: Parathyroid hormone.
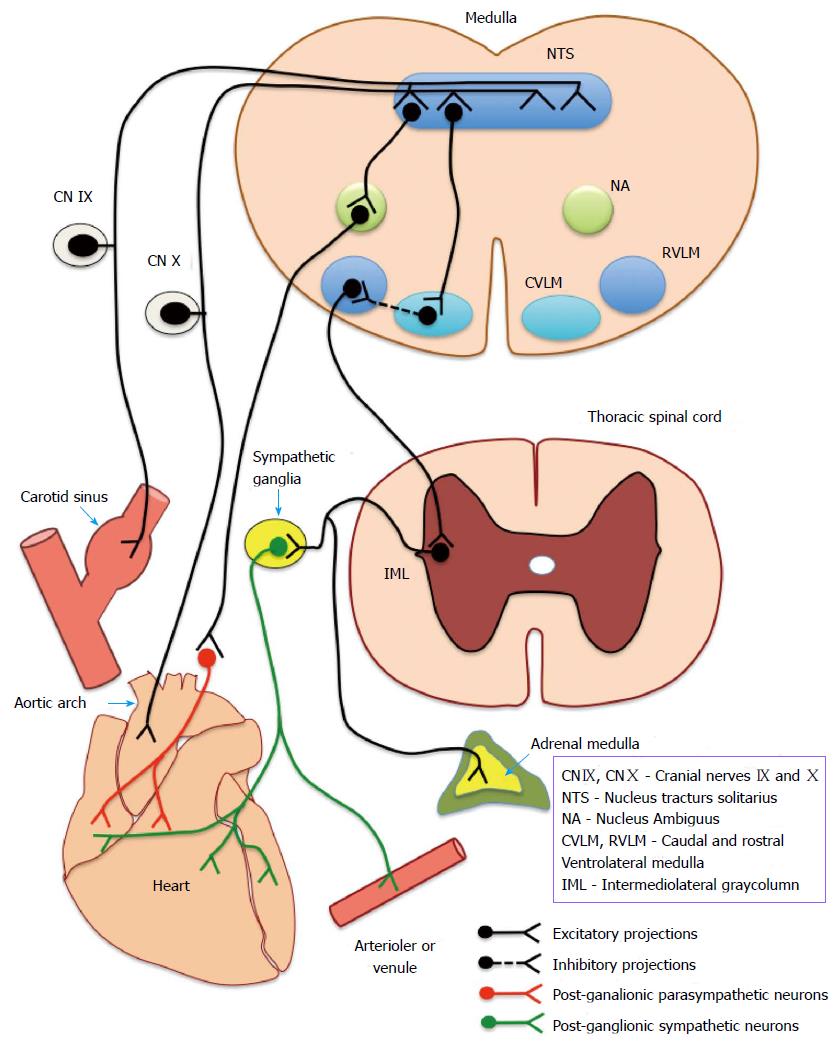
Figure 2 Neuronal circuitry of the baroreflex arc.
Depicts the complete baroreflex arc - beginning from the baroreceptors (located in carotid sinus and aortic arch), afferents (IX and X cranial nerve) ascend to medullary centres and send efferents (sympathetic and parasympathetic) to end organs (heart and vasculature). CN IX and CN X: Cranial nerve IX and X; NTS: Nucleus tractus solitarius; NA: Nucleus ambiguous; CVLM: Caudal ventrolateral medulla; RVLM: Rostral ventrolateral medulla; IML: Intermediolateral gray column.
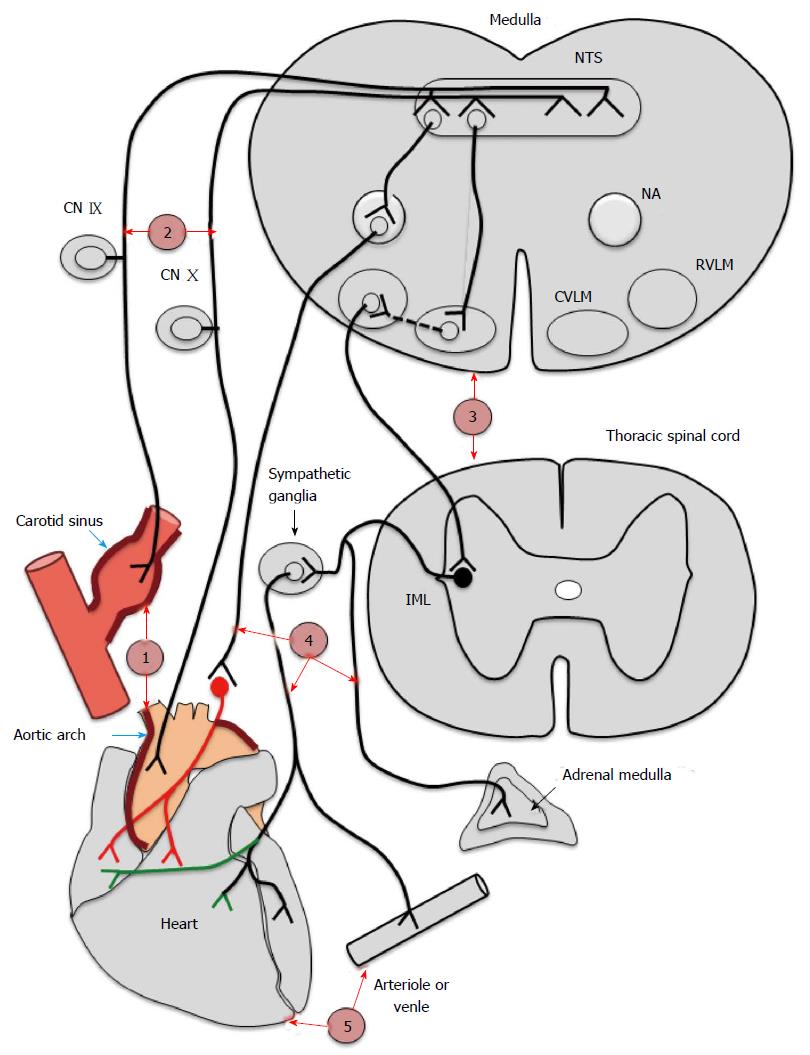
Figure 3 Probable levels of defect in baroreflex arc in chronic kidney disease.
Depicts the different probable levels of defect in chronic kidney disease. Level 1 represents the baroreceptors affected by calcification of central arteries. Level 2, 3, 4 and 5 represents afferents (IX and X nerves), centres, efferents and endorgans (heart and vessels) respectively. CN IX and CN X: Cranial nerve IX and X; NTS: Nucleus tractus solitarius; NA: Nucleus ambiguous; CVLM: Caudal ventrolateral medulla; RVLM: Rostral ventrolateral medulla; IML: Intermediolateral gray column.
- Citation: Kaur M, Chandran DS, Jaryal AK, Bhowmik D, Agarwal SK, Deepak KK. Baroreflex dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. World J Nephrol 2016; 5(1): 53-65
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v5/i1/53.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v5.i1.53