©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Crit Care Med. Jul 9, 2022; 11(4): 228-235
Published online Jul 9, 2022. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v11.i4.228
Published online Jul 9, 2022. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v11.i4.228
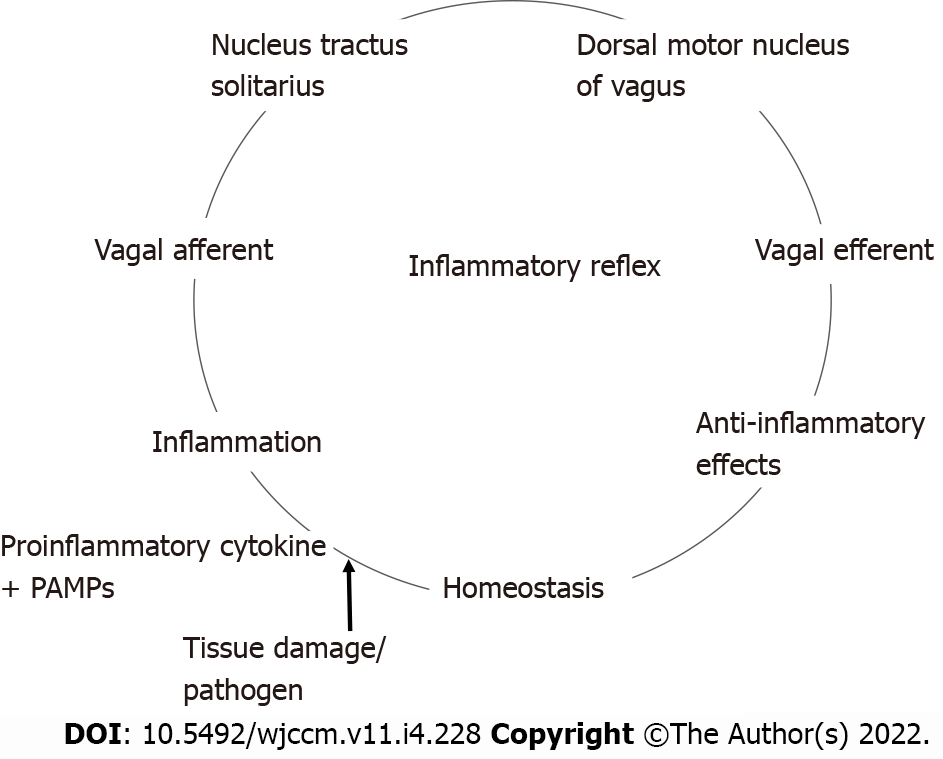
Figure 1 The inflammatory reflex.
The above graphic demonstrates the inflammatory reflex. The afferent limb is activated by pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1βor by pathogen-associated molecular patterns via Toll-like receptors. The afferent limb connects to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), the primary vagal afferent nuclei. The mammalian febrile response is initiated at the NTS. Interneurons connect NTS to dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (DMV) incoming signals. The DMV is the primary efferent nuclei of the vagus nerve. This efferent signal initiates an anti-inflammatory effect, reestablishing homeostasis. PAMPS: pathogen-associated molecular patterns.
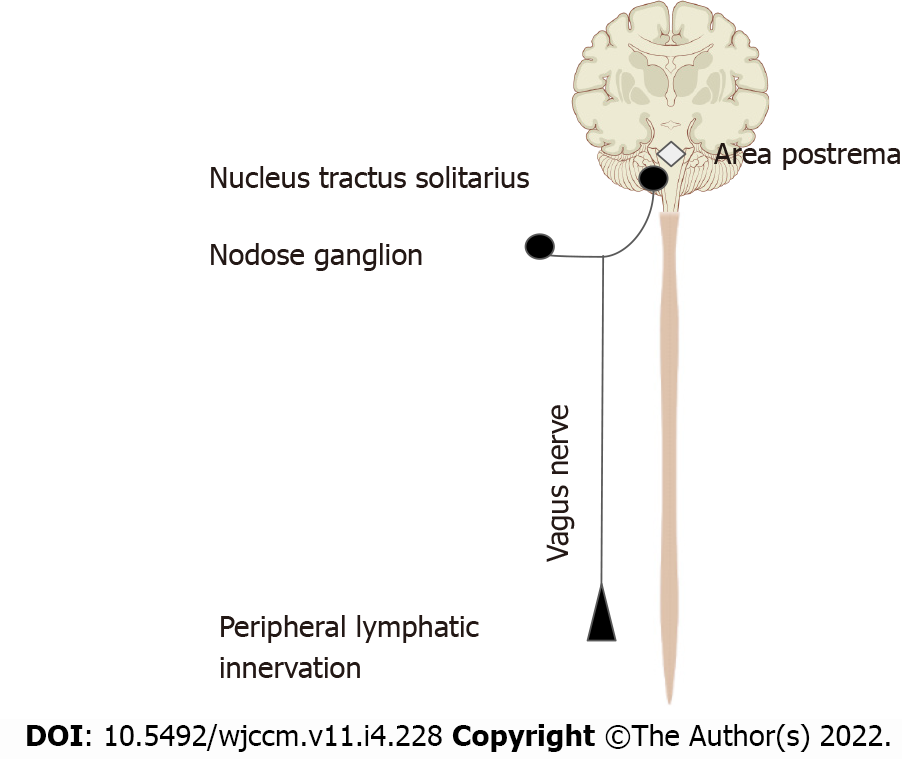
Figure 2 Afferent limb of the inflammatory reflex.
This figure demonstrates the mechanisms by which the vagus nerve senses inflammation. Vagal sensory neurons directly express receptors for various pro-inflammatory cytokines such as, tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 1β, neuropeptide Y and prostaglandins. Vagal fibers innervating the lymphatic system demonstrate sensitivity to interleukin-1β. In addition, the nodose ganglion has been shown to express Toll-like receptors. Area postrema directly expresses proinflammatory cytokine receptors[22]. The signal is transmitted via the vagal afferents to the bilateral nucleus tractus solitarius, the primary vagal afferent nucleus[19].
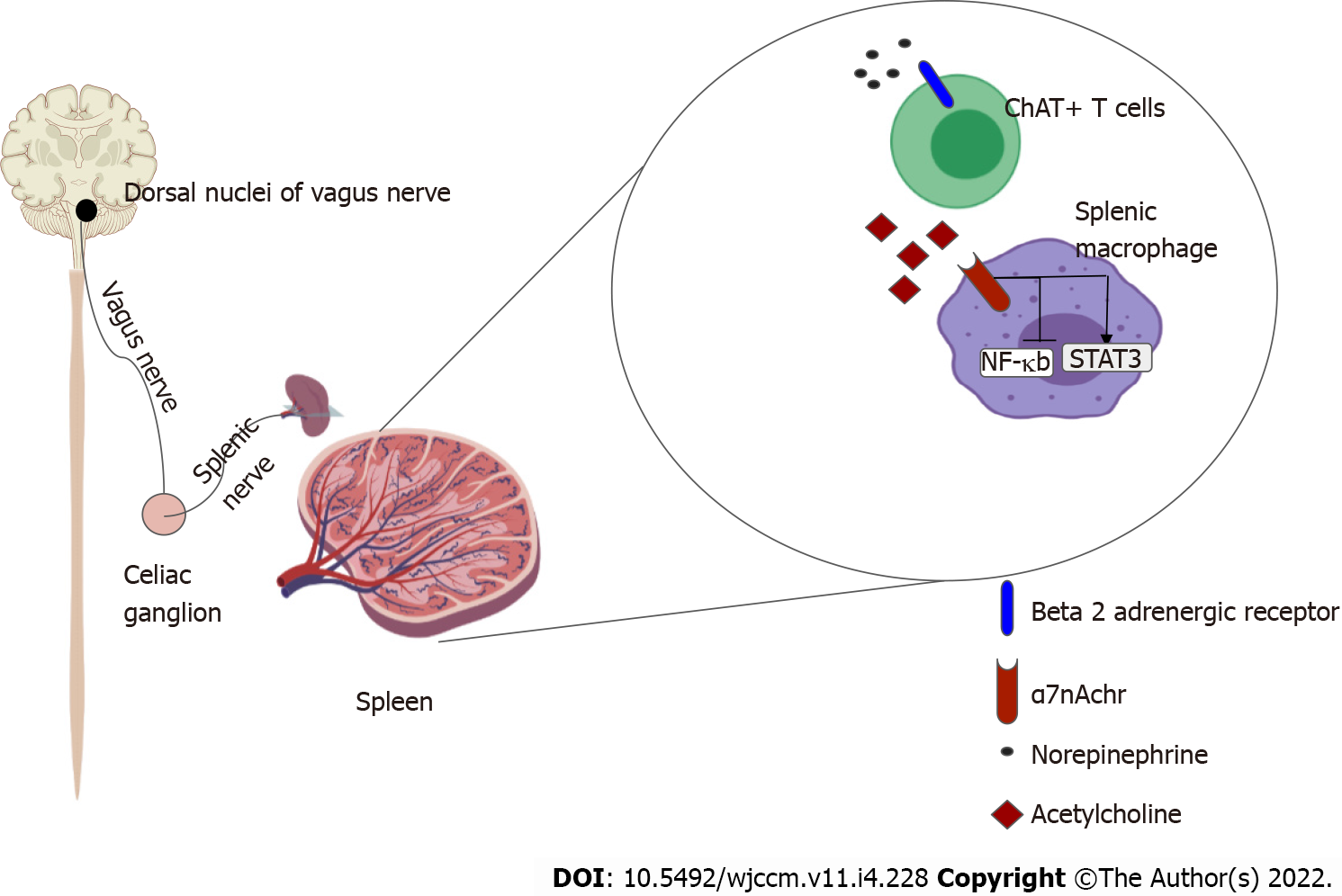
Figure 3 Efferent limb of the inflammatory reflex.
Signal from the dorsal nuclei of vagus is transmitted via cholinergic fibers of the vagus nerve to the celiac ganglion. Noradrenergic neurons from the celiac ganglion via the splenic nerve innervate the spleen. Choline-acetyltransferase positive T cells that reside in the spleen express β-2 adrenergic receptors. Activation of this receptor causes the release of Acetylcholine which binds to the α-7 nicotinic acetylcholinergic receptor on splenic macrophages causing the inhibition of NF-kappa β pathway and upregulation of STAT3, ultimately suppressing inflammation[16,23].
- Citation: Ahmad F. Medicinal nicotine in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome, the new corticosteroid. World J Crit Care Med 2022; 11(4): 228-235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v11/i4/228.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v11.i4.228