©2013 Baishideng.
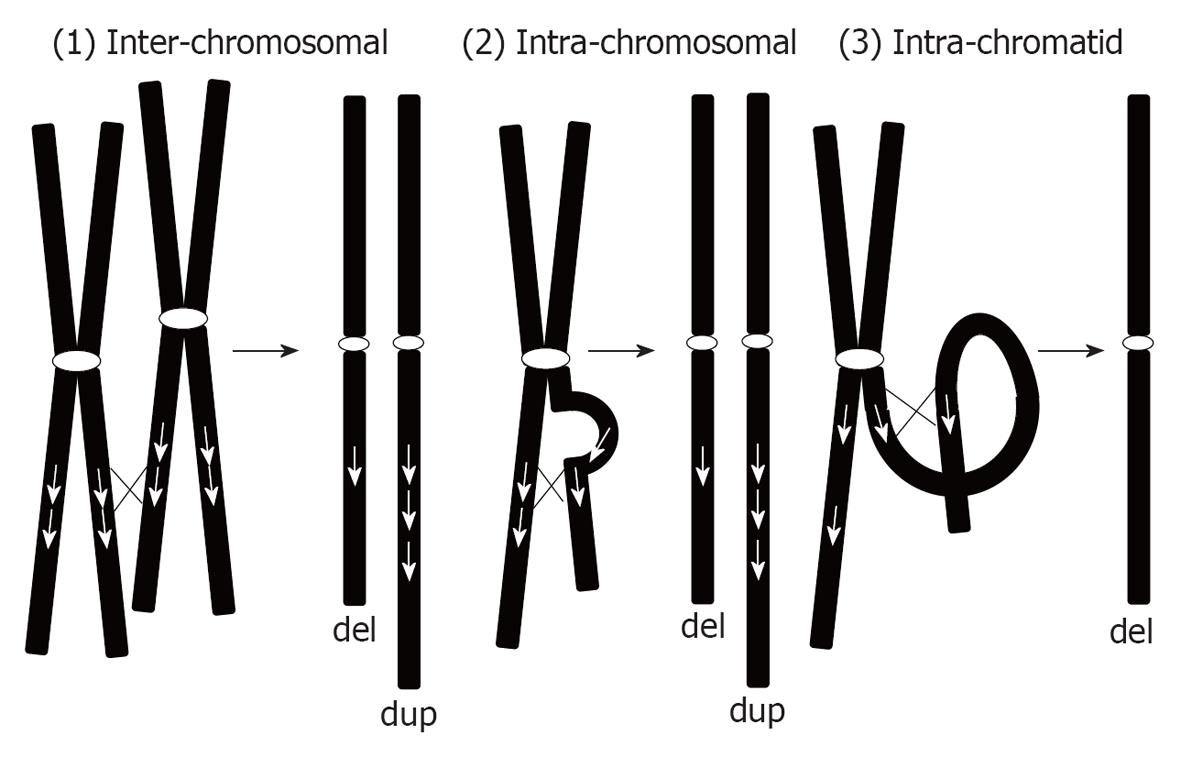
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the mechanism of non-allelic homologous recombination.
The mechanism can occur in 3 ways. Chromosomal duplications can be created by (1) inter-chromosomal exchange; (2) intra-chromosomal exchange; and (3) intra-chromatid exchange. Although inter-chromosomal and intra-chromosomal exchanges can lead to deletions and duplications equally, intra-chromatid exchange only creates microdeletions and not microduplications. Microduplications created by non-allelic homologous recombination invariably show tandem orientations. White arrows indicate the directions of the segments. This figure is referring the report by Gu et al[6].
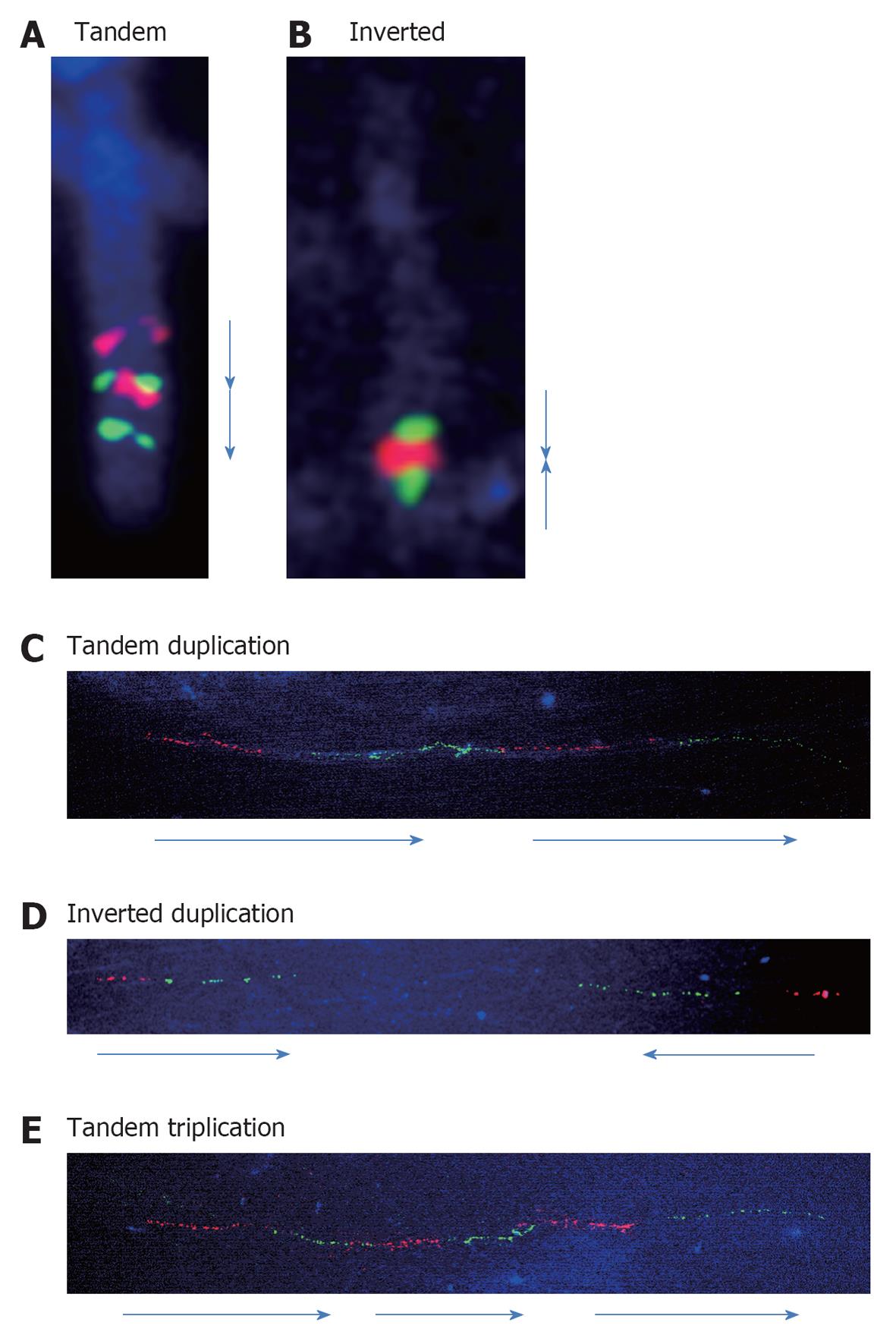
Figure 2 Results of fluorescence in situ hybridization in metaphase and fiber-fluorescence in situ hybridization.
A: Tandem duplication aligned in red-green-red-green is shown; B: Inverted duplication aligned in green-red-red-green is shown; C: Tandem duplication aligned in red-green-red-green is shown in a single DNA fiber; D: Inverted duplication aligned in red-green-green-red is shown; E: Tandem triplication with 3 repeats of red-green units. Arrows indicate the directions of the segments.
-
Citation: Yamamoto T, Shimada S, Shimojima K. Fiber-fluorescence
in situ hybridization analyses as a diagnostic application for orientation of microduplications. World J Med Genet 2013; 3(2): 5-8 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3184/full/v3/i2/5.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5496/wjmg.v3.i2.5