©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Orthop. Feb 18, 2026; 17(2): 115848
Published online Feb 18, 2026. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v17.i2.115848
Published online Feb 18, 2026. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v17.i2.115848
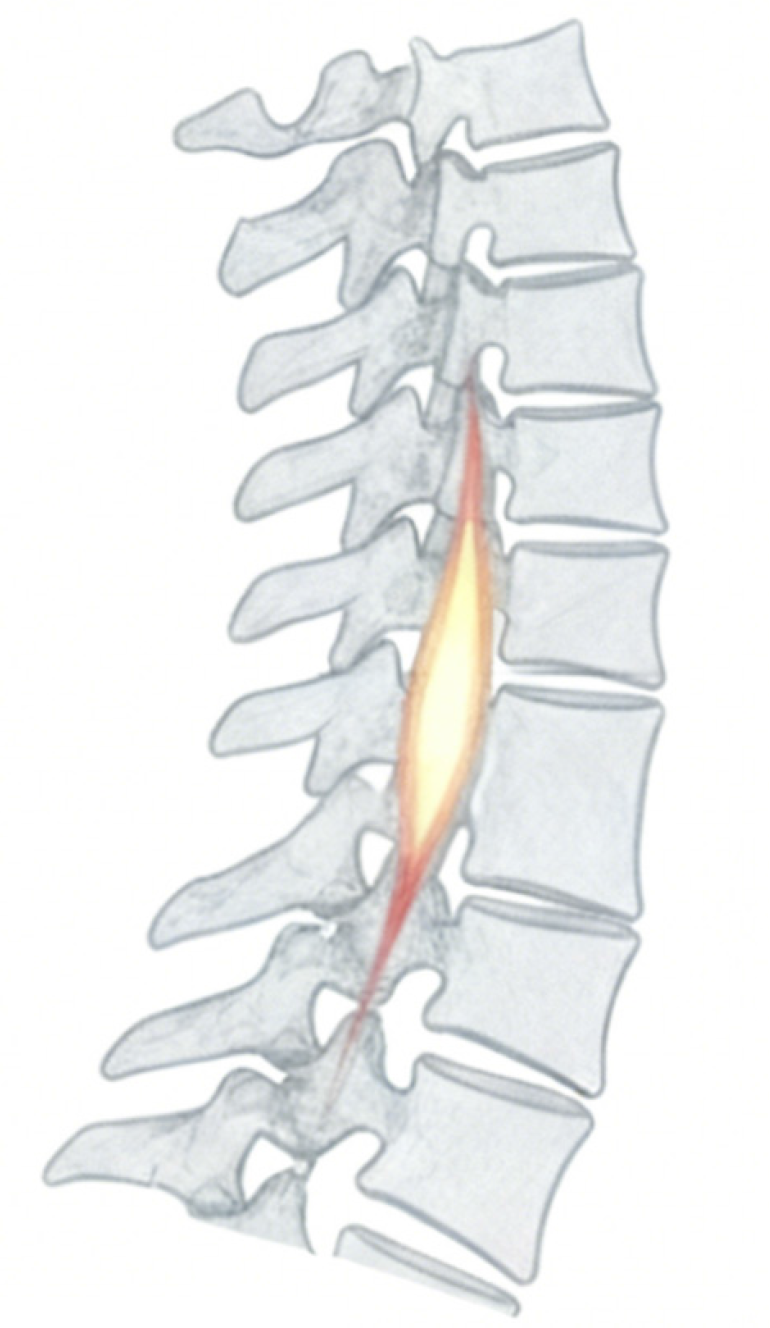
Figure 1
T2-weighted sagittal magnetic resonance imaging of the spine, where the highlighted region denotes the tissue bridge between adjacent vertebral segments.
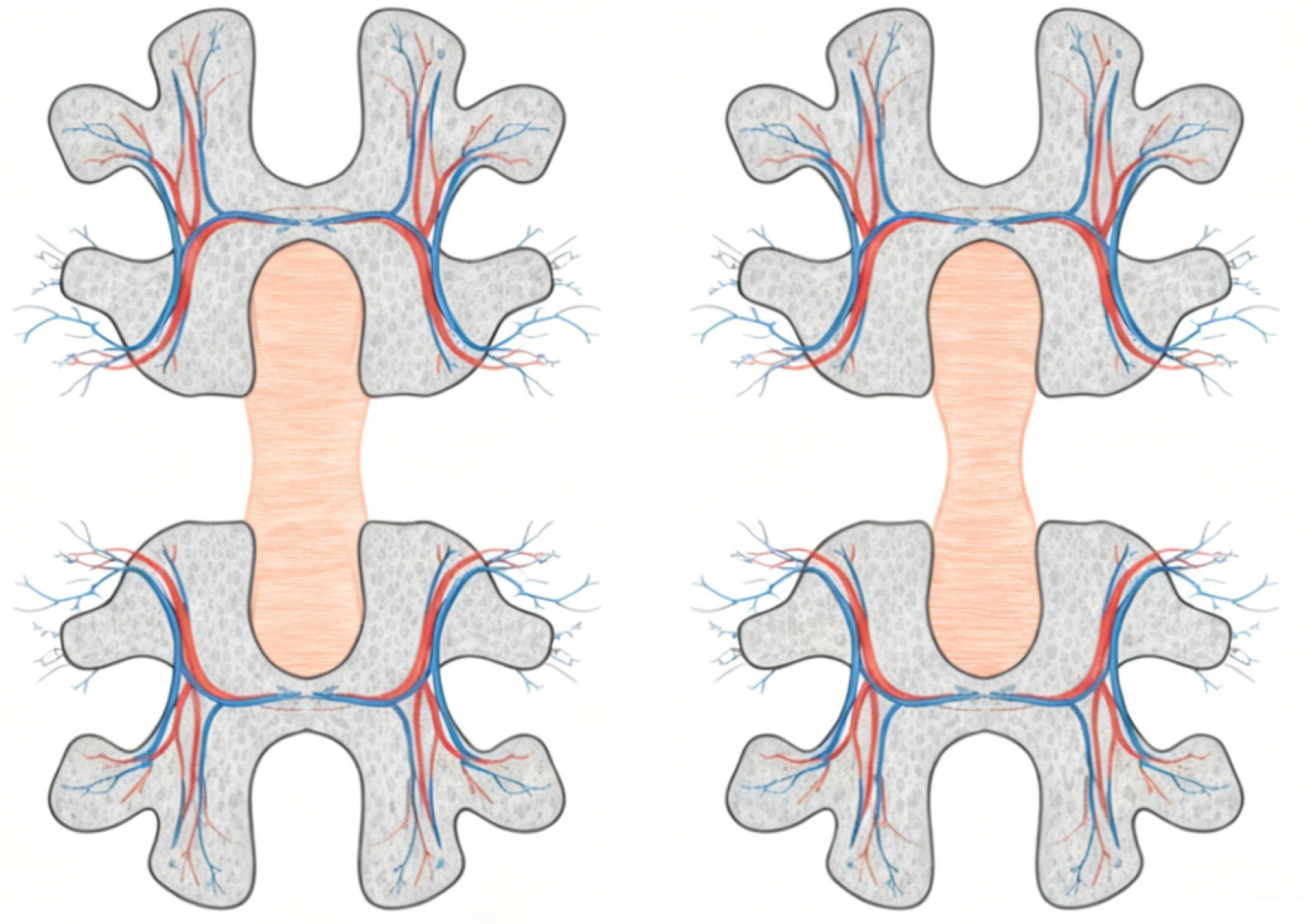
Figure 2
Axial schematic of adjacent vertebral segments, demonstrating the comparison of intact (left) and altered (right) tissue bridge morphology together with associated vascular networks.
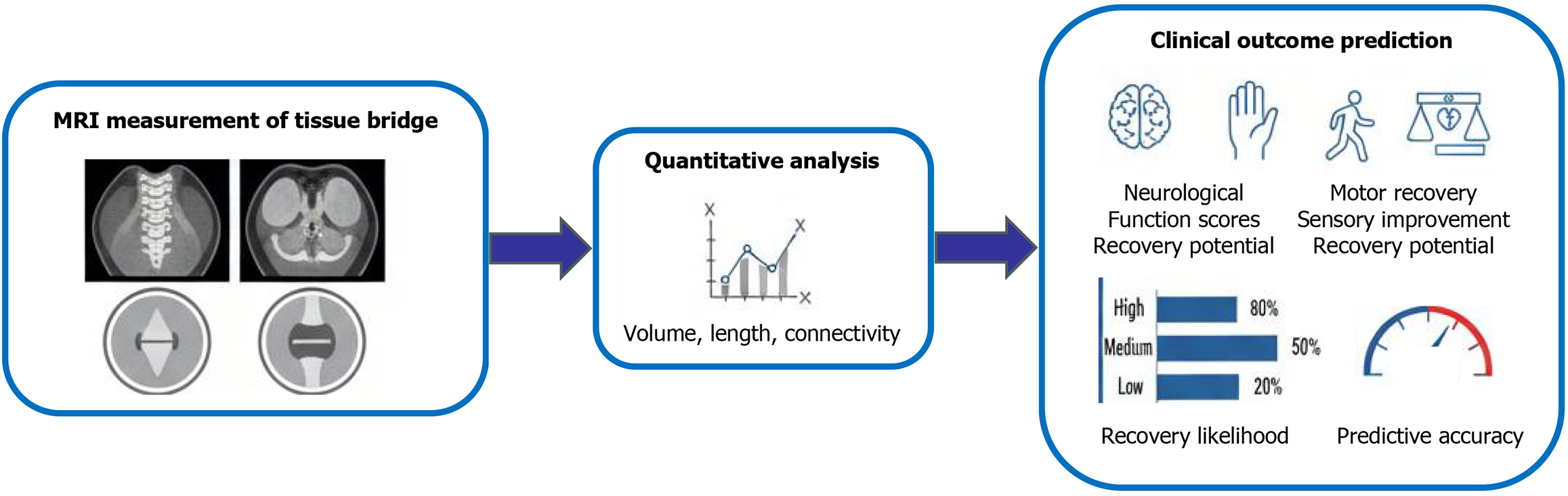
Figure 3 Flowchart depicting the workflow of tissue bridge assessment - from magnetic resonance imaging-based measurement (sagittal/axial imaging) through quantitative analysis (volume, length, connectivity) to the prediction of clinical outcomes (e.
g., neurological function, motor/sensory recovery potential) and associated prognostic metrics. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Peng Y, Luo NN, Gan L, Zhang JQ. Magnetic resonance imaging tissue bridges: An emerging biomarker for prognostication in traumatic spinal cord injury. World J Orthop 2026; 17(2): 115848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v17/i2/115848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v17.i2.115848