©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Exp Med. Sep 20, 2024; 14(3): 96269
Published online Sep 20, 2024. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v14.i3.96269
Published online Sep 20, 2024. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v14.i3.96269
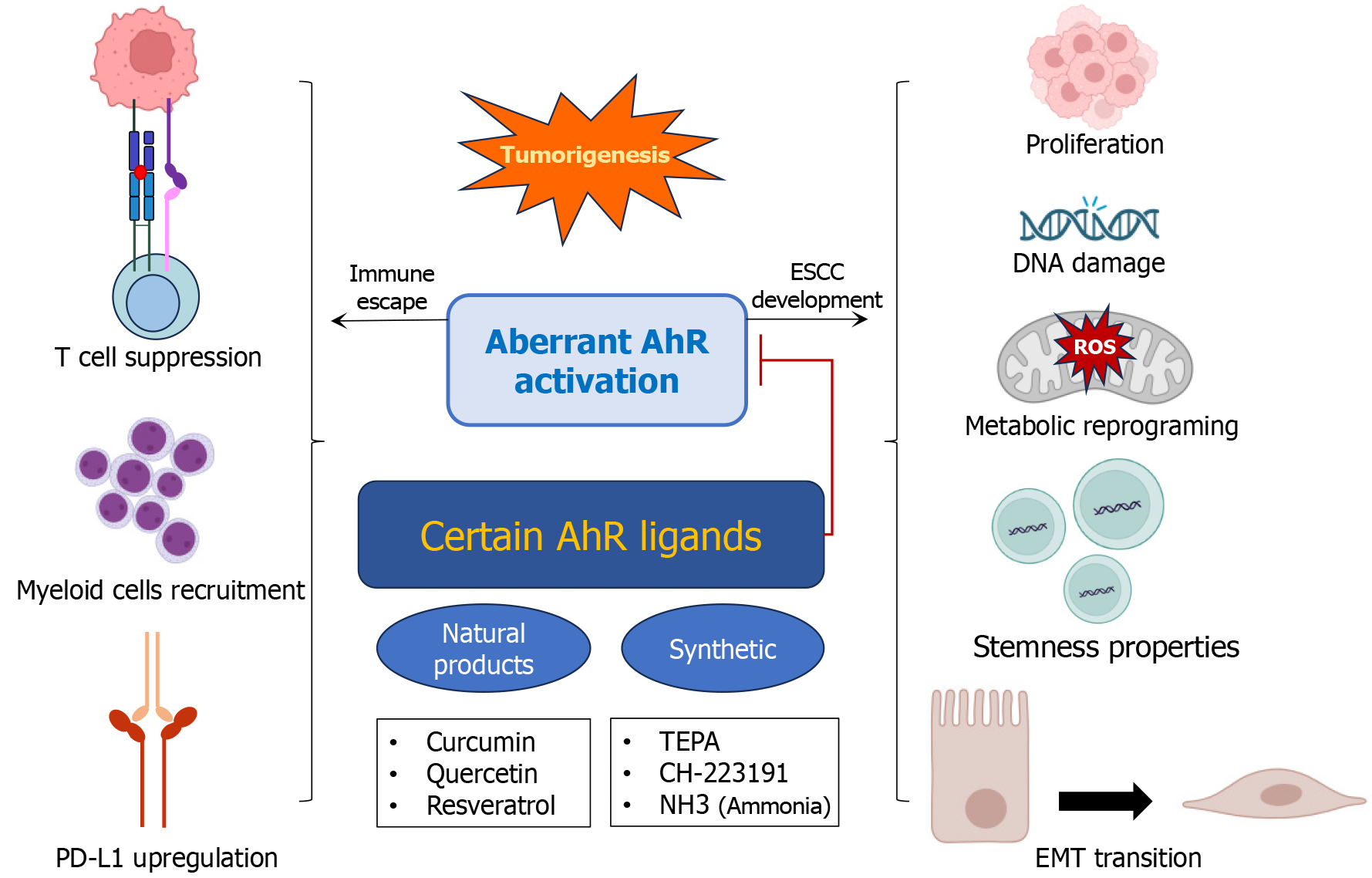
Figure 1 Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development and immune escape.
This figure illustrates the multifaceted influence of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) signaling on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) development and immune escape. Activation of AhR by environmental carcinogens or other ligands initiates a cascade of cellular processes that contribute to tumorigenesis. EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; NH3: Ammonia; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TEPA: Triethylenetetramine.
- Citation: Rahmati M, Moghtaderi H, Mohammadi S, Al-Harrasi A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor dynamics in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: From immune modulation to therapeutic opportunities. World J Exp Med 2024; 14(3): 96269
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v14/i3/96269.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v14.i3.96269