©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2017; 9(4): 391-395
Published online Apr 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i4.391
Published online Apr 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i4.391
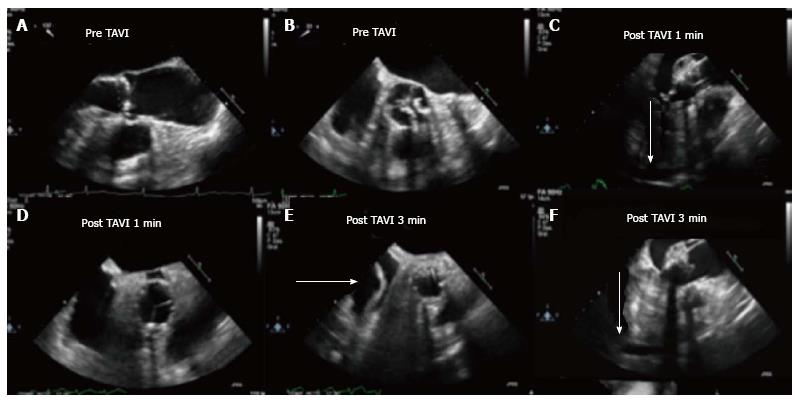
Figure 1 Aortic root rupture and aortic root hematoma (Case 1).
A and B: Aortic valve assessment before TAVI, TEE mid esophageal long axis view (A) and short axis view (B); C and D: Aortic valve assessment post TAVI 1 min; E and F: Aortic valve assessment post-TAVI 3 min. We can observe the development of the aortic root hematoma and the pericardial effusion (arrowhead). TAVI: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation; TEE: Trans-esophageal echocardiography.
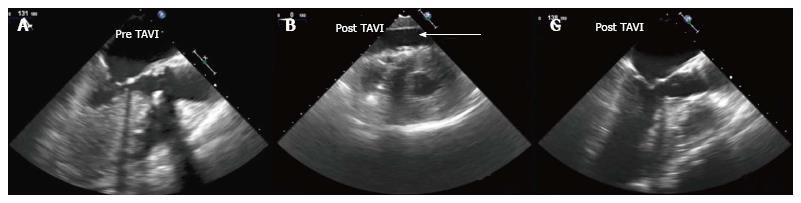
Figure 2 Aortic root rupture and cardiac tamponade (Case 2).
A: Aortic valve assessment before TAVI, TEE mid esophageal long axis view; B: Aortic valve assessment after TAVI, TEE transgastric mid-ventricular short axis. Severe pericardial effusion is evidenced (arrow); C: Aortic valve assessment after TAVI, TEE mid esophageal long axis view. No signs of aortic root hematoma were observed in this case. TAVI: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation; TEE: Trans-esophageal echocardiography.
- Citation: Vannini L, Andrea R, Sabaté M. Conservative management of aortic root rupture complicated with cardiac tamponade following transcatheter aortic valve implantation. World J Cardiol 2017; 9(4): 391-395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i4/391.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i4.391