©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Transplant. Sep 18, 2021; 11(9): 372-387
Published online Sep 18, 2021. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i9.372
Published online Sep 18, 2021. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i9.372
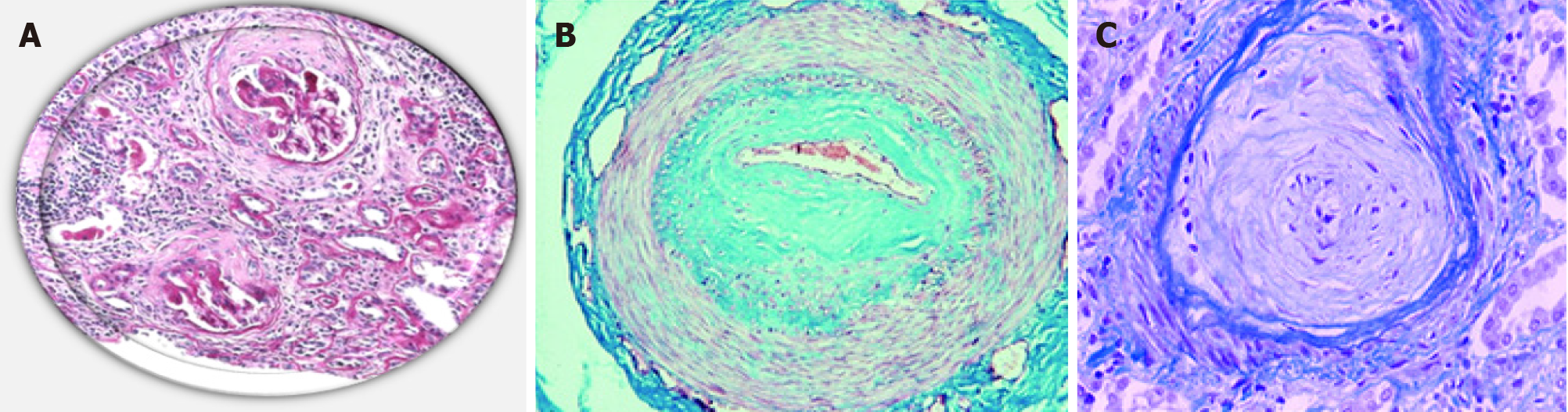
Figure 1 Pathology of scleroderma renal crisis.
A: Normotensive patient with systemic sclerosis (SS) and acute renal failure. End-stage renal disease: Crescentic glomerulonephritis showing fibrous crescents. A mixed mononuclear cell infiltrate and considerable tubular loss[21,70] (Open access); B: Masson’s trichrome staining of a digital artery from a patient with SS[21,70] (Open access); C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of a renal artery from a patient with SS. Note the striking fibrotic intimal hyperplasia and the adventitial fibrosis in the digital artery and the onion skin–like intimal thickening composed of smooth muscle cells and increased connective tissue matrix in the renal artery. The intimal hyperplasia results in critical luminal narrowing and even occlusion[21,70] (Open access). Citation: Soukup T, Toms J, Oreska S, Honsova E, Safranek R. Renal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis, 9 July 2019. Copyright© The Authors 2019. Published by Open access peer-reviewed chapter. Matucci-Cerinic M, Kahaleh B, Wigley FM. Review: evidence that systemic sclerosis is a vascular disease. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 65: 1953-1962. Copyright© The Authors 2013. Published by Wiley Online Library.
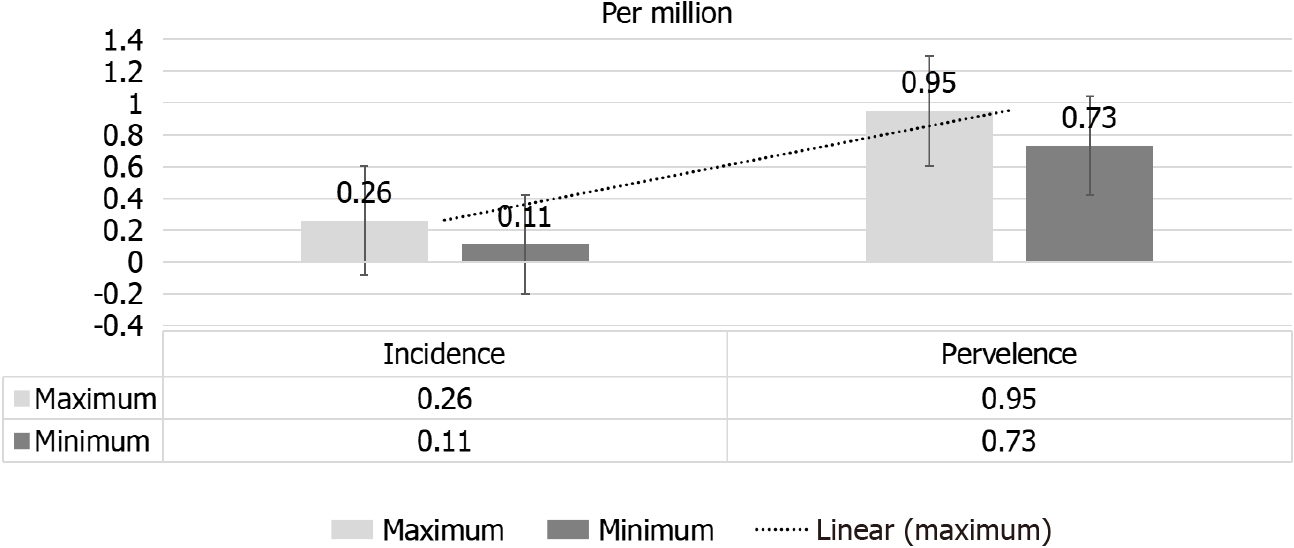
Figure 2 Range of adjusted annual incidence and prevalence rates of renal replacement therapy for end-stage renal disease due to scleroderma.
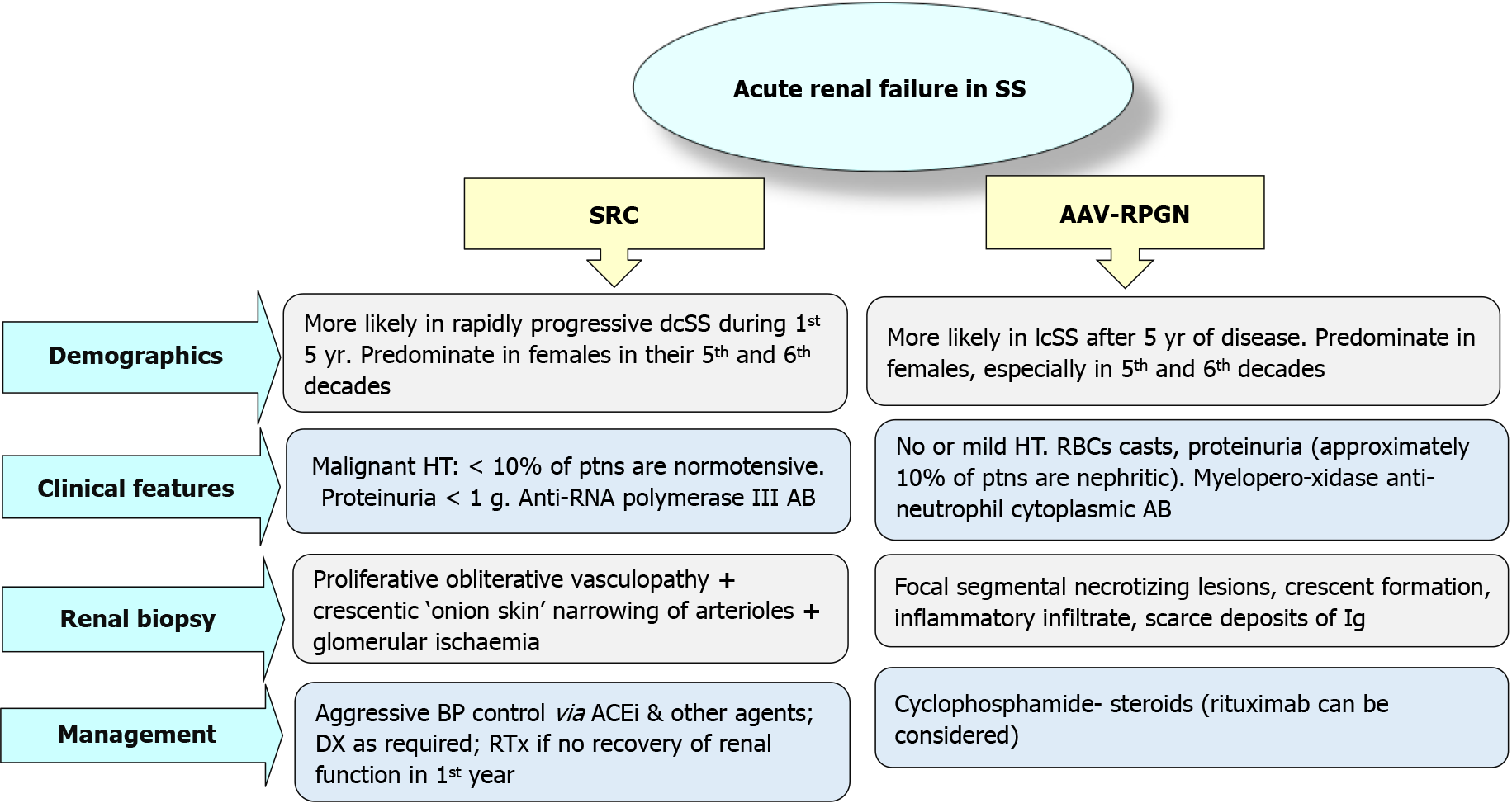
Figure 3 Differential diagnosis of acute renal failure in scleroderma: Associated vasculitis–rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
SS: Systemic sclerosis; ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; dcSS: Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis; lcSS: Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis; SRC: Scleroderma renal crisis; AB: Antibodies, Ig: Immunoglobulin; DX: Dialysis; RTx: Renal transplant.
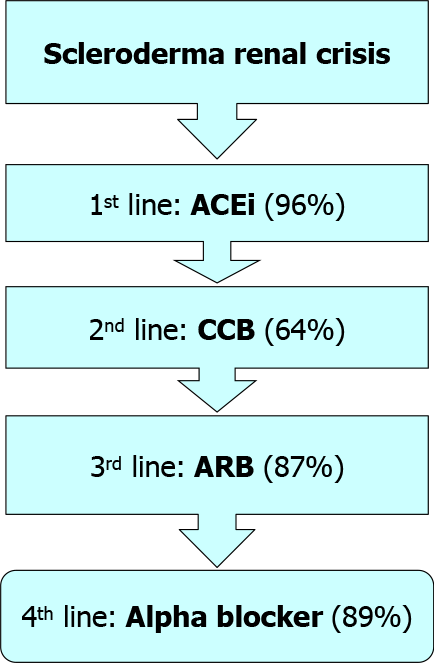
Figure 4 Algorithm for scleroderma renal crises therapy.
ACE: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; CCB: Calcium channel blockers; ARB: Angiotensin receptor blockers.
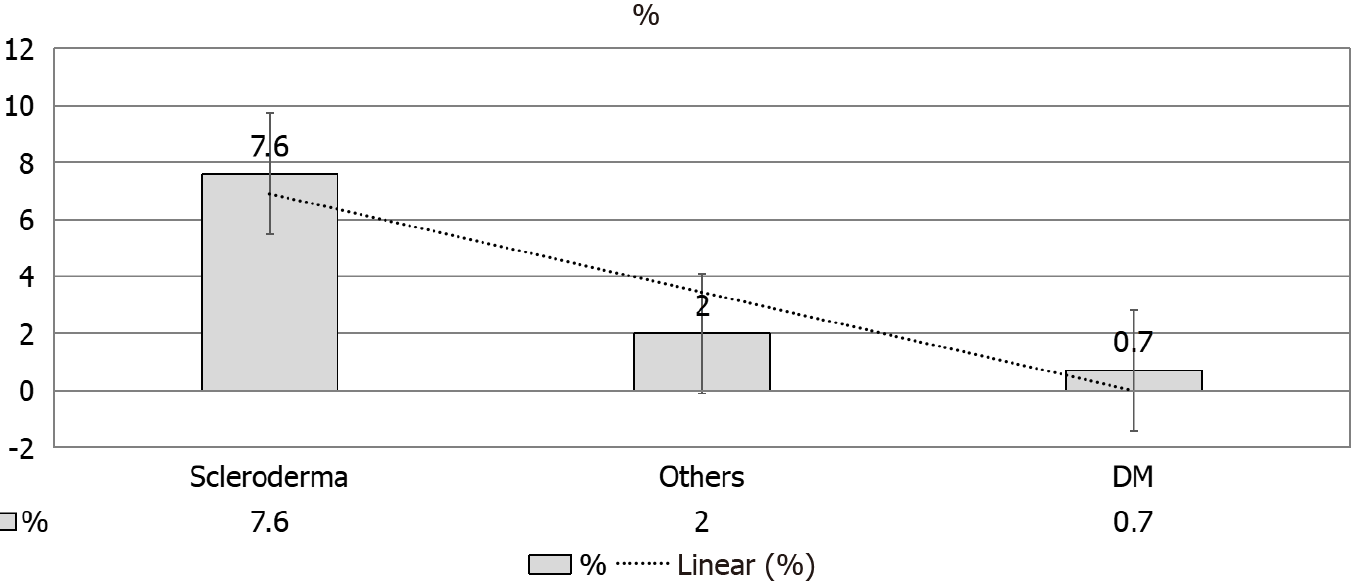
Figure 5 Recovery of independent kidney function.
DM: Diabetes mellitus.
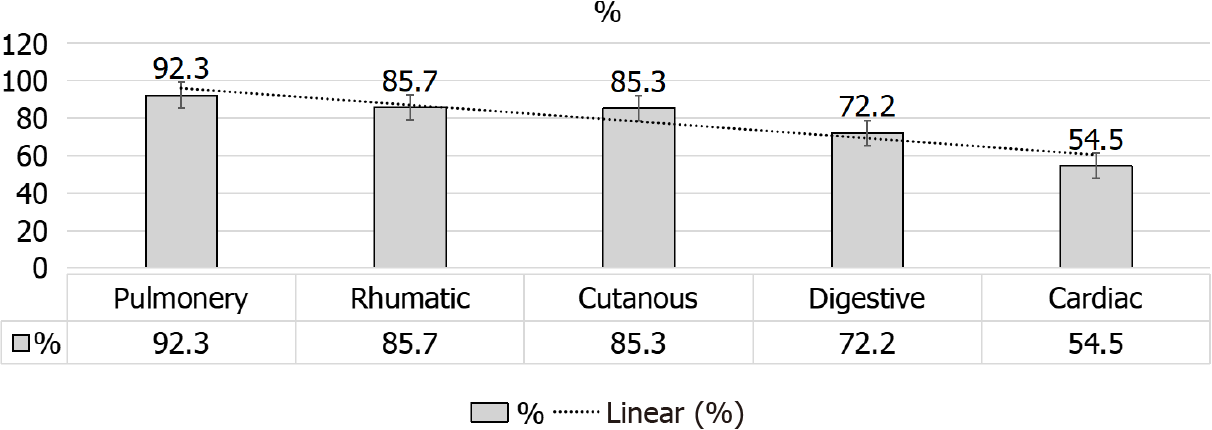
Figure 6 Stable or improved extrarenal manifestation after kidney transplantation.
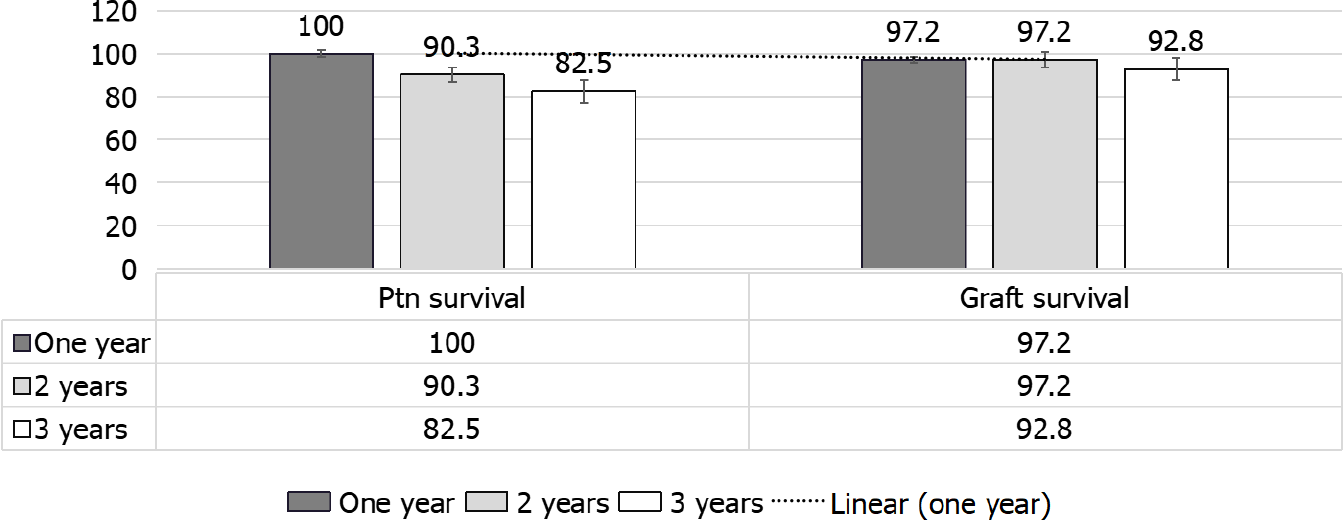
Figure 7 Patients and death-censored graft survival.
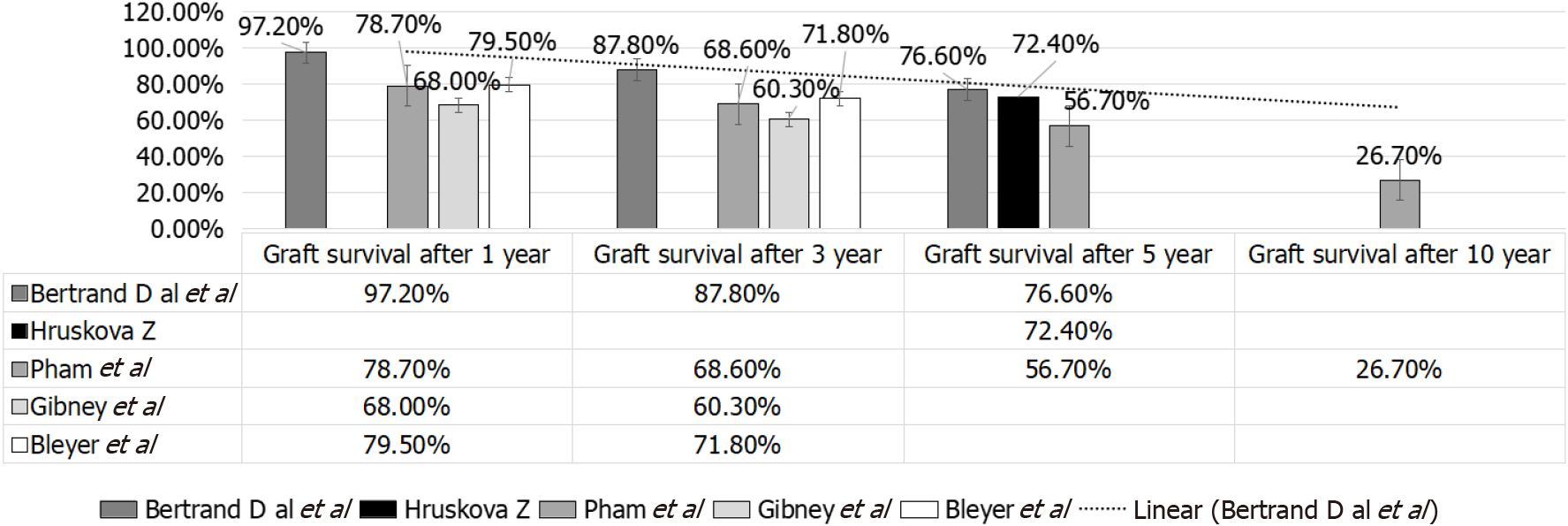
Figure 8 Graft survival after one, three, five and ten years in various studies.
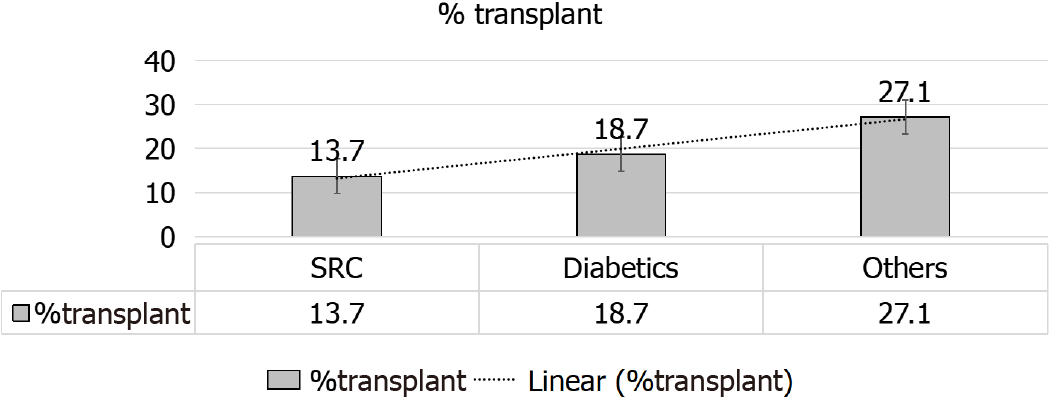
Figure 9 Percentage of scleroderma renal crisis patients received kidney allograft compared to other groups.
SRC: Scleroderma renal crisis.
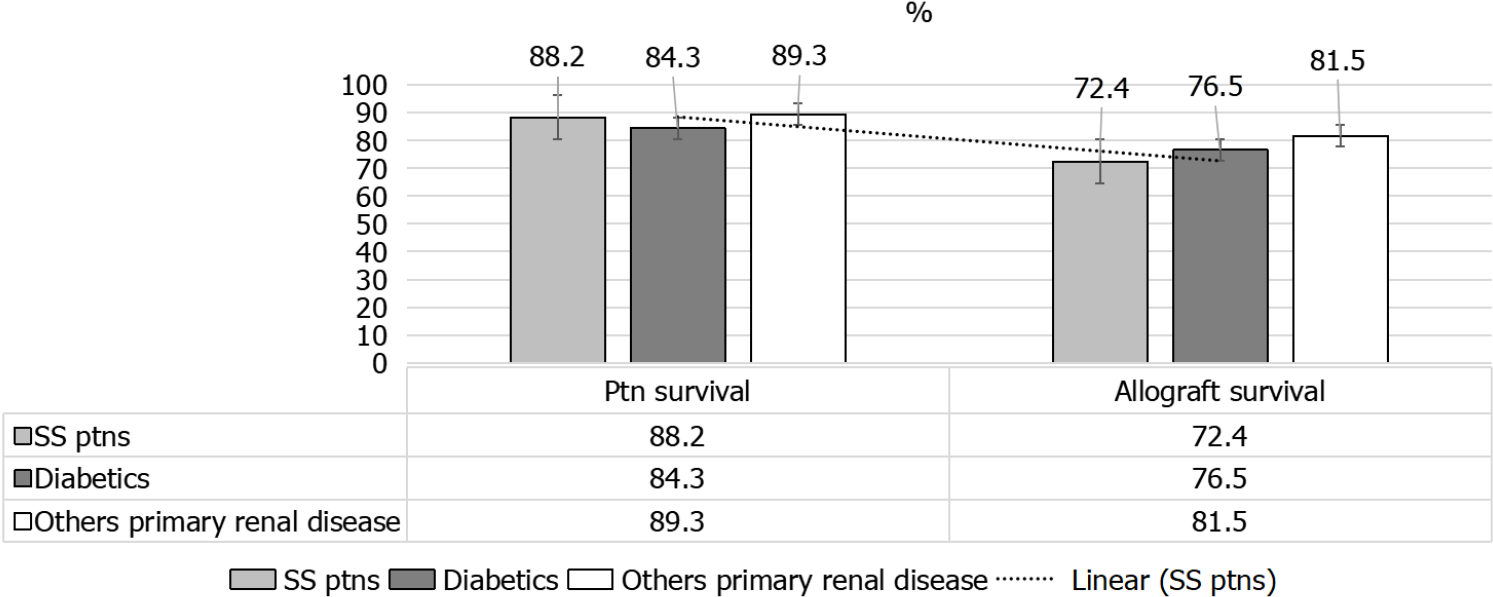
Figure 10 Patient and graft survival after receiving 1st kidney transplant, for systemic sclerosis, diabetes mellitus and other primary kidney diseases.
SS: Systemic sclerosis.
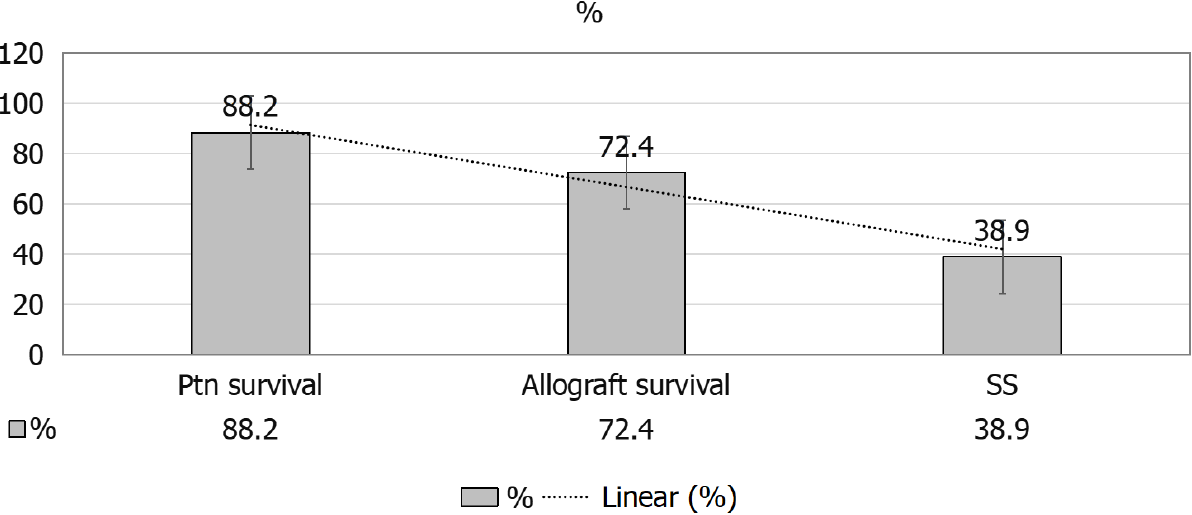
Figure 11 5-yr survival probability from day 91 of renal replacement therapy in systemic sclerosis patients, posttransplant patients’ survival and 5-yr allograft survival.
- Citation: Abbas F, El Kossi M, Shaheen IS, Sharma A, Halawa A. Journey of a patient with scleroderma from renal failure up to kidney transplantation. World J Transplant 2021; 11(9): 372-387
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v11/i9/372.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v11.i9.372