©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Med Genet. Jul 20, 2023; 11(3): 28-38
Published online Jul 20, 2023. doi: 10.5496/wjmg.v11.i3.28
Published online Jul 20, 2023. doi: 10.5496/wjmg.v11.i3.28
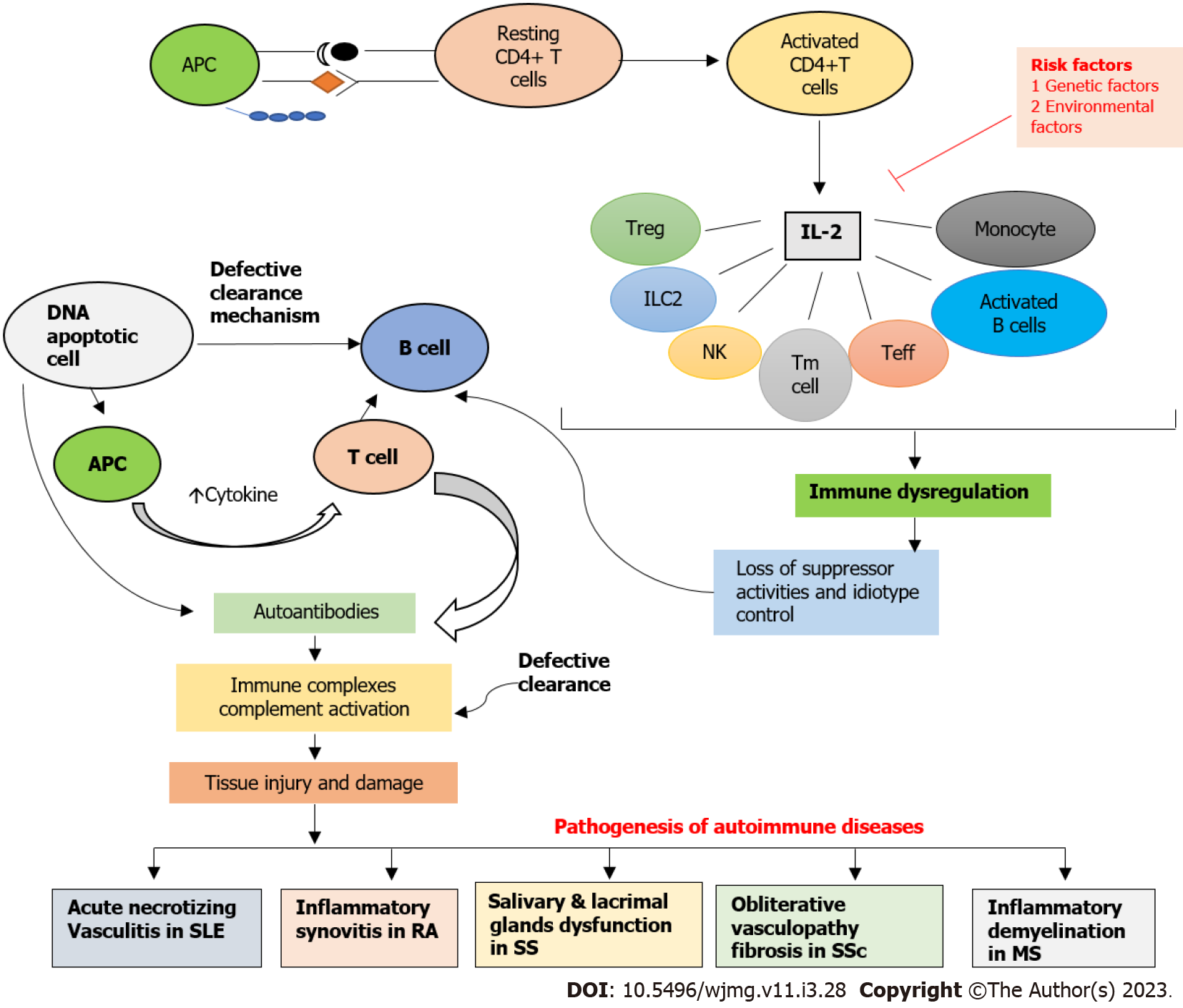
Figure 1 Overview of the role of interleukin (IL)-2/IL-2 receptor in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
Activation of T cells by antigen-presenting cells leads to the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2) by CD4+ T-helper cells then IL-2 interacts with IL-2 receptor expressed on several immune cells i.e., Treg, ILC2 cells, natural killer, memory T cells, activated T cells, B cells, and monocytes to mediate the immune regulation. However, the function of IL-2 is disrupted by multiple risk factors such as genetic, environmental, neuroendocrine system, sex hormones, and defective clearance mechanism that are involved in the pathogenesis of acute necrotizing vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematous, inflammatory synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis, salivary and lacrimal glands dysfunction in Sjogren syndrome, obliterative vasculopathy fibrosis in systemic sclerosis, and inflammatory demyelination in multiple sclerosis[54]. APC: Antigen presenting cells; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; MS: Multiple sclerosis; NK: Natural killer; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; IL: Interleukin; SLE: Systemic lupus erythematous; SS: Sjogren syndrome; SSc: Systemic sclerosis.
- Citation: Rafaqat S, Rafaqat S. Role of IL-2/IL-2 receptor in pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders: Genetic and therapeutic aspects. World J Med Genet 2023; 11(3): 28-38
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3184/full/v11/i3/28.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5496/wjmg.v11.i3.28