©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Jul 18, 2025; 16(7): 107698
Published online Jul 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107698
Published online Jul 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107698
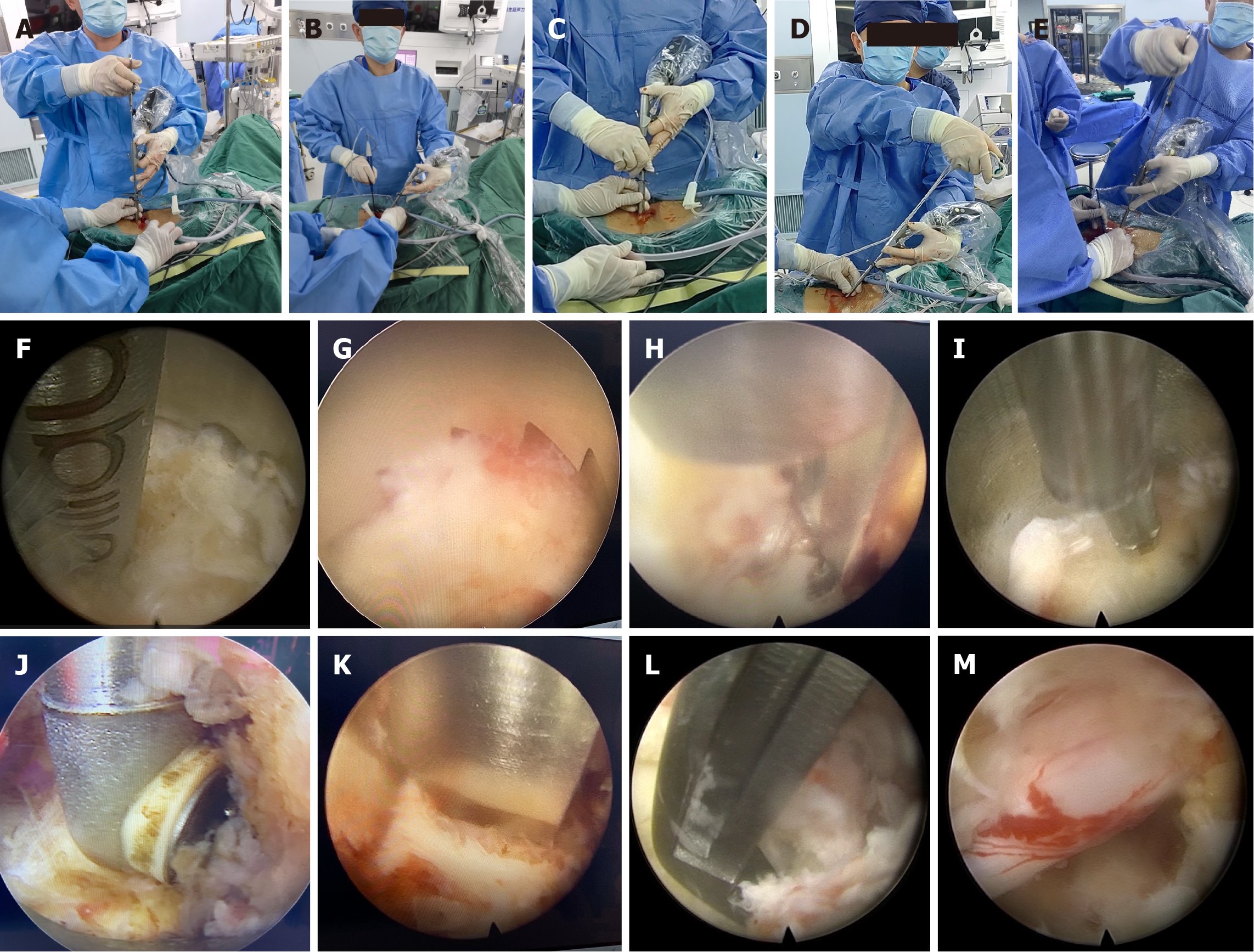
Figure 1 Illustrative cases utilizing the spine biportal full-endoscopy technique for managing lumbar spinal stenosis with bilateral symp
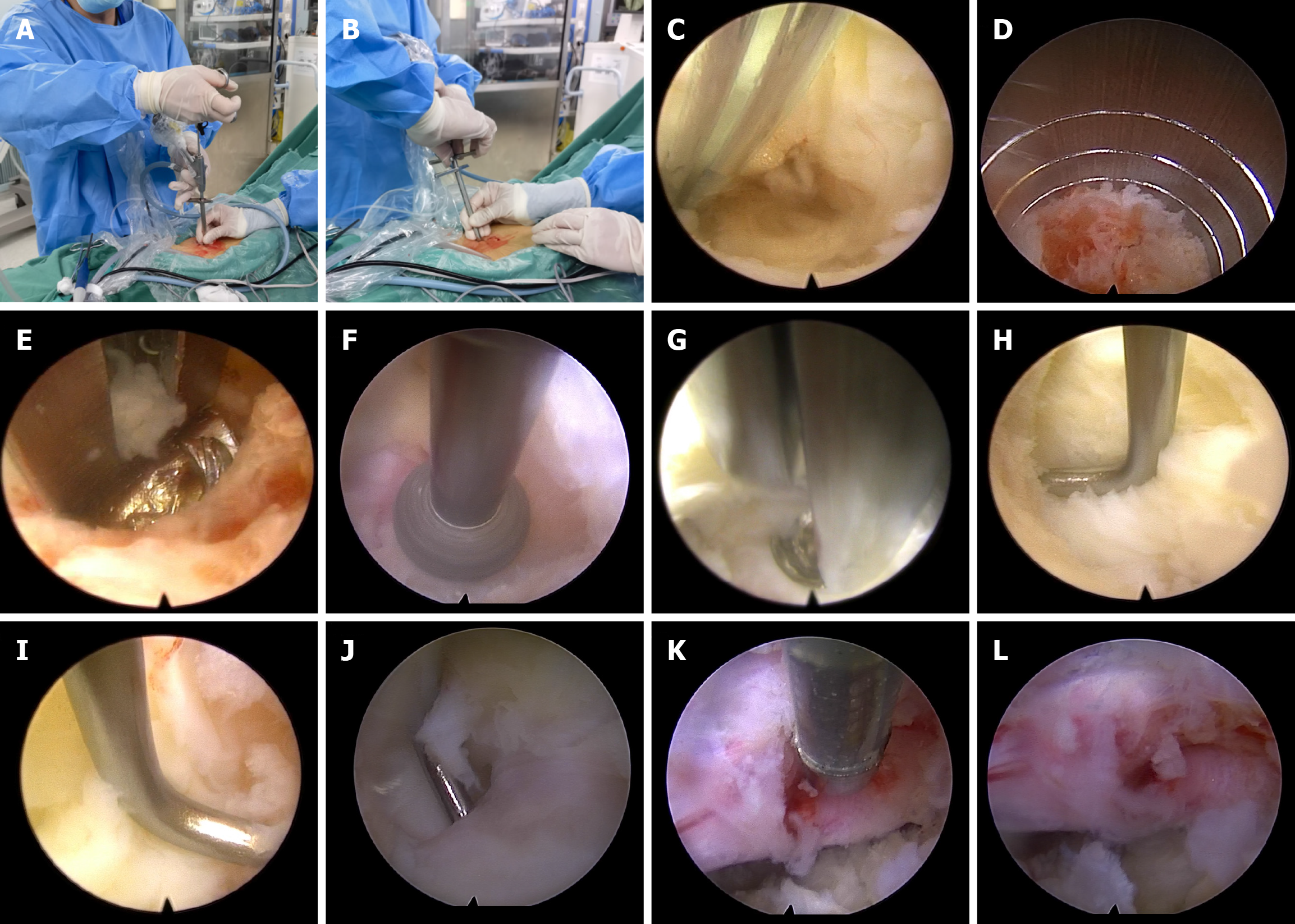
Figure 2 Illustrative instances of bilateral symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis managed using the uniportal full-endoscopy technique.
A: Uniportal full-endoscopy technique (single channel); B: Articular process resection executed with a trephine in uniportal endoscopy; C: Radiofrequency hemostasis under uniportal endoscopy; D: Articular process resection executed with a trephine in uniportal endoscopy; E: Laminectomy by endoscopic punch; F: Osteophyte decompression by endoscopic high-speed grinding drill; G: Resection of ligamentum flavum by endoscopic punch; H: Exploring the proximal endpoint of the ligamentum flavum using a nerve hook; I: Exploring the distal endpoint of the ligamentum flavum using a nerve hook; J: Exploring the lateral endpoint of the ligamentum flavum using a nerve hook; K: Hemostasis on nerve tissue using spinal radiofrequency; L: Neural relaxation post-decompression.
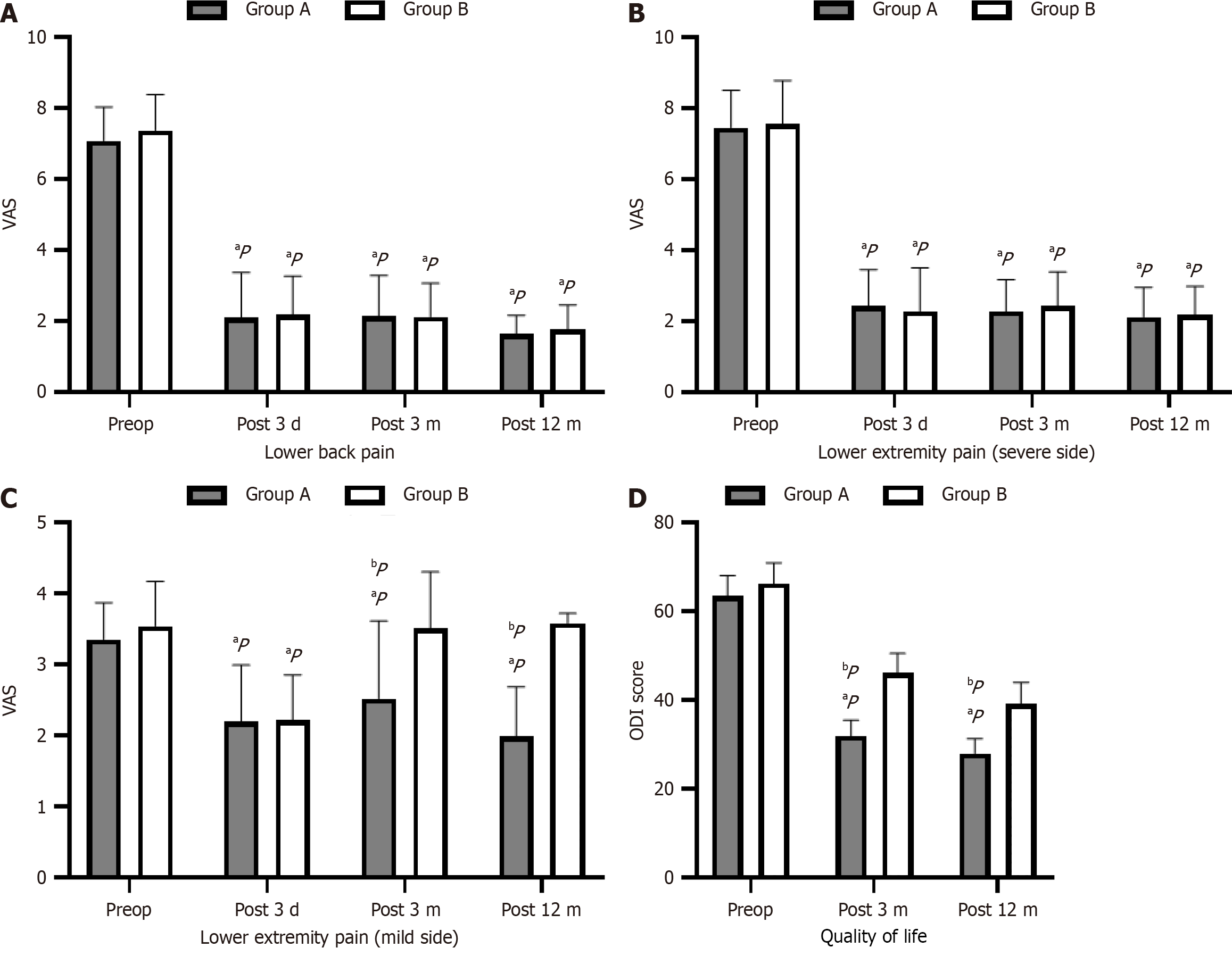
Figure 3 Clinical outcomes in both groups.
A: Comparison of lower back pain scores between the two groups; B: Comparison of lower extremity pain (severe side) between the two groups; C: Comparison of lower extremity pain (mild side) between the two groups; D: Comparison of quality of life Oswestry Disability Index scores between the two groups. aP < 0.05: Means there was significant difference before and after operation (P < 0.05); bP < 0.05: Means there was significant difference between groups (P < 0.05). ODI: Oswestry Disability Index; VAS: Visual analogue scale.
- Citation: Guo S, Hang RN, Zhu K, Wu CQ, Yan MJ, Li XH, Liu YB, Fu Q. Comparison of clinical outcomes between biportal and uniportal full-endoscopy techniques in lumbar spinal stenosis with bilateral symptoms. World J Orthop 2025; 16(7): 107698
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i7/107698.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107698