©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Orthop. Oct 18, 2020; 11(10): 442-452
Published online Oct 18, 2020. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v11.i10.442
Published online Oct 18, 2020. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v11.i10.442
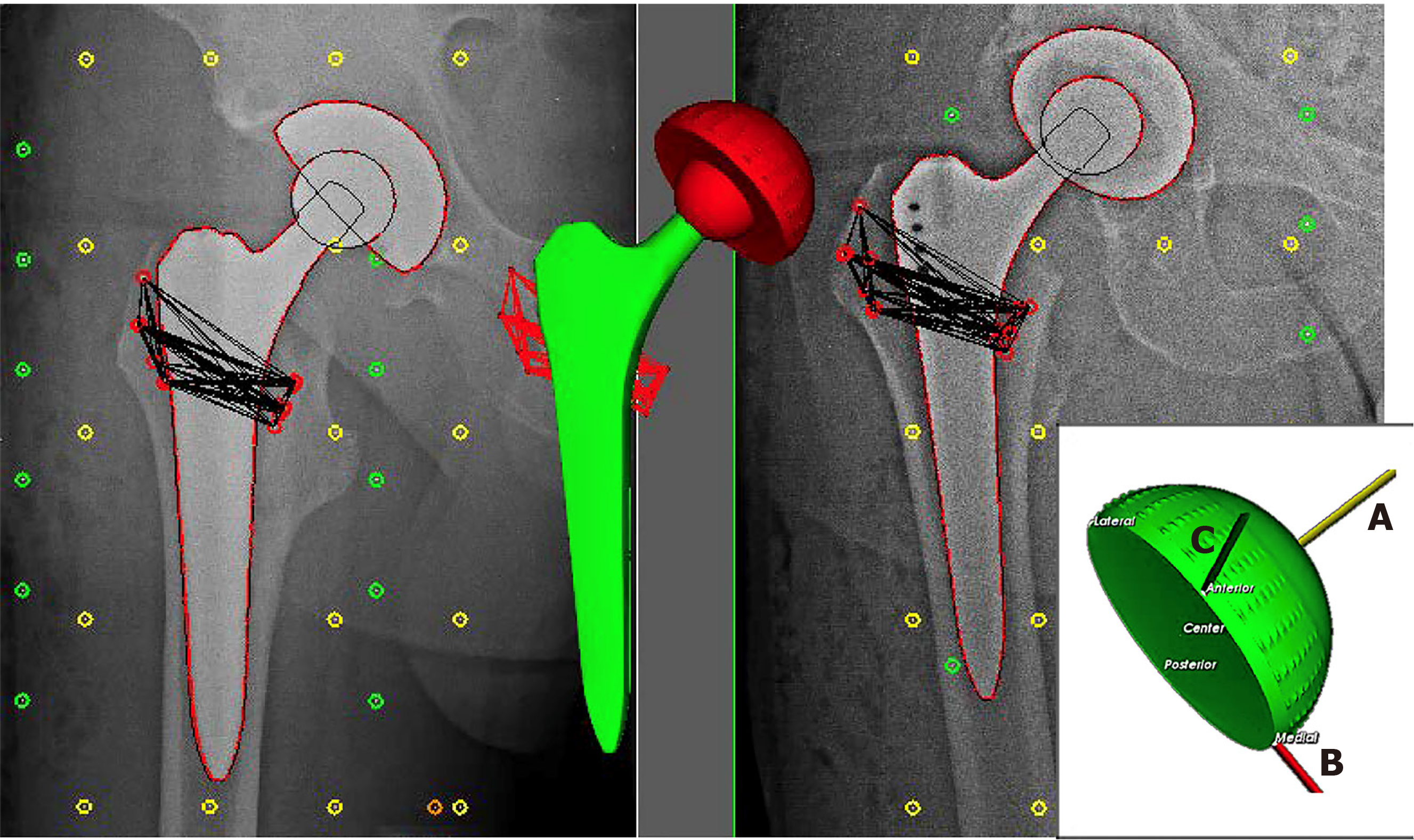
Figure 1 Model of Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis technique.
Model of Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis technique on right-sided acetabular component after insertion of tantalum markers, by measuring the penetration of the head in the proximal-distal (A-axis), medial-lateral (B-axis) and anterior-posterior migration (C-axis) direction.
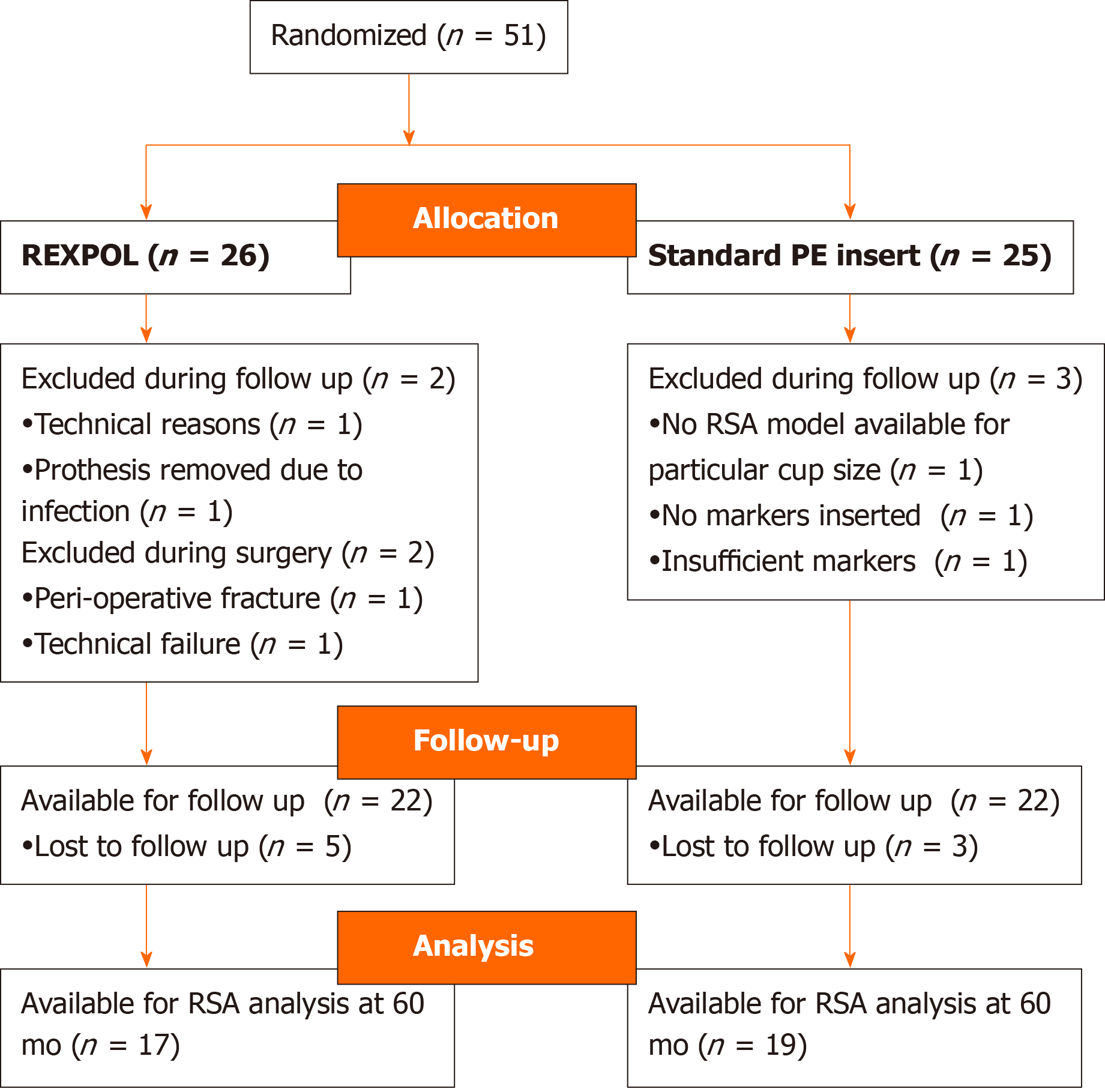
Figure 2 Flow chart of follow-up.
PE: Polyethylene; RSA: Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis.
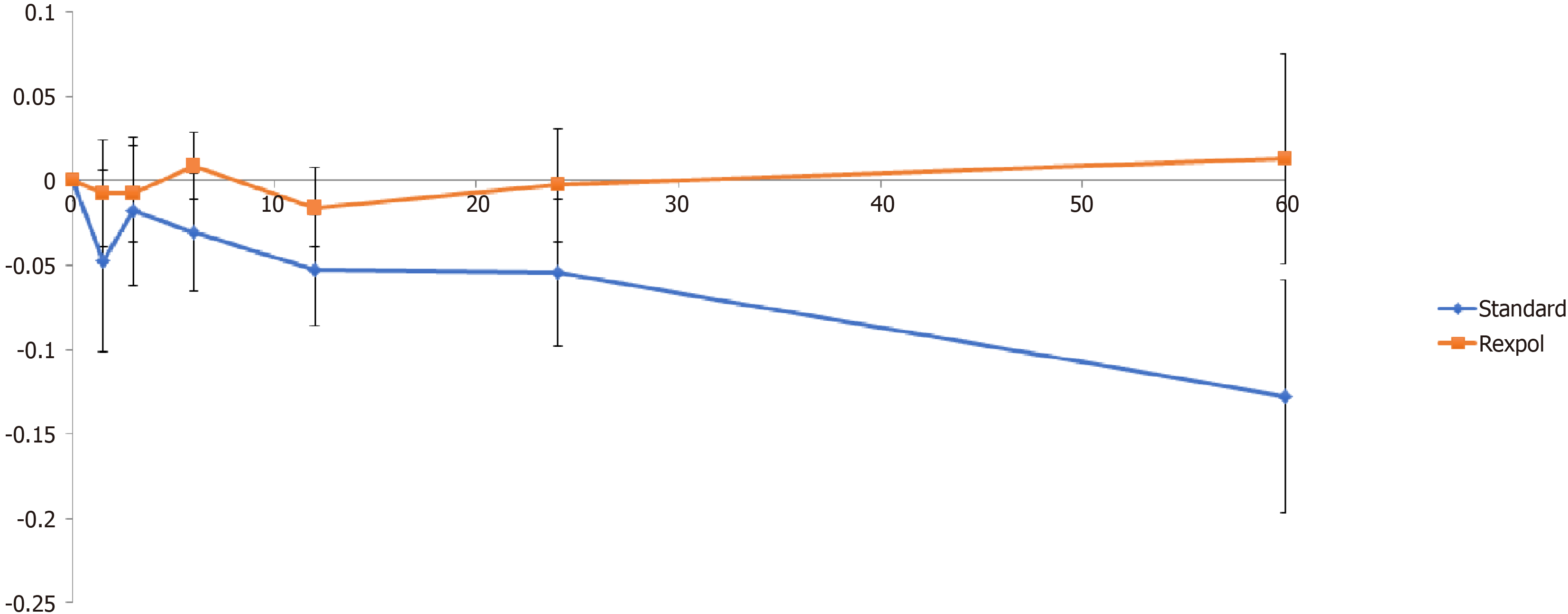
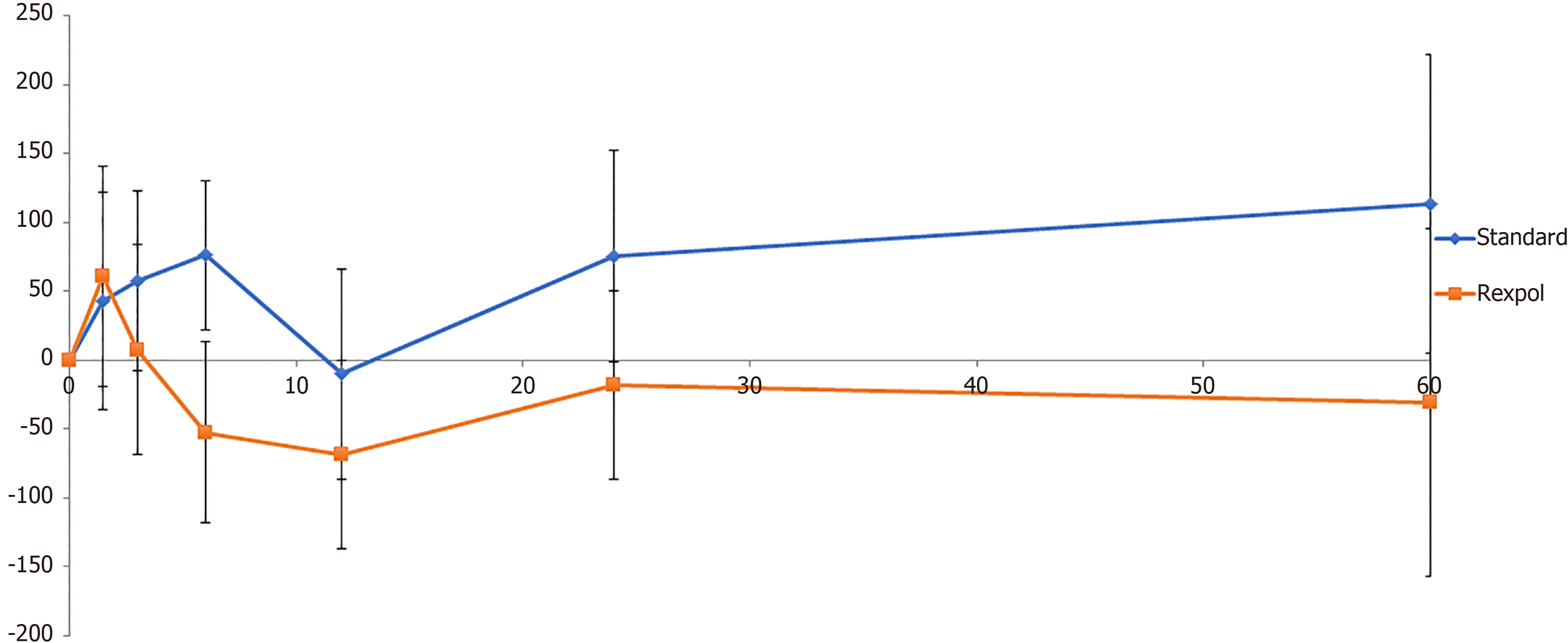
Figure 3 Wear of the inlay in the medial direction in mm over time (months).
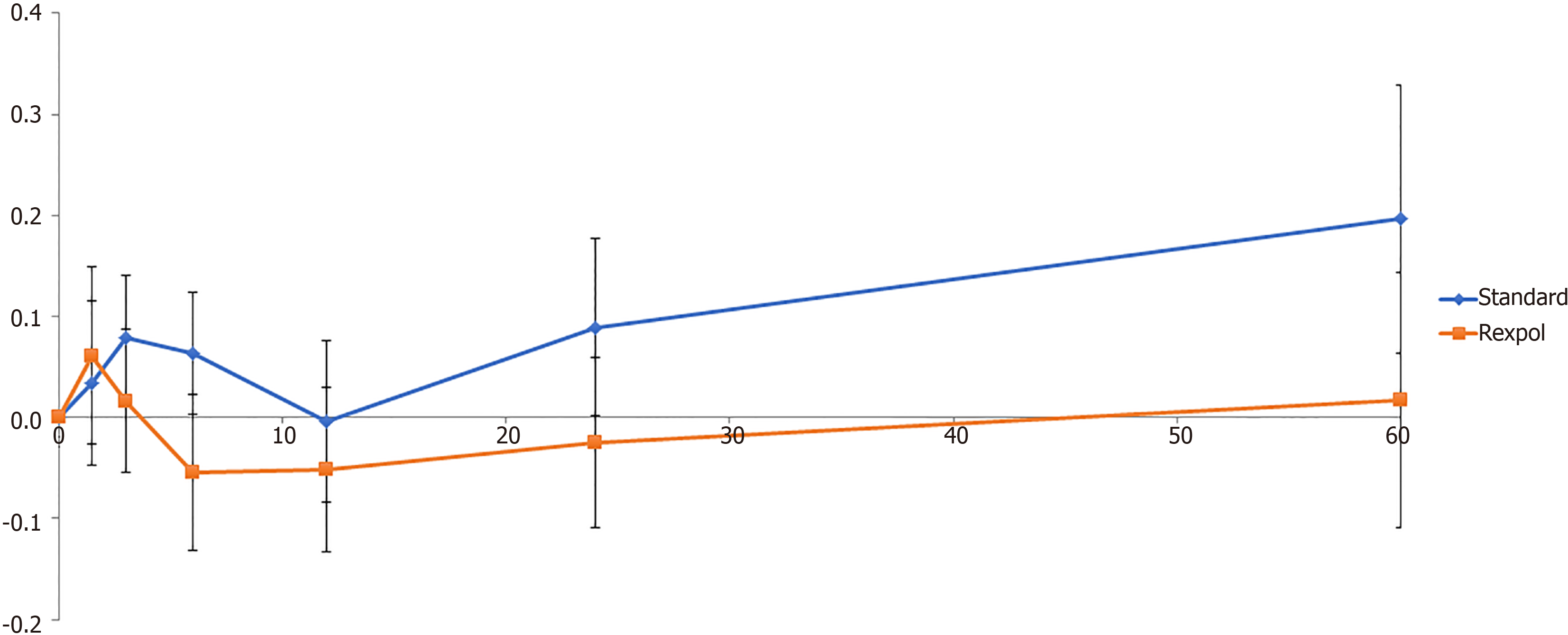
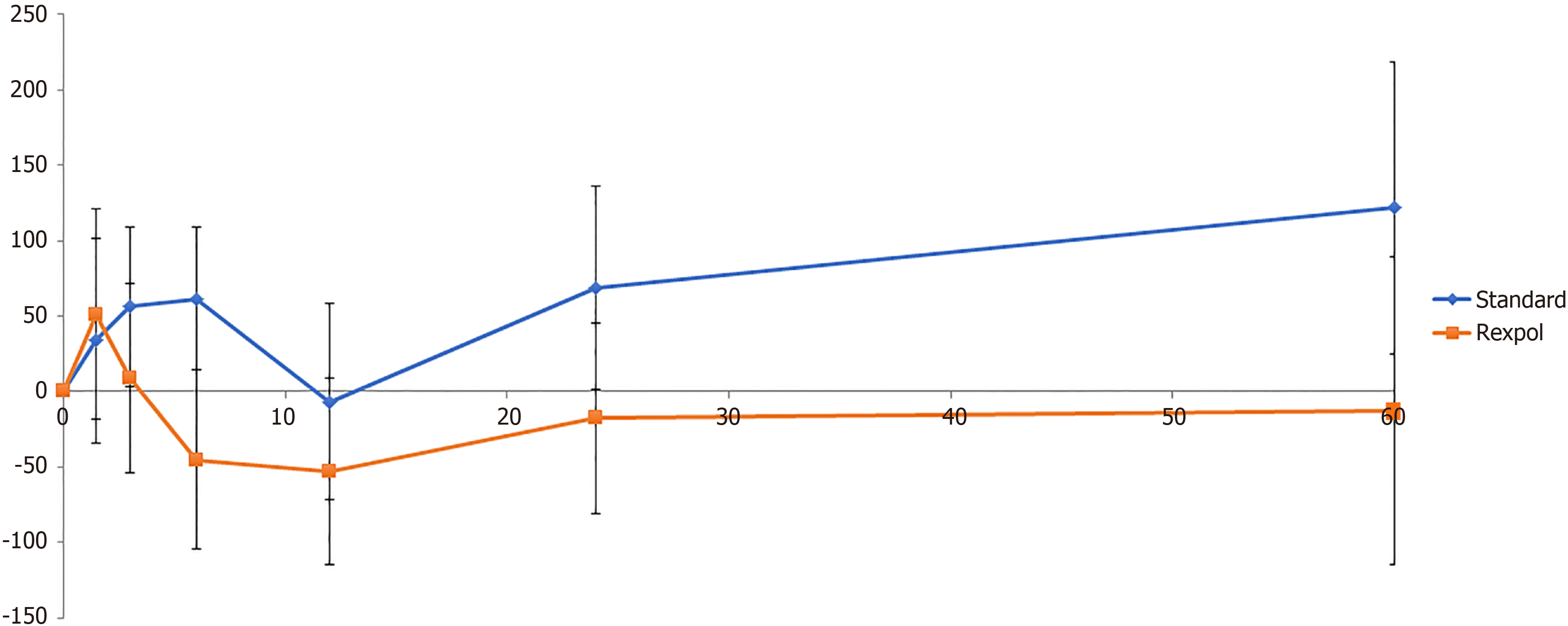
Figure 4 Wear of the inlay in the proximal direction in mm over time (months).
Figure 5 Volumetric wear of the inlay in mm3 over time (months).
Figure 6 Corrected volumetric wear of the inlay in mm3 over time (months).
- Citation: van Loon J, Hoornenborg D, Sierevelt I, Opdam KT, Kerkhoffs GM, Haverkamp D. Highly cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene inserts in total hip arthroplasty, a five-year Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis randomised controlled trial. World J Orthop 2020; 11(10): 442-452
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v11/i10/442.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v11.i10.442