©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Immunol. Jul 27, 2014; 4(2): 98-106
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i2.98
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i2.98
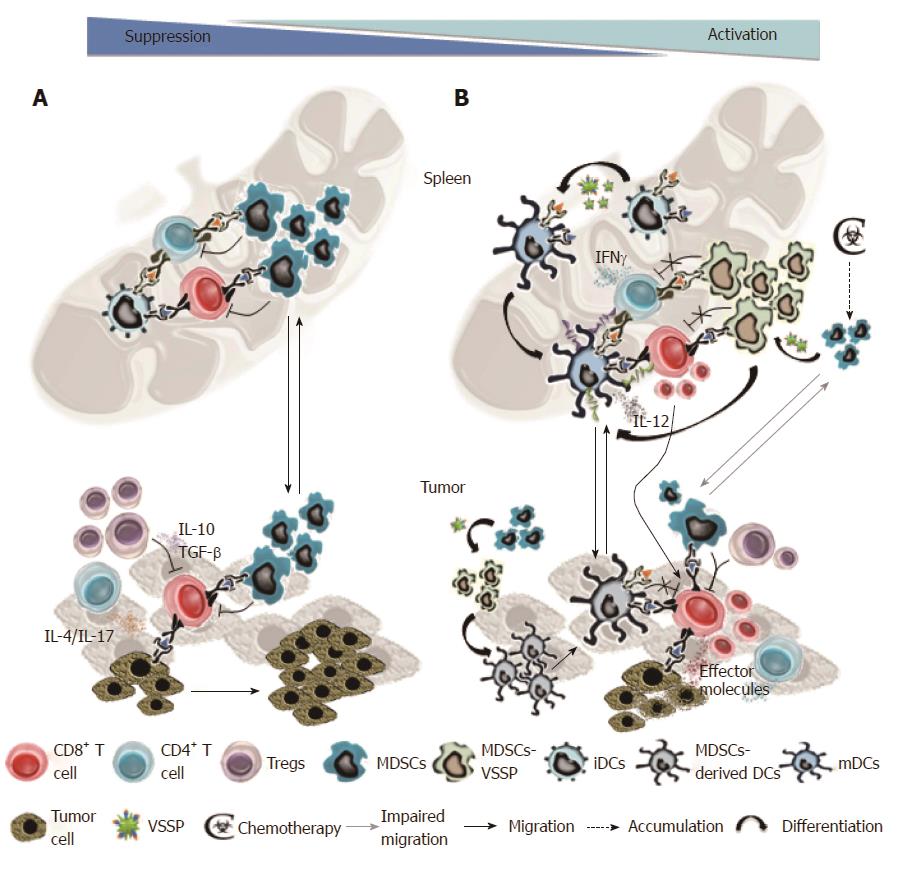
Figure 1 Schematic of potential immunomodulatory effects of very small size proteoliposomes in tumor-bearing hosts.
A: Tumor-associated immunosuppressive networks prevent the elimination of neoplastic cells by specific T cells, thus contributing to tumor growth and metastasis; B: VSSP administration reduces the suppressive function of tumor-induced MDSCs, impairs their migration to the tumor microenvironment and promotes their differentiation towards DCs, both at the tumor and secondary lymphoid organs. VSSP also stimulates the activation and effector function of tumor-specific CTL, and combined with the concomitant reduction in the frequency of suppressive MDSCs and Tregs at the tumor site, further enhances elimination of neoplastic cells. An accelerated recovery from chemotherapy-induced leukopenia with VSSP treatment also contributes to a better anti-tumor response. VSSP: Very small size proteoliposomes; MDSCs: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; DCs: Dendritic cells; CTL: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
- Citation: Fernández A, Oliver L, Alvarez R, Fernández LE, Mesa C. GM3-containing nanoparticles in immunosuppressed hosts: Effect on myeloid-derived suppressor cells. World J Immunol 2014; 4(2): 98-106
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v4/i2/98.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v4.i2.98