©2012 Baishideng.
World J Crit Care Med. Jun 4, 2012; 1(3): 80-93
Published online Jun 4, 2012. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v1.i3.80
Published online Jun 4, 2012. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v1.i3.80
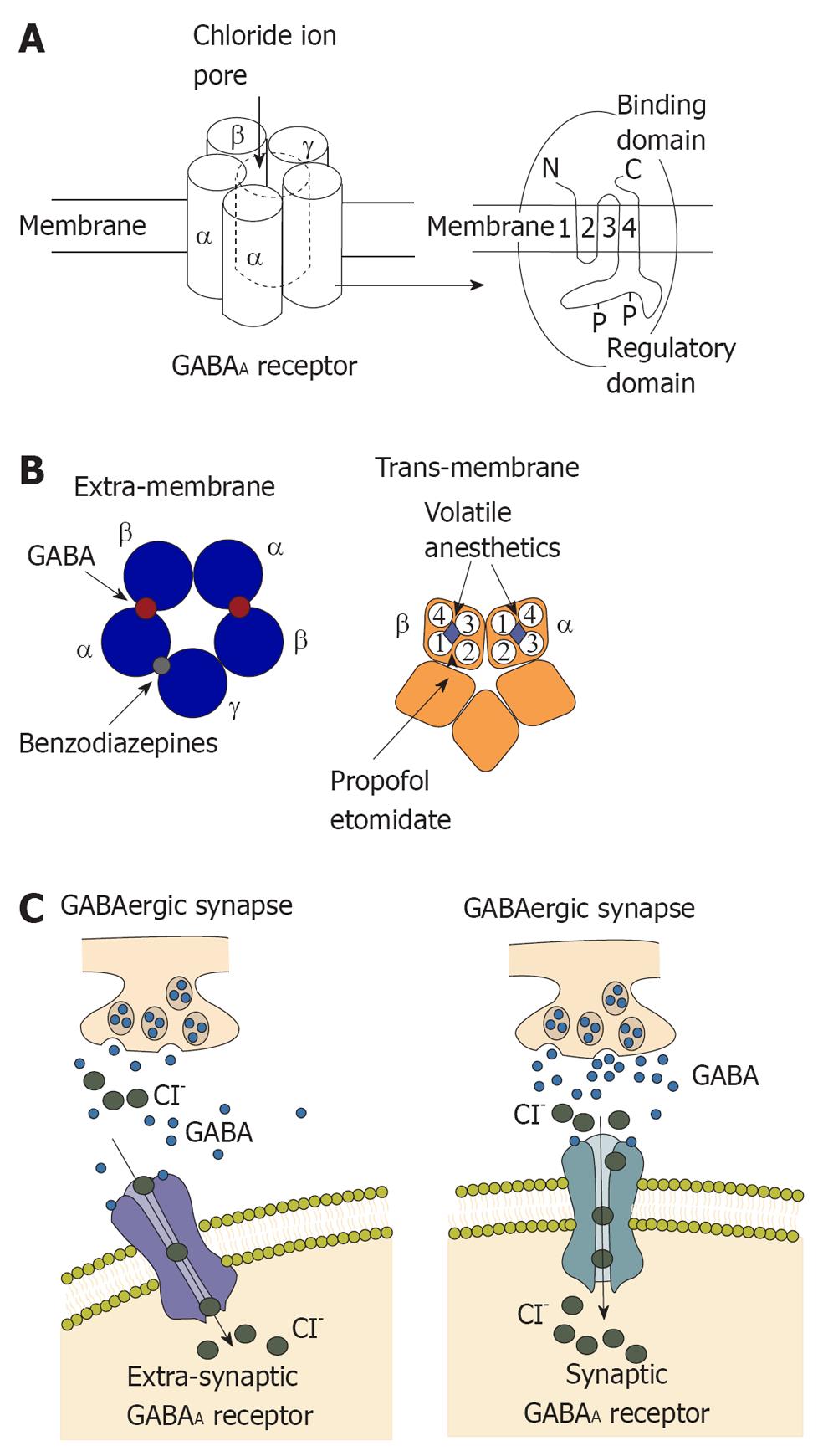
Figure 1 Structure and function of γ- aminobutyric acid type A receptor.
A: γ- aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors commonly contain two α subunits, two β subunits and one γ subunit. Chloride influx through the pore could hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane; B: Left: Extra-membrane region of GABAA receptor. The binding sites for GABA are located between α and β subunits and the binding site for benzodiazepines is located between γ and α subunits; Right: Trans-membrane region of GABAA receptor. Four trans-membrane segments form the α subunit. It has been shown that the trans-membrane segment of β subunit is the binding site for propofol and etomidate. This binding site is close to a binding site for volatile anesthetics; C: Activation of the GABAA receptor could increase conductance of the postsynaptic membrane and alter the potential of the membrane because of influx of chloridion. Synaptic receptors could detect GABA at mmol concentration to produce fast inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), and extra-synaptic receptors that detect GABA at μmol concentrations to produce slower IPSPs.
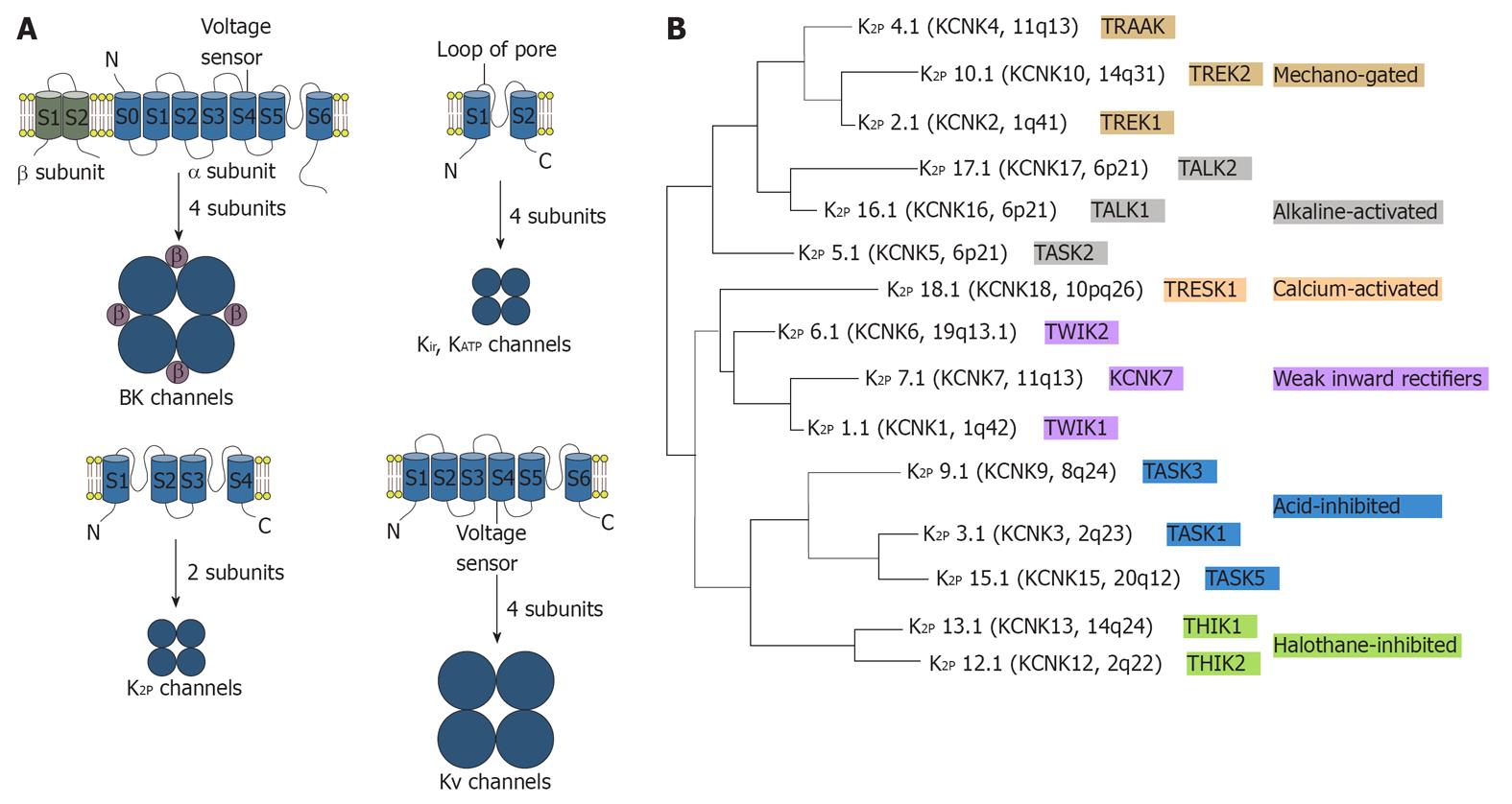
Figure 2 The trans-membrane structures and subunit formulation of the potassium channels and phylogenetic tree of K2P channels in humans.
A: The trans-membrane structures and subunit formulation of the potassium channels. BK channels (background) are made up of four α-subunits and the four β subunits. Structures of Kir or KATP channels are the simplest. Their subunit has two trans-membrane segments connected by a pore loop. Four subunits form a functional channel pore. K2P channels are made of a tetrameric pore made up of two subunits. Subunits of KV channels have six trans-membrane regions and trans-membrane domain S4 acts as the voltage sensor; B: Phylogenetic tree of K2P channels from humans. The chromosomal localization, nomenclature and functional properties of each subunit are indicated. Different colors indicate the functional subgroups. TASK1: TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+; K2P: Two-pore-domain K+.
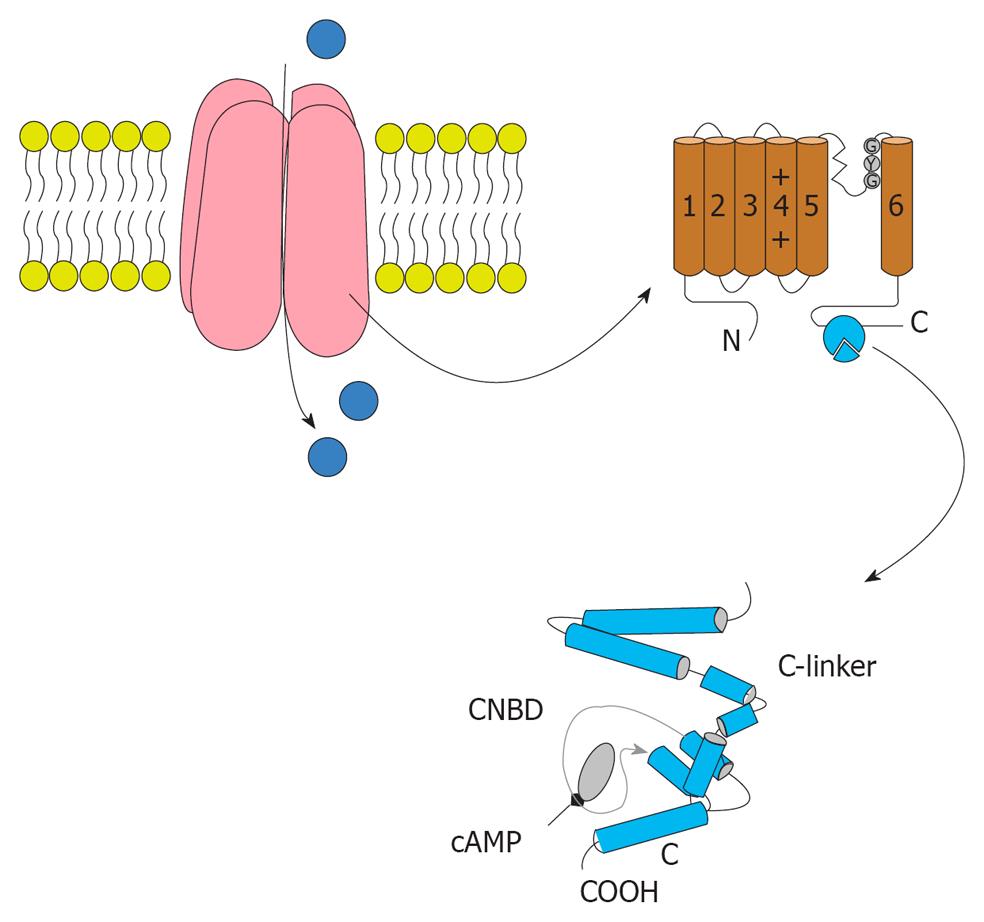
Figure 3 The structure of Hyperpolarization activated cyclic nucleotide channels.
Hyperpolarization activated cyclic nucleotide (HCN) channels are made of four subunits. Each subunit contained six trans-membrane segments and S4 acts as the voltage sensor. The pore and filter for ion selection is between S5 and S6. The C-terminal of the HCN channel domain includes the cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (bottom). The domain of the C-linker consists of six a-helices.
- Citation: Zhou C, Liu J, Chen XD. General anesthesia mediated by effects on ion channels. World J Crit Care Med 2012; 1(3): 80-93
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v1/i3/80.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v1.i3.80