©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Pharmacol. Jan 19, 2026; 15(1): 113080
Published online Jan 19, 2026. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v15.i1.113080
Published online Jan 19, 2026. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v15.i1.113080
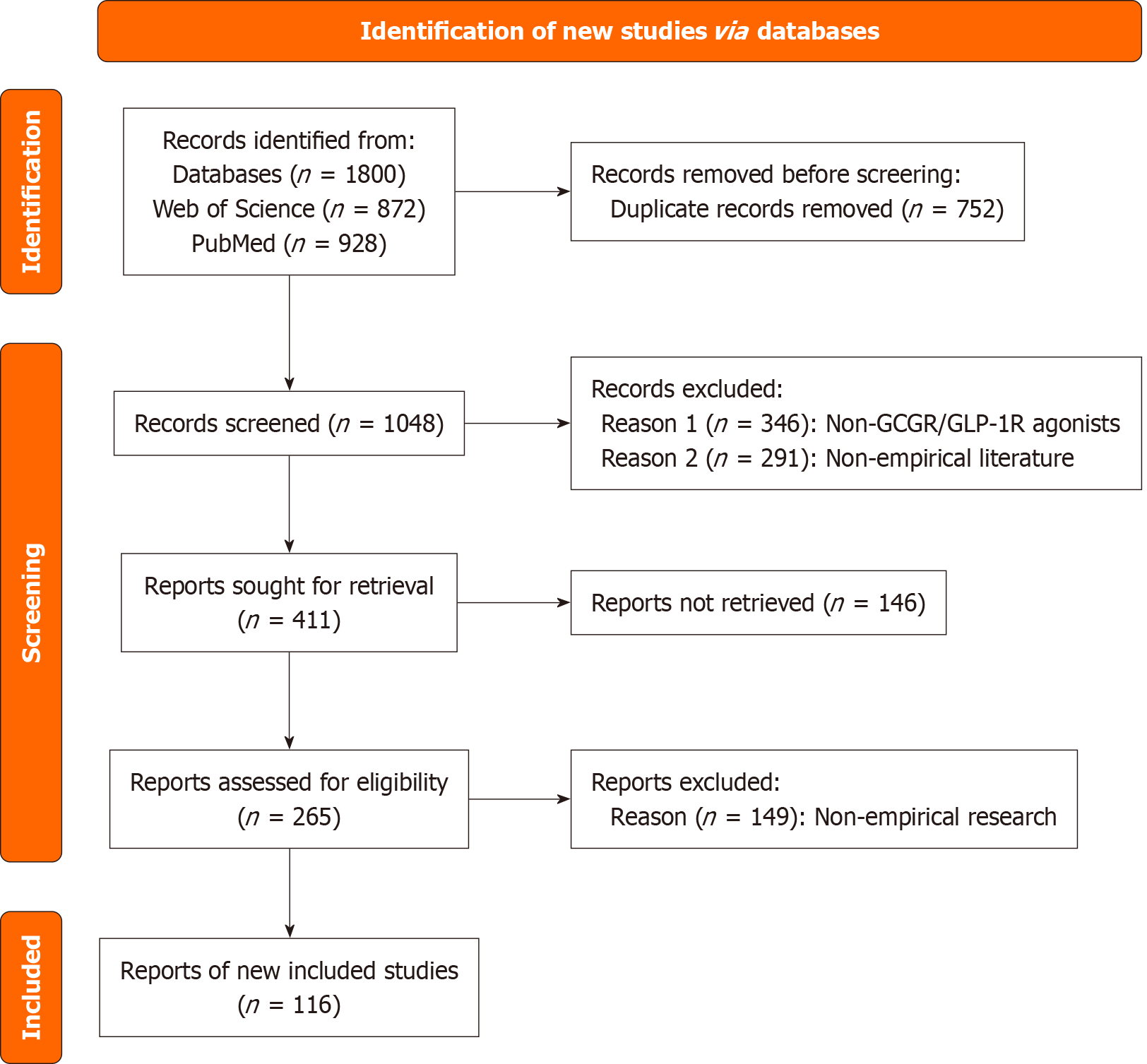
Figure 1 The screening process.
GCGR: Glucagon receptor; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor.
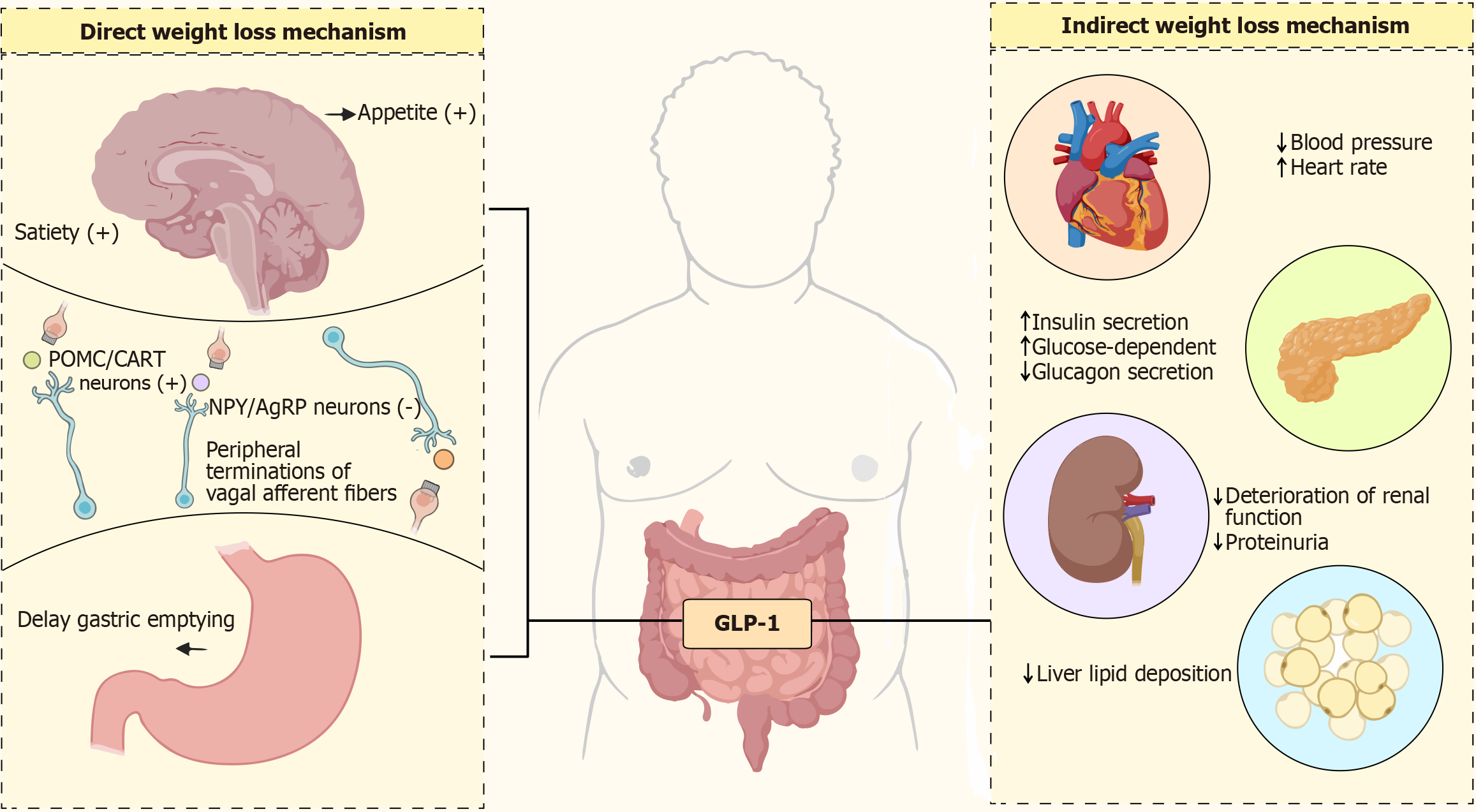
Figure 2 Physiological effects of glucagon-like peptide-1.
The physiological effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) are extensive. GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; POMC: Pro-opiomelanocortin; CART: Cocaine amphetamine regulated transcript; NPY: Neuropeptide Y; AgRP: Agouti-related peptide.
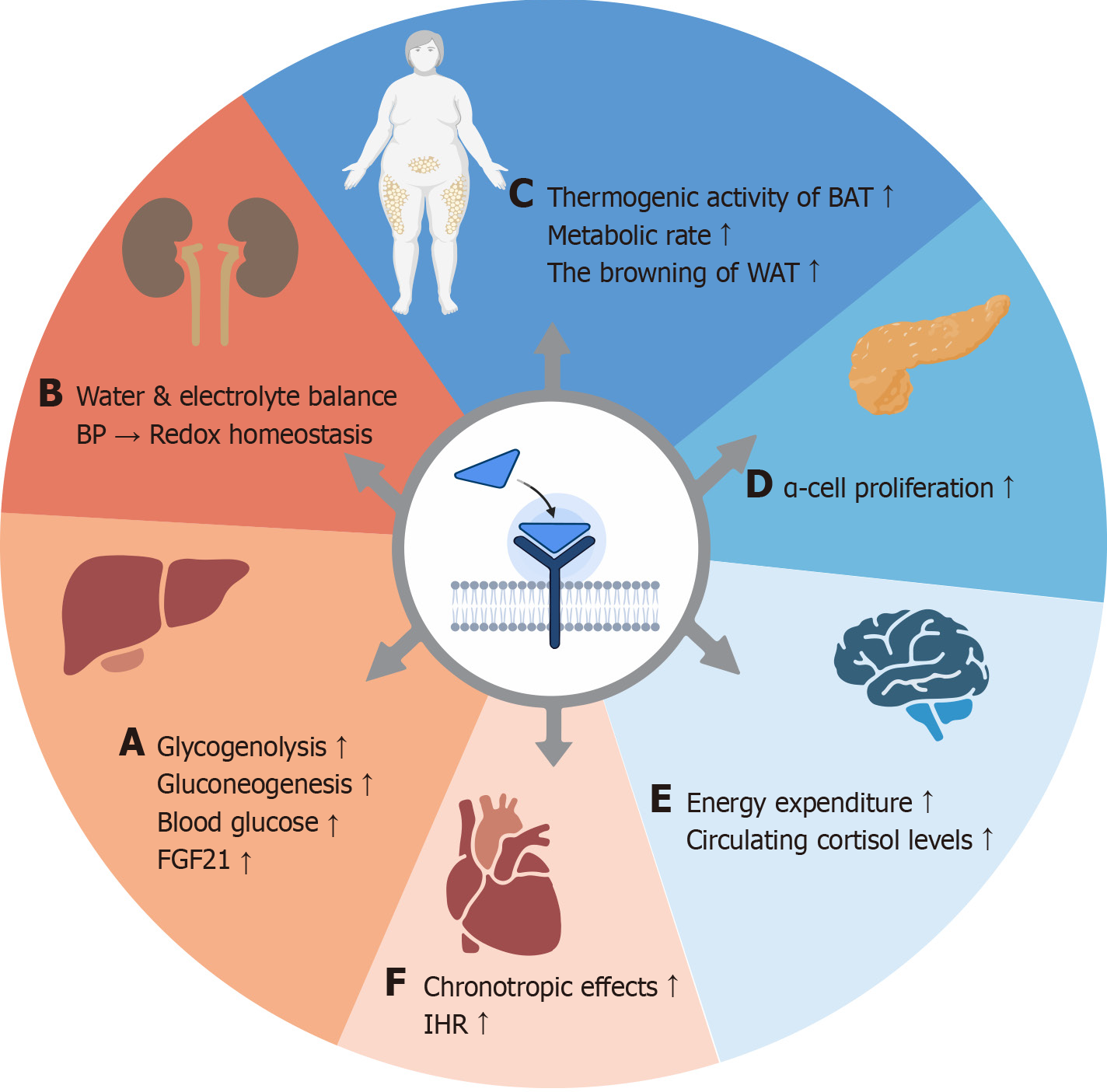
Figure 3 Physiological effects of glucagon.
The physiological effects of glucagon are extensive. A: In the liver, glucagon activation stimulates glycogen phosphorylase kinase, increases circulating fibroblast growth factor 21, upregulates the expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase, promotes glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, and thus increases blood glucose; B: In the kidney, glucagon is crucial for maintaining water and electrolyte balance, blood pressure, and redox homeostasis; C: In adipose tissue, glucagon can act on brown adipose tissue and white adipose tissue and augment the metabolic rate; D: In the pancreas, glucagon activation may cause the proliferation of α cells; E: In the central nervous system, glucagon can influence energy expenditure; F: In the heart, glucagon participates in the enhancement of intrinsic heart rate. BP: Blood pressure; BAT: Brown adipose tissue; WAT: White adipose tissue; FGF21: Fibroblast growth factor 21; IHR: Intrinsic heart rate.
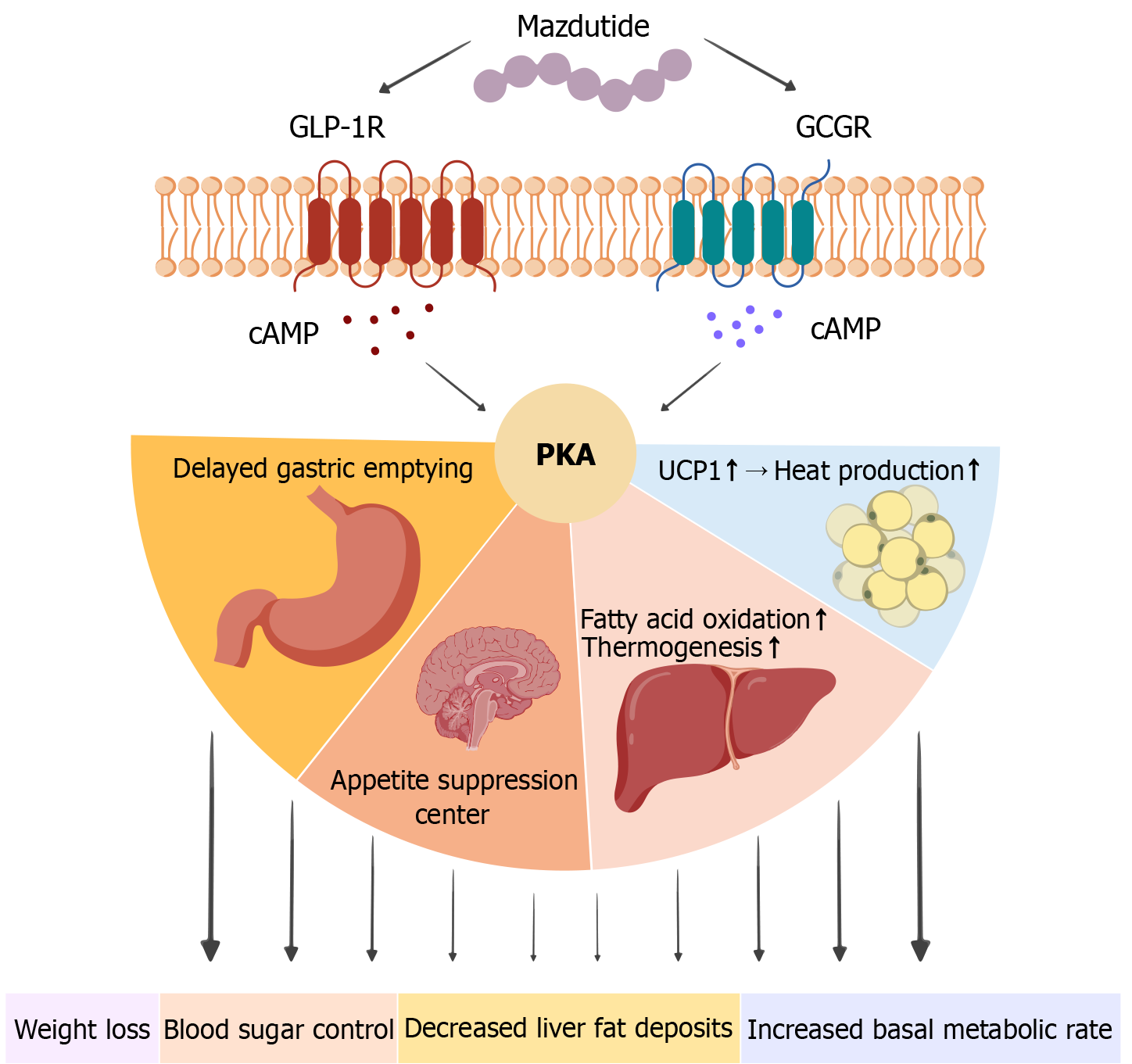
Figure 4 Pharmacological effects of mazdutide.
Mazdutide binds to both glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and glucagon receptor on cell membranes, triggering cyclic adenosine monophosphate–protein kinase A signaling. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation delays gastric emptying and stimulates central appetite suppression, while glucagon receptor activation enhances hepatic fatty acid oxidation, thermogenesis, and uncoupling protein 1-mediated heat production in adipose tissue. Together, these effects contribute to weight loss, improved glycemic control, reduced hepatic fat deposits, and increased basal metabolic rate. PKA: Protein kinase A; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; GCGR: Glucagon receptor; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; UCP1: Uncoupling protein 1.
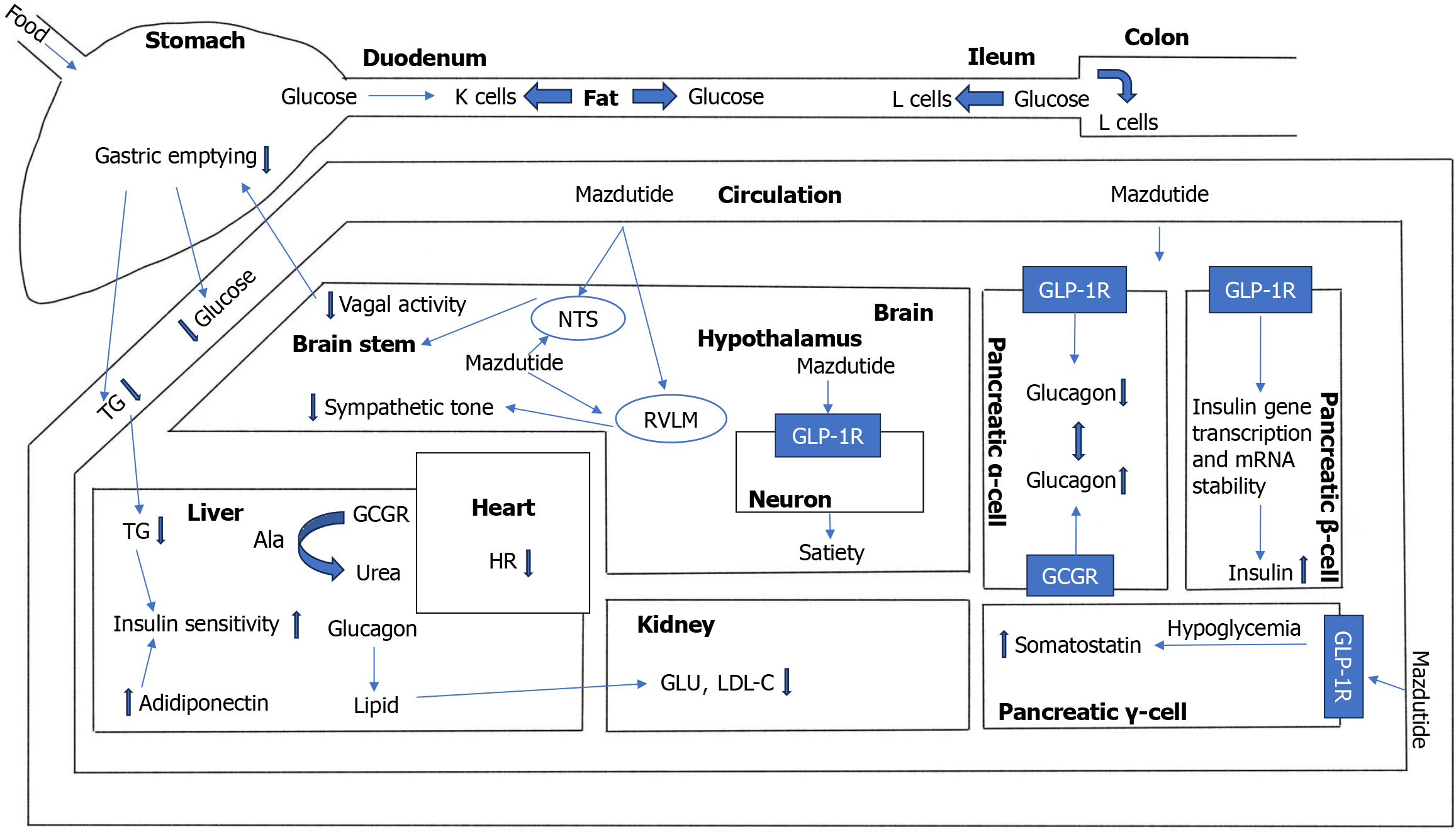
Figure 5 Mechanistic pathways of mazdutide via dual glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and glucagon receptor activation.
Mazdutide plays an important role in the digestive system (stomach, pancreas, and liver), cardiovascular system, and central nervous system (brain), and it regulates weight, metabolism, blood glucose, and cardiovascular risk factors. TG: Triglycerides; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GCGR: Glucagon receptor; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; GLU: Glutamate; NTS: Nucleus of the solitary tract; RVLM: Rostral ventrolateral medulla.
- Citation: Deng CX, Chen ZM, Tang YX, Xi ZX, Wang SY, Wu HY, Xu B, Xu TC. Mazdutide: An emerging glucagon/GCG-like peptide-1 dual receptor agonist for obesity—a comparison of therapeutic effects and potential side effects with GCG-like peptide-1 inhibitors. World J Pharmacol 2026; 15(1): 113080
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v15/i1/113080.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v15.i1.113080