©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Pediatr. Jun 9, 2023; 12(3): 77-85
Published online Jun 9, 2023. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v12.i3.77
Published online Jun 9, 2023. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v12.i3.77
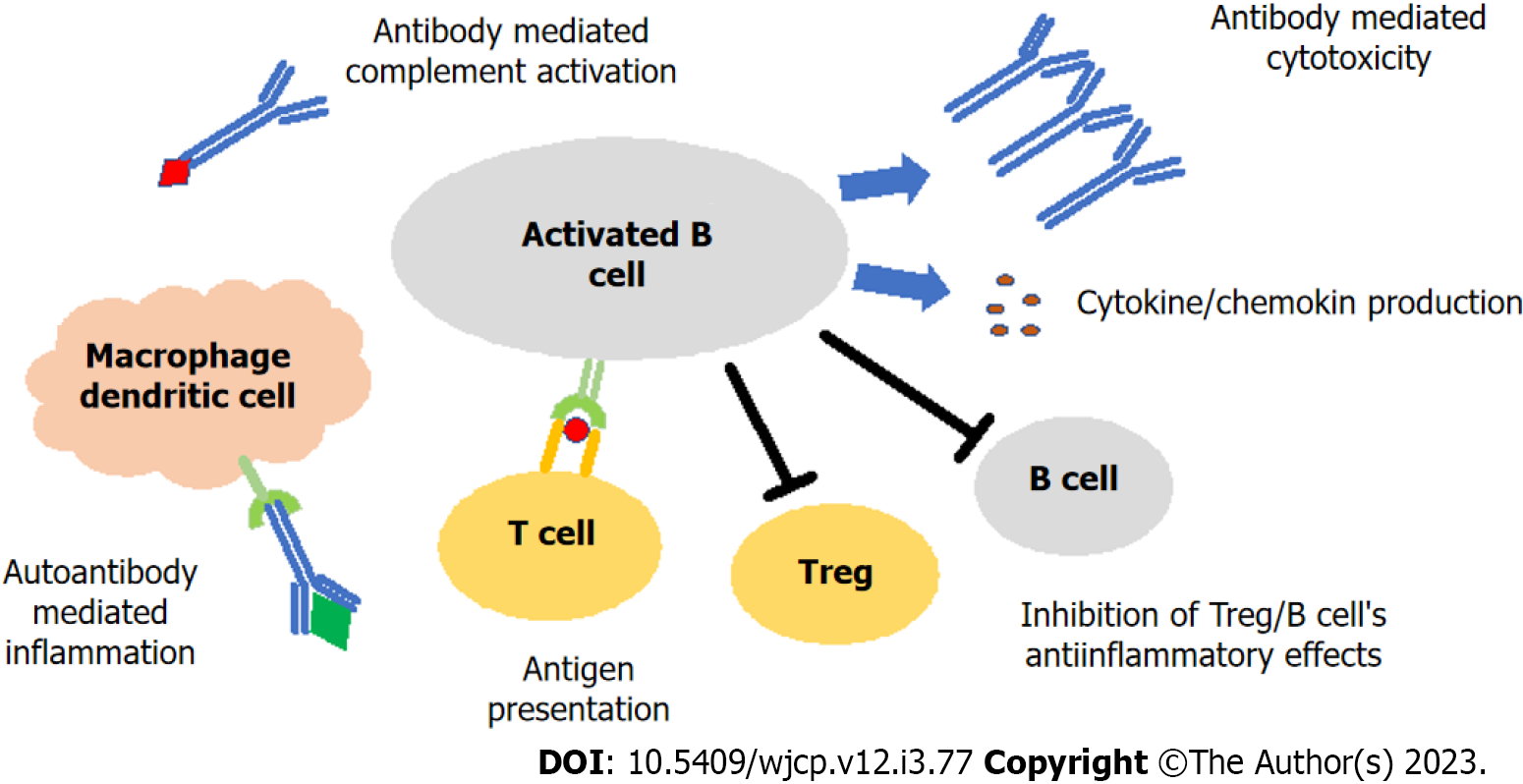
Figure 1 B cell role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis.
T cells allow B cells to switch to antibody-producing plasma cells. Autoreactive B cells release autoantibody and cytokine/chemokines. B cells continue to contribute to inflammation by presenting antigen to T cells and cause autoantibody-mediated activation of macrophage/dendritic cells, while suppressing the anti-inflammatory effects of Treg and B cells. Treg: Regulatory T cell.
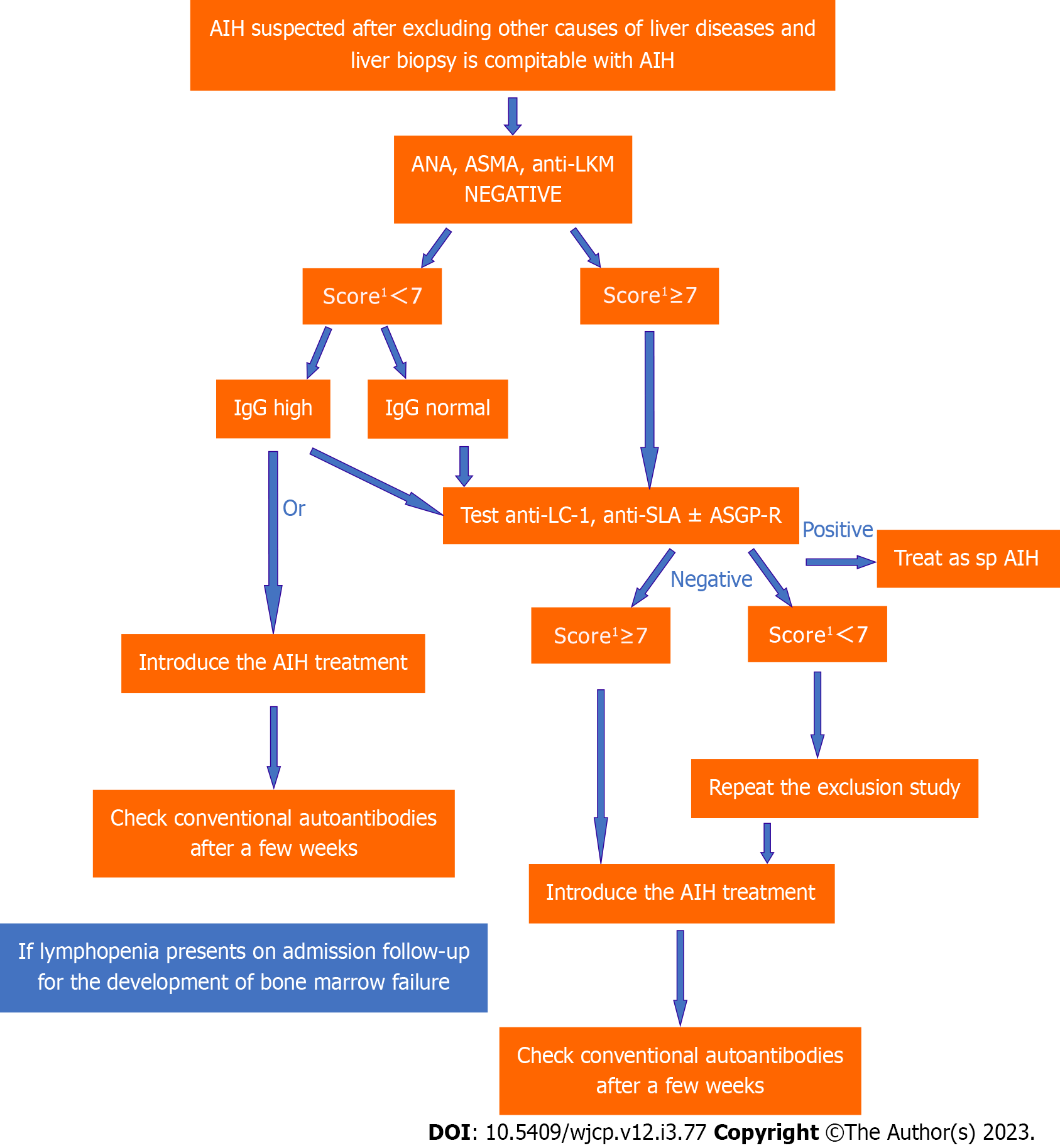
Figure 2 Algorithm for the diagnosis of seronegative autoimmune hepatitis.
1Proposed scoring criteria for the diagnosis of juvenile autoimmune liver disease by ESPGHAN 2018 (10). AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; ANA: Anti-nuclear antibody; ASMA: Anti-smooth muscle antibody; LKM: liver-kidney microsomal antibody; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; LC-1: Liver cytosol type-1 antibody; SLA: Anti-soluble liver antigen/liver–pancreas antigen; ASGP-R: Asialoglycoprotein receptor.
- Citation: Islek A, Tumgor G. Seronegative autoimmune hepatitis in childhood. World J Clin Pediatr 2023; 12(3): 77-85
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v12/i3/77.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v12.i3.77