©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Exp Med. Aug 20, 2013; 3(3): 43-49
Published online Aug 20, 2013. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v3.i3.43
Published online Aug 20, 2013. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v3.i3.43
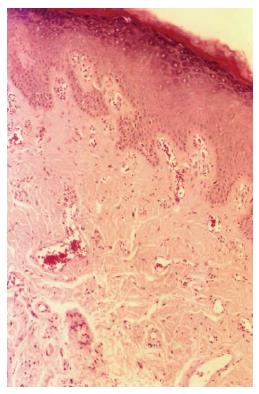
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of actinic cheilitis lesion presenting epithelial hyperplasia, drop-shaped rete ridges, mild inflammatory infiltrate, vasodilatation, and elastosis (Original magnification × 100).
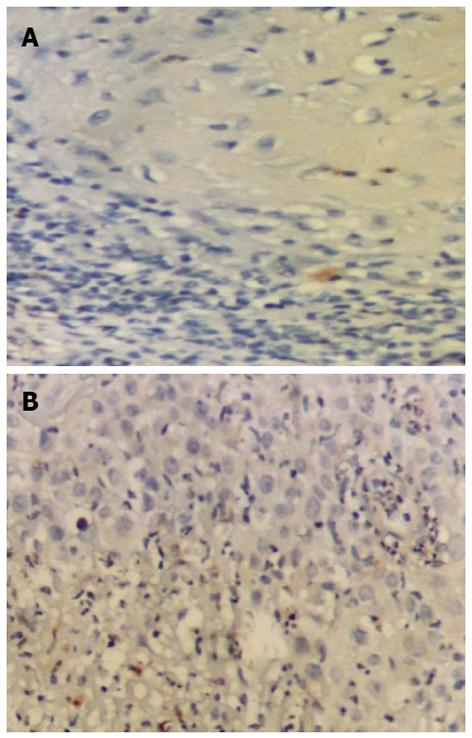
Figure 2 Minimal to negative immunostaining (Original magnification × 200).
A: Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in normal lower lip specimen; B: MMP-12 in normal lower lip specimen.
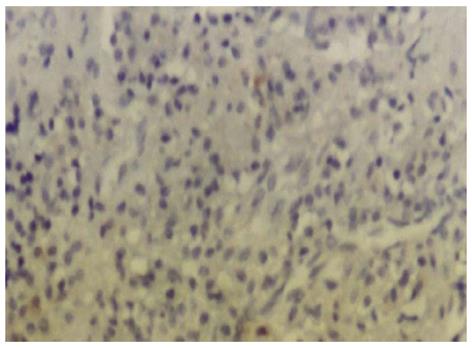
Figure 3 Negative control specimen of the lower lip specimen (Original magnification × 200).
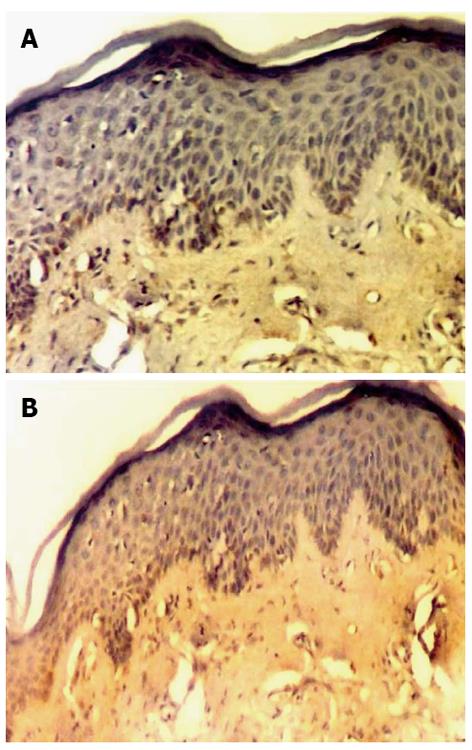
Figure 4 Weak immunostaining of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (A, Original magnification × 100), and strong immunoexpression of Matrix metalloproteinase-12 (B, Original magnification × 100) in actinic cheilitis lesion.
Figure 5 Strong immunostaining of matrix metalloproteinase-12 in chronic inflammatory cells in actinic cheilitis lesion (Original magnification × 200).
- Citation: Poulopoulos AK, Andreadis D, Markopoulos AK. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 9 and 12 in actinic cheilitis. World J Exp Med 2013; 3(3): 43-49
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v3/i3/43.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v3.i3.43