©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Exp Med. May 20, 2017; 7(2): 49-57
Published online May 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i2.49
Published online May 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i2.49
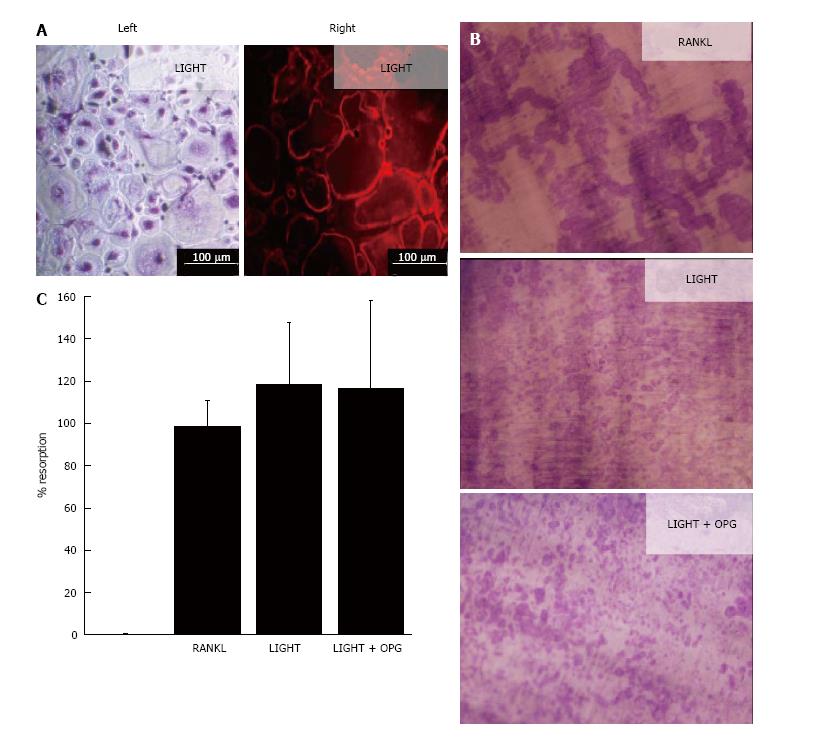
Figure 1 LIGHT induces receptor-activator nuclear factor kappa-B ligand-independent osteoclastogenesis from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid macrophages.
A: Osteoclast differentiation in 14-d cultures of RA SF macrophages incubated with M-CSF and LIGHT showing (left) TRAP+ multinucleated osteoclasts and (right) F actin-ring formation; B: Dentine slices stained with Toluidine blue showing lacunar resorption in 14-d RA SF macrophage cultures treated with M-CSF and sRANKL, LIGHT or LIGHT ± OPG; C: Percentage surface area lacunar resorption on dentine slices in LIGHT- (± OPG) treated SF macrophage cultures relative to sRANKL - treated controls; data is expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments where each condition was carried out in triplicate. RANKL: Receptor-activator nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; SF: Synovial fluid; M-CSF: Macrophage-colony stimulating factor; OPG: Osteoprotegerin.
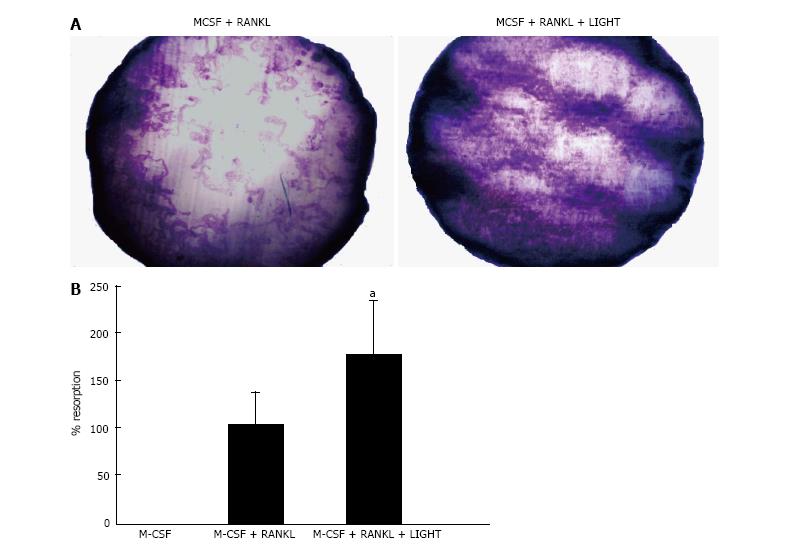
Figure 2 LIGHT augments receptor-activator nuclear factor kappa-B ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid macrophages.
A: Dentine slice stained with Toluidine blue showing lacunar resorption pits in 14-d RA SF macrophage cultures incubated with M-CSF and sRANKL ± LIGHT; B: Percentage surface area lacunar resorption on dentine slices in 14-d RA SF macrophage cultures incubated with M-CSF and sRANKL ± LIGHT. Data is expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments where each condition was carried out in triplicate; aP < 0.05. RANKL: Receptor-activator nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; SF: Synovial fluid; M-CSF: Macrophage-colony stimulating factor.
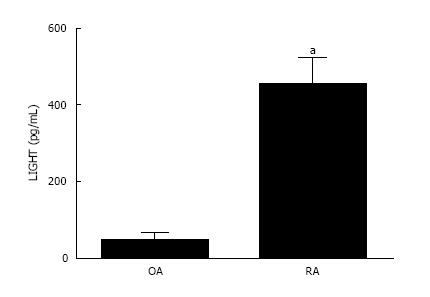
Figure 3 LIGHT levels are significantly higher in rheumatoid arthritis than osteoarthritis synovial fluid.
LIGHT concentration is significantly increased in SF of RA patients compared with OA joints. Data is expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments where each condition was carried out in triplicate; aP < 0.05. RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; SF: Synovial fluid; OA: Osteoarthritis.
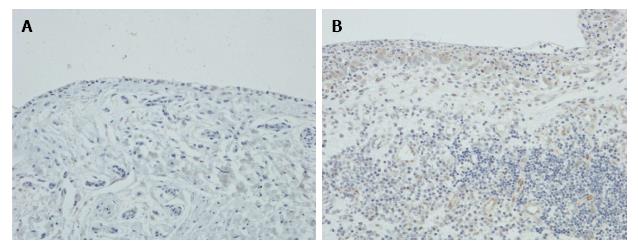
Figure 4 Expression of LIGHT in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis synovium.
Immunohistochemical staining of (A) RA and (B) OA synovium, showing expression of LIGHT on synovial lining cells and subintimal macrophages in RA synovium with no staining for LIGHT in OA synovium. Magnification × 200. RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; OA: Osteoarthritis.
- Citation: Sabokbar A, Afrough S, Mahoney DJ, Uchihara Y, Swales C, Athanasou NA. Role of LIGHT in the pathogenesis of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. World J Exp Med 2017; 7(2): 49-57
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v7/i2/49.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v7.i2.49