©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Orthop. Jan 18, 2026; 17(1): 111824
Published online Jan 18, 2026. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v17.i1.111824
Published online Jan 18, 2026. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v17.i1.111824
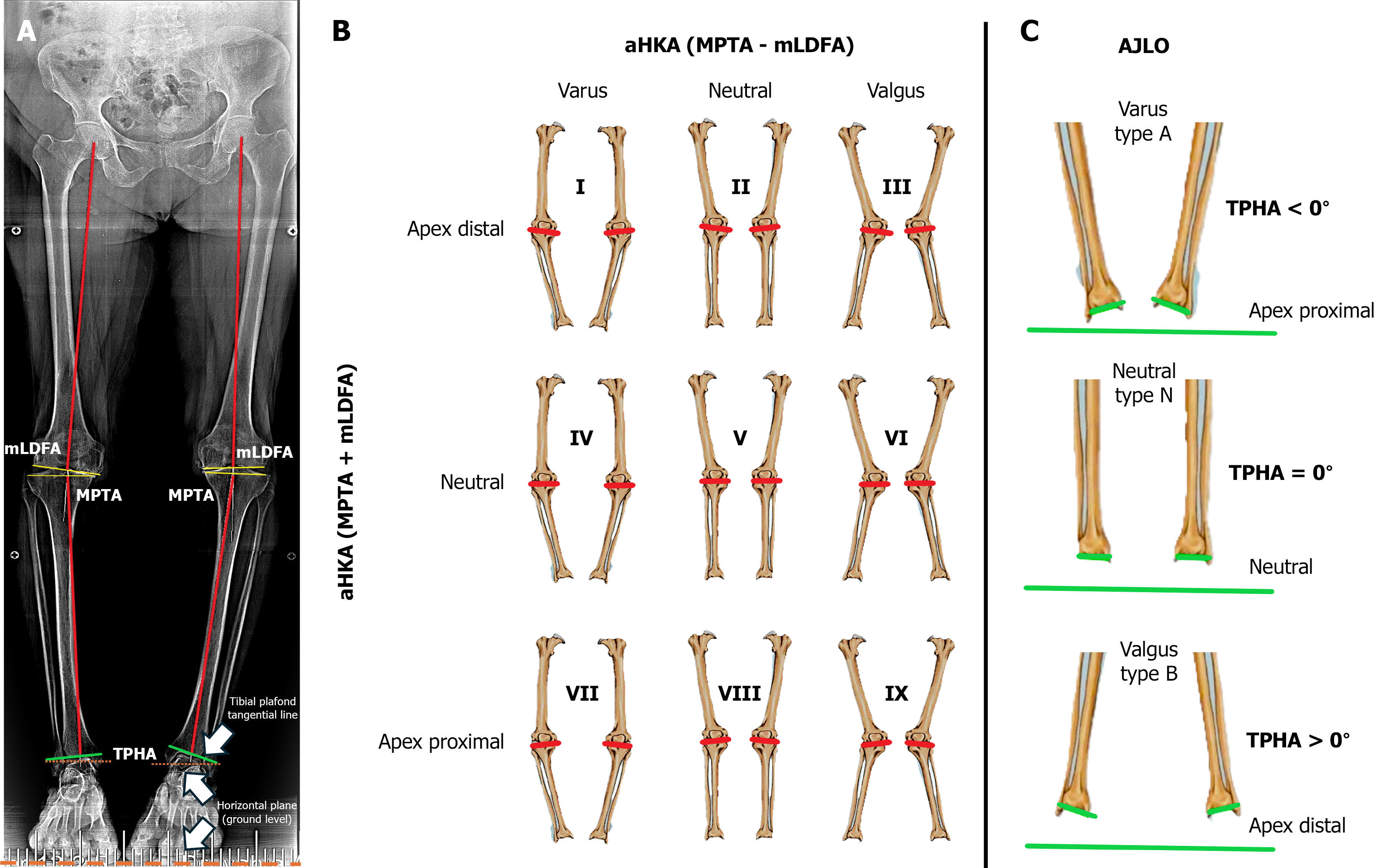
Figure 1 Radiological assessment and classification details.
A: Long-leg, standing anteroposterior (hip to knee to ankle radiograph showing how mechanical lateral distal femoral angle, medial proximal tibial angle, and tibial plafond horizontal angle were measured; B: Schematic representation of the coronal plane alignment of the knee classification following MacDessi et al[5] description; C: Ankle joint line orientation directions and types. mLDFA: Mechanical lateral distal femoral angle; MPTA: Medial proximal tibial angle; TPHA: Tibial plateau horizontal angle; aHKA: Arithmetic hip, knee, and ankle; AJLO: Ankle joint line orientation.
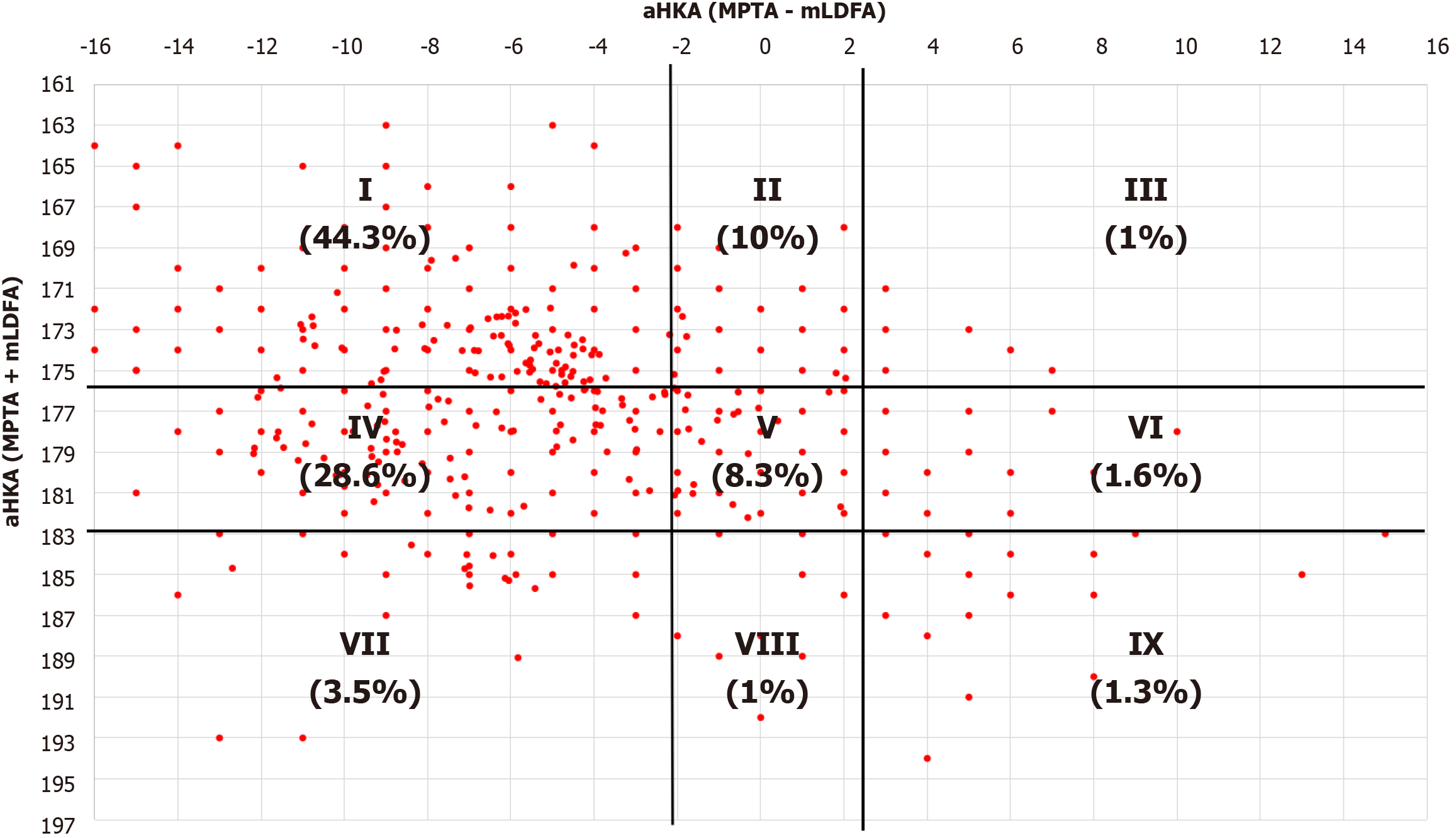
Figure 2 Scatterplot of knee joint line orientation against arithmetic hip, knee, and ankle (aHKA) showing distribution by percentage of the nine coronal plane alignment of the knee phenotypes.
aHKA: Arithmetic hip, knee, and ankle; mLDFA: Mechanical lateral distal femoral angle; MPTA: Medial proximal tibial angle.
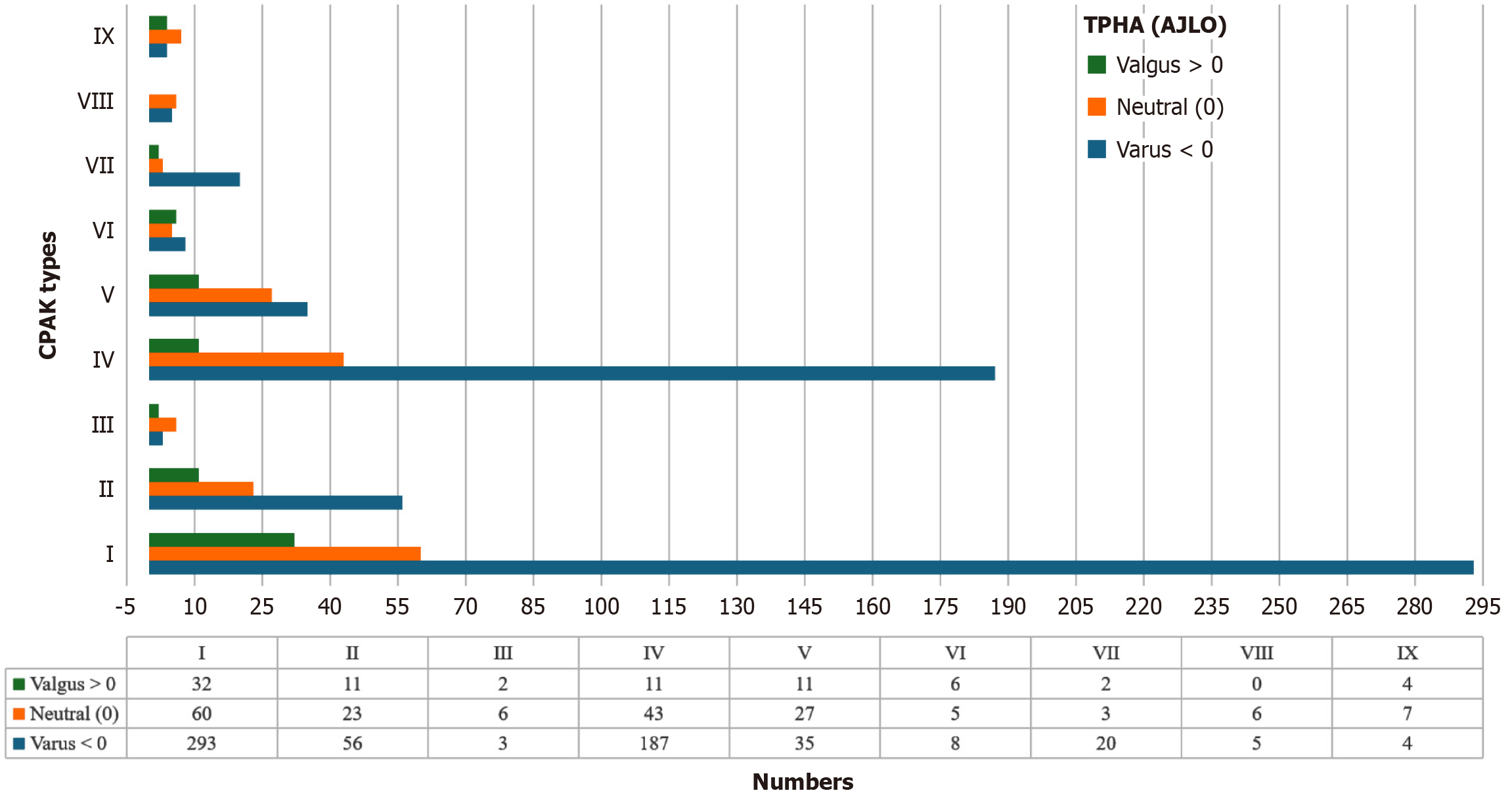
Figure 3 A bar chart showing the distribution of coronal plane alignment of the knee subtypes (ankle joint line orientation types against each coronal plane alignment of the knee type).
CPAK: Coronal plane alignment of the knee; AJLO: Ankle joint line orientation; TPHA: Tibial plateau horizontal angle.
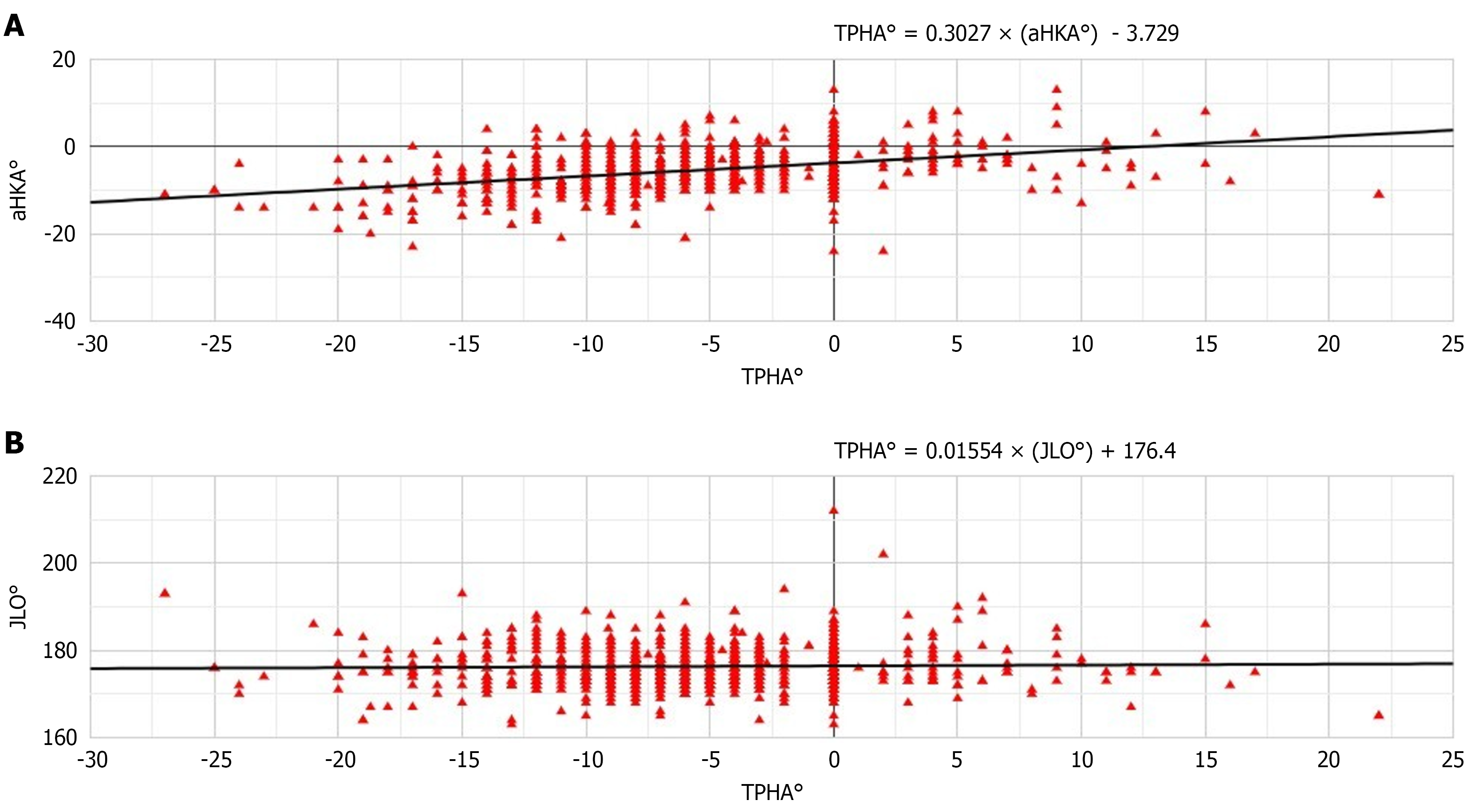
Figure 4 Correlation analysis between tibial plateau horizontal angle, representing the ankle joint line orientation.
A: The arithmetic hip, knee, and ankle; B: The knee joint line orientation. aHKA: Arithmetic hip, knee, and ankle; JLO: Joint line obliquity; TPHA: Tibial plateau horizontal angle.
- Citation: Khalifa AA, Moustafa M, Lemma S, Fayez M, Abdelaal AM, Fadle AA. Coronal plane alignment of the knee phenotypes and ankle joint coronal plane alignment patterns in Egyptian population. World J Orthop 2026; 17(1): 111824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v17/i1/111824.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v17.i1.111824