©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Med Genet. May 27, 2014; 4(2): 34-38
Published online May 27, 2014. doi: 10.5496/wjmg.v4.i2.34
Published online May 27, 2014. doi: 10.5496/wjmg.v4.i2.34
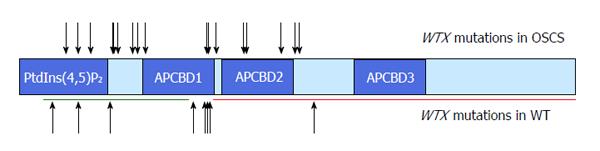
Figure 1 WTX mutations in osteopathia striata with cranial sclerosis and Wilms’ tumor.
The full length WTX protein possesses two phosphatidylinositol(4,5)-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] binding domains, three adenomatous polyposis coli binding domains (APCBD) and a β-catenin binding region (red line)[2,3]. The smaller WTX isoform lacks amino acids 50-326 (green line)[1,5]. Functionally relevant mutations include whole gene deletions and truncating mutations. Arrows indicate the position of mutations introducing a stop codon or causing a frameshift of the reading frame and a premature stop codon[1,6-8,12,24,38,39,44,46,47].
-
Citation: Cattaneo E, Ciceri S, Liberati N, Radice P, Tarani L, Selicorni A, Perotti D. Osteopathia striata with cranial sclerosis, Wilms’ tumor and the
WTX gene. World J Med Genet 2014; 4(2): 34-38 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3184/full/v4/i2/34.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5496/wjmg.v4.i2.34