©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Surg Proced. Mar 28, 2014; 4(1): 13-20
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v4.i1.13
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.5412/wjsp.v4.i1.13
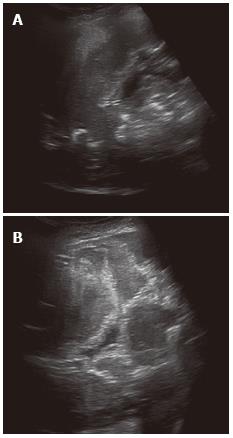
Figure 1 Alveolar echinococcosis in a 41-year-old woman.
Abdominal gray-scale ultrasonography (US) image shows a heterogeneous mass lesion in the right lobe of the liver. The mass is generally hypoechoic but contains hyperechoic foci of calcifications (A). Alveolar echinococcosis in a 38 year old woman. Abdominal gray-scale US image shows a heterogeneous, hyperechoic lesion without calcifications (B).
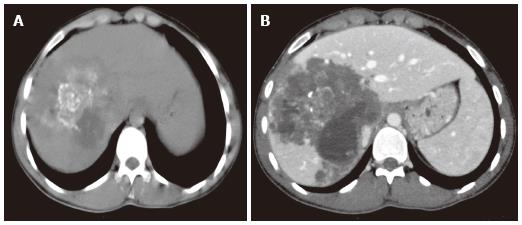
Figure 2 Alveolar echinococcosis in a 34-year-old man.
Axial unenhanced computed tomography (CT) image demonstrates an infiltrating tumor-like hepatic mass with irregular margins and heterogeneous contents, including scattered hyperattenuating foci of calcification and areas of hypoattenuation corresponding to necrosis and parasite tissue (A). Alveolar echinococcosis in a 29 year old man. Abdominal CT images obtained after the administration of intravenous contrast medium show a poor enhancement, hypoattenuating lesion in the portal venous phase (B).
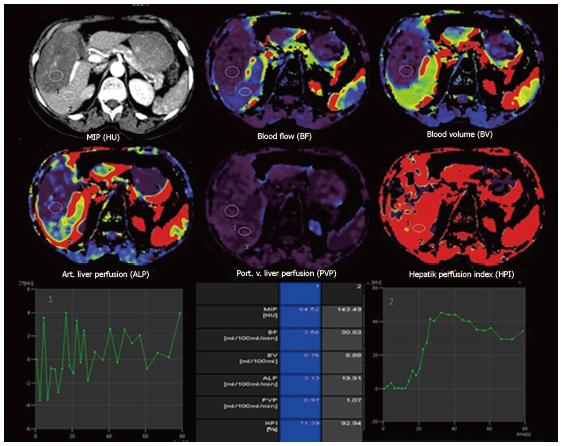
Figure 3 Transverse computed tomography perfusion functional maps of the blood volume, blood flow, portal-venous perfusion, arterial liver perfusion and hepatic perfusion index in a 49-year-old woman show a large alveolar echinococcosis lesion in the right lobe of the liver that has a distinct range of colors compared with the background liver parenchyma.
Perfusion values from an ROI drawn in the solid component without calcification of alveolar echinococcosis (ROI 1) and normal tissue (ROI 2) show lower blood flow, blood volume, arterial liver perfusion and portal-venous perfusion values compared with normal liver parenchyma.
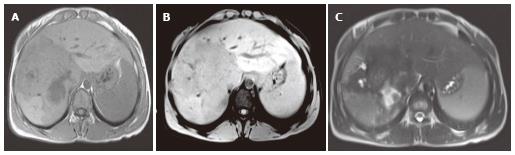
Figure 4 Alveolar echinococcosis in a 39-year-old man.
Axial unenhanced T1-weighted image show an infiltrating hypointense mass in the right lobe of the liver (A). Axial magnetic resonance imaging obtained after the administration of intravenous contrast medium show no contrast enhancement within the mass (B). Axial T2-weighted image show an infiltrating hypointense mass in the right lobe of the liver (C).
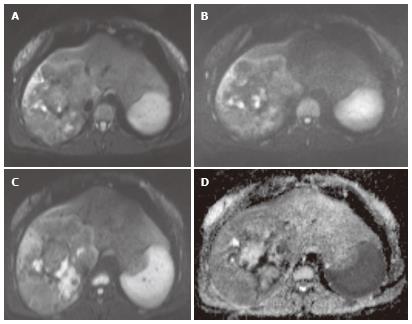
Figure 5 Alveolar echinococcosis in a 44-year-old man.
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images obtained with b values of 400 sec/mm2 (A), 800 sec/mm2 (B), and 1000 sec/mm2 (C) and corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient map (D) show signal hyperintensity in a hepatic mass.
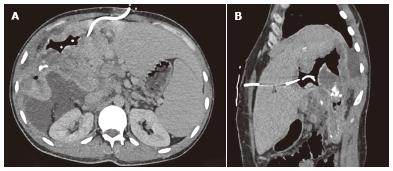
Figure 6 Non-contrast enhanced axial (A) and sagittal (B) computed tomography images show the percutaneous drainage of an infected parasitic cyst in a 43 year old woman with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis.
- Citation: Kantarci M, Pirimoglu B, Kizrak Y. Diagnostic imaging and interventional procedures in a growing problem: Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. World J Surg Proced 2014; 4(1): 13-20
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2832/full/v4/i1/13.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5412/wjsp.v4.i1.13