©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Pediatr. Sep 9, 2021; 10(5): 106-111
Published online Sep 9, 2021. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v10.i5.106
Published online Sep 9, 2021. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v10.i5.106
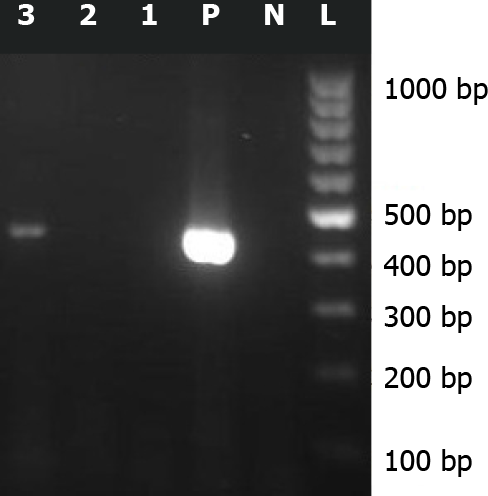
Figure 1 Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay amplification of Sabin-like type 1 poliovirus RNA isolated from cerebrospinal fluid samples of this case.
3: Amplified product (approximately 438 bp) on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; L: 100 bp DNA ladder; N: Negative control; P: Positive control.
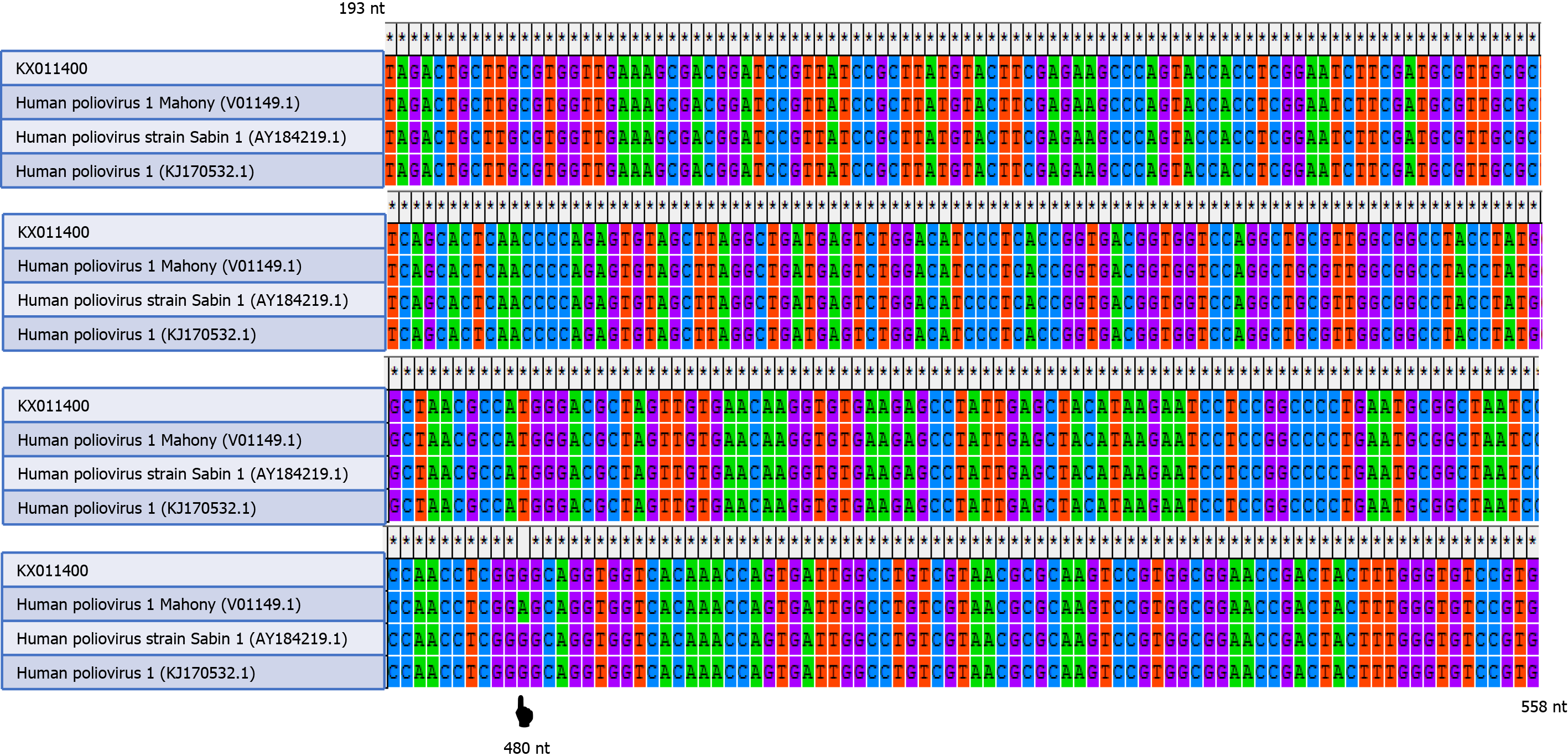
Figure 2 Alignment of the partial nucleotide sequences (193 nt to 558 nt) of this case (KX011400).
Wild-type poliovirus (V01149.1), vaccine-strain poliovirus (AY184219.1), and vaccine-derived poliovirus (KJ170532.1) by MEGA software version 4.0 (Biodesign Institute, Tempe, AZ, United States) and appearance of a nucleotide difference at position 480 of the 5’ untranslated region. A denotes wild-type poliovirus and G denotes vaccine-strain poliovirus.
- Citation: Taherkhani R, Farshadpour F. Pediatric case with vaccine-related poliovirus infection: A case report. World J Clin Pediatr 2021; 10(5): 106-111
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v10/i5/106.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v10.i5.106