©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Crit Care Med. Jan 31, 2020; 9(1): 1-12
Published online Jan 31, 2020. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v9.i1.1
Published online Jan 31, 2020. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v9.i1.1
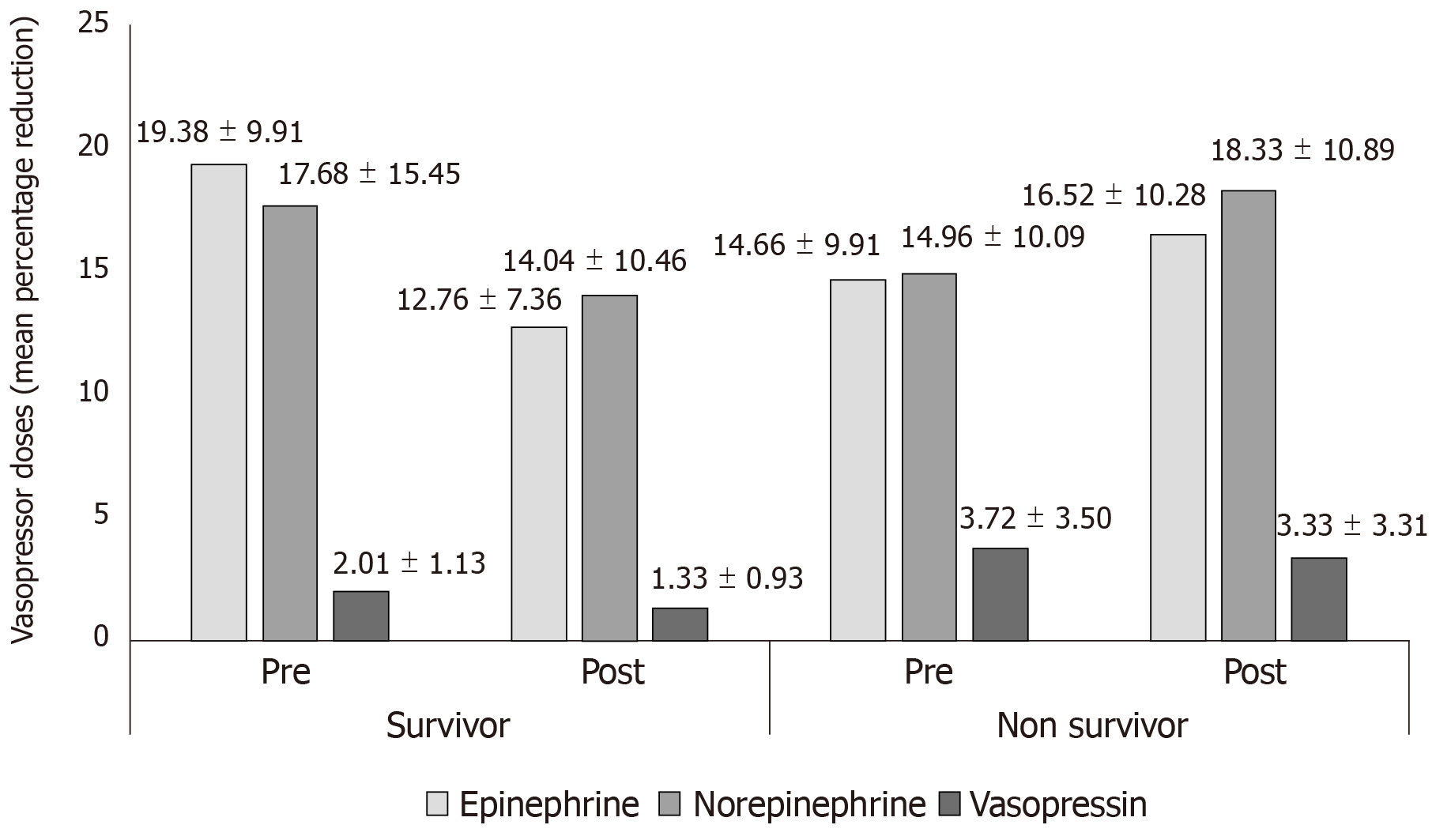
Figure 1 Comparison of percentage reduction in vasopressor doses among survivor and non-survivor patients.
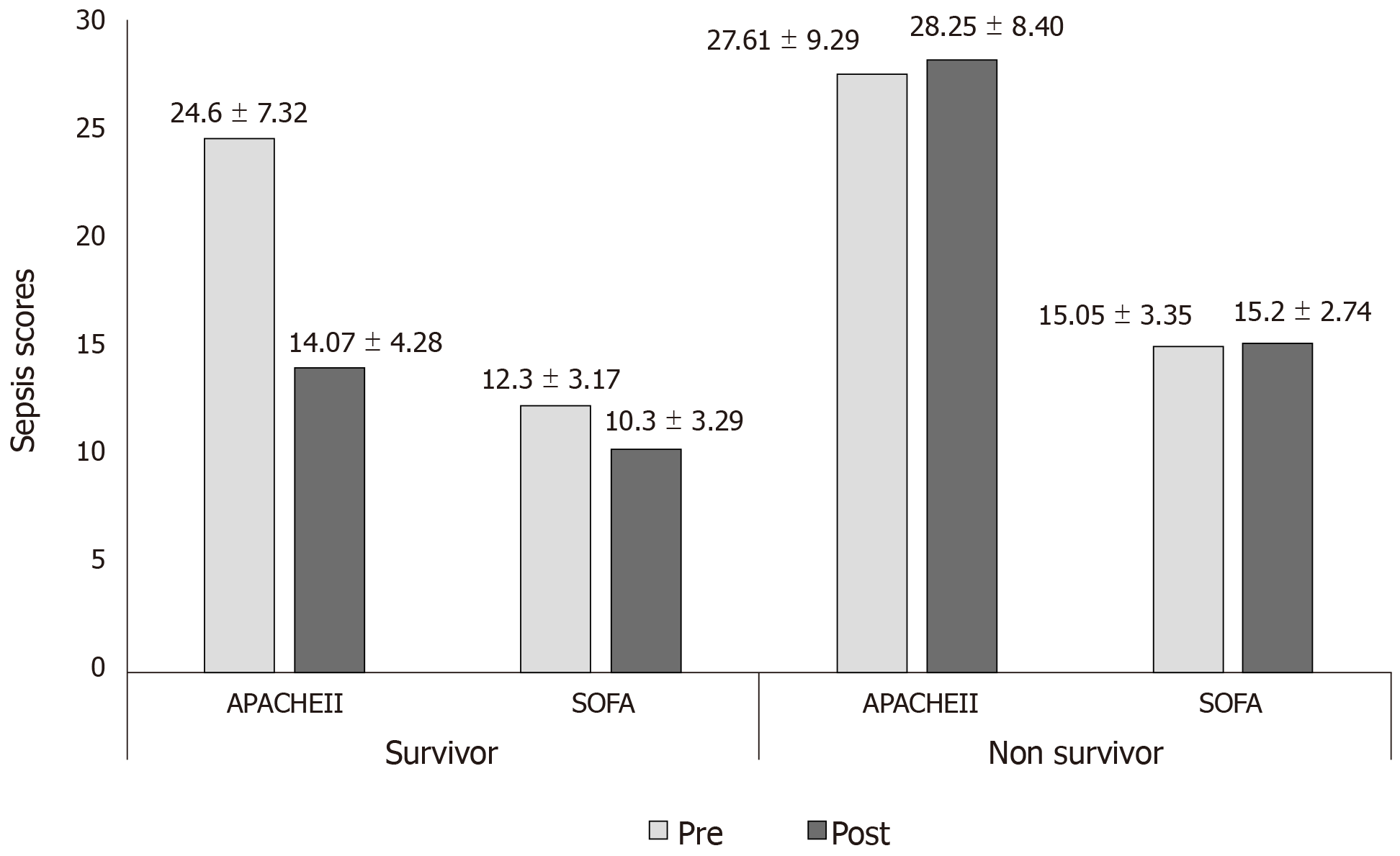
Figure 2 Comparison of sepsis scores among survivor and non-survivor patients.
Significant reduction in acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (P < 0.0001) and sequential organ failure assessment (P = 0.0070) scores in survivor group. APACHE: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; SOFA: Sequential organ failure assessment.
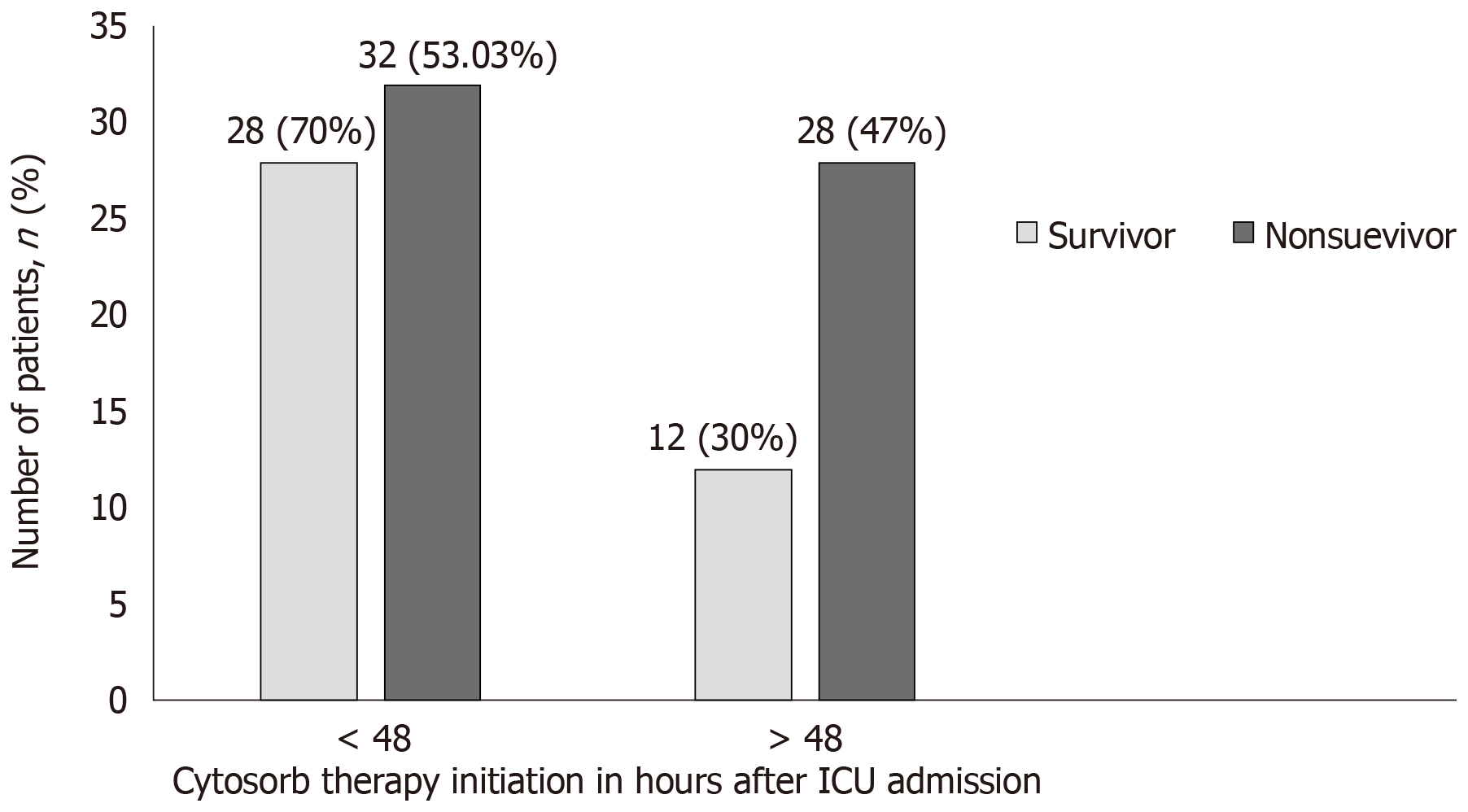
Figure 3 Initiation of CytoSorb® treatment after onset of septic shock.
ICU: Intensive care units.
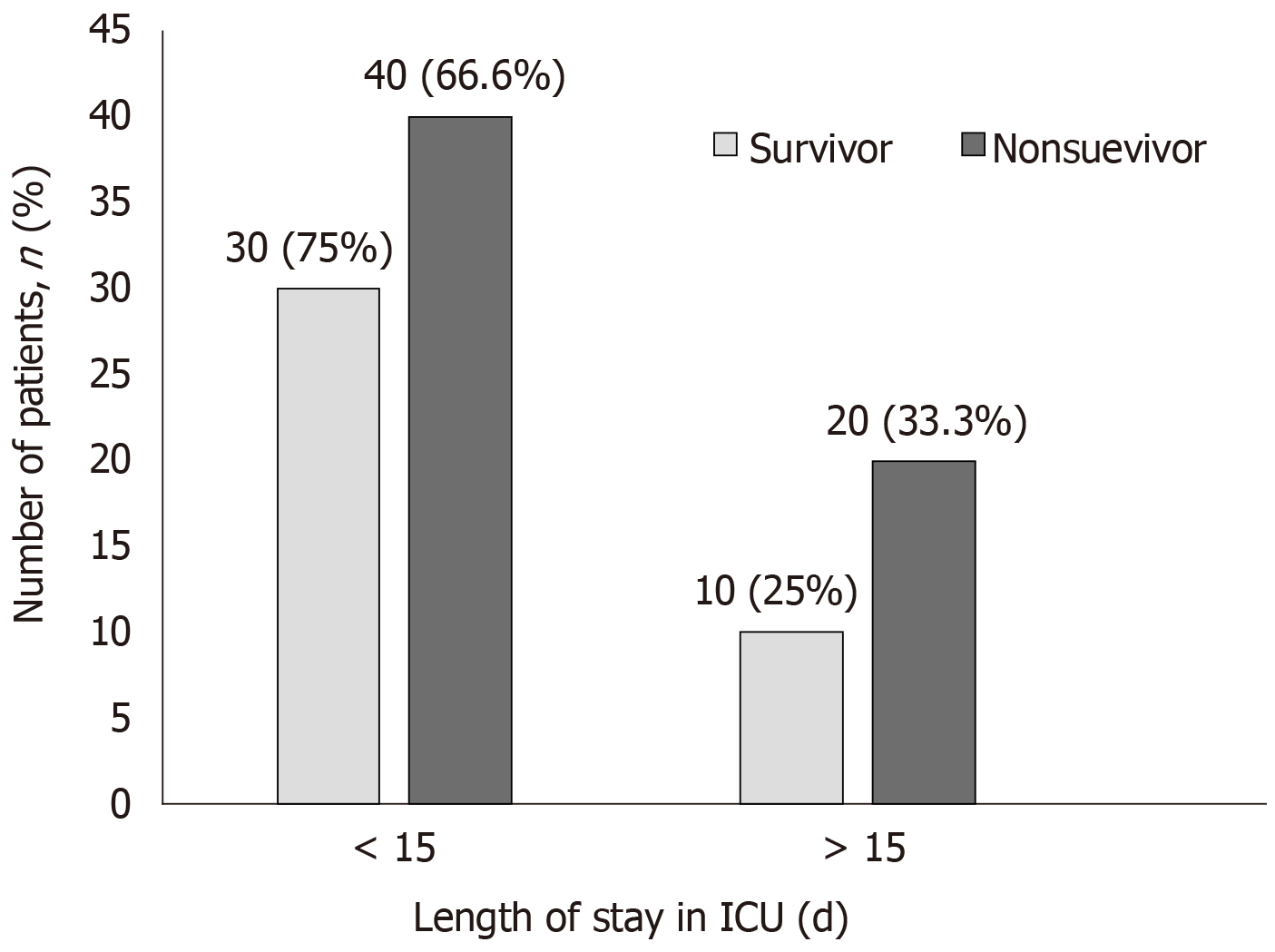
Figure 4 Length of patients’ stay in intensive care units (d).
ICU: Intensive care units.
- Citation: Mehta Y, Mehta C, Kumar A, George JV, Gupta A, Nanda S, Kochhar G, Raizada A. Experience with hemoadsorption (CytoSorb®) in the management of septic shock patients. World J Crit Care Med 2020; 9(1): 1-12
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v9/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v9.i1.1