©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2017; 9(4): 304-311
Published online Apr 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i4.304
Published online Apr 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i4.304
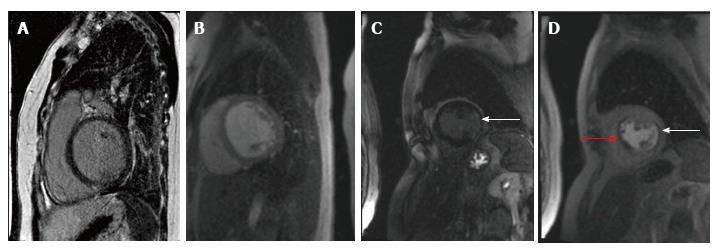
Figure 1 Two patients underwent cardiac stress magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of significant left ventricular dysfunction systolic dysfunction.
Patient 1 with Idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy, EF 30%: Panel A shows post gadolinium contrast images with absence of delayed enhancement in the left ventricular myocardium and Panel B shows lack of perfusion defect with adenosine stress imaging. Patient 2 with Ischemic cardiomyopathy, EF 15%: Panel C shows subendocardial delayed enhancement in the inferolateral wall (arrow) and Panel D shows stress perfusion defect in the anteroseptum (red arrow) consistent with ischemia and another matched perfusion defect caused by the inferolateral infarction (arrow).
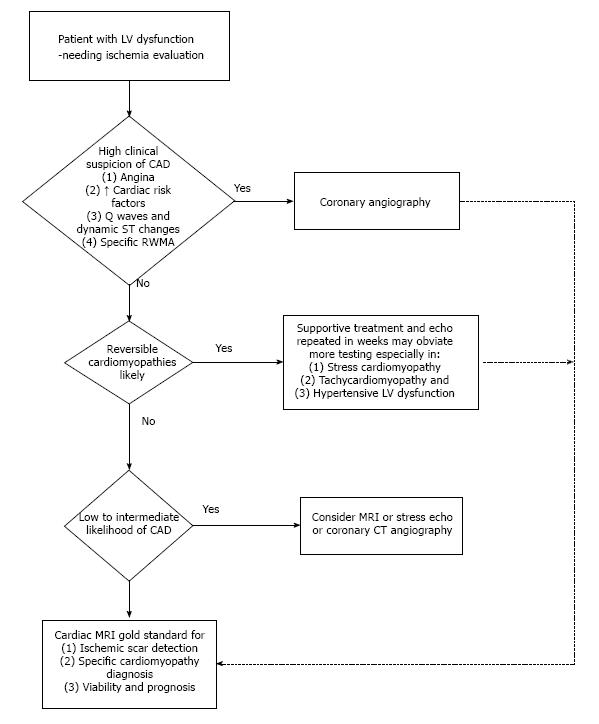
Figure 2 Algorithm for management of left ventricular dysfunction based on clinical presentation to optimize outcomes with cost-effective cardiac testing.
LV: Left ventricular; CAD: Coronary artery disease; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; CT: Computerized tomography; RWMA: Regional wall motion abnormality.
- Citation: Bomb R, Kumar S, Chockalingam A. Coronary artery disease detection - limitations of stress testing in left ventricular dysfunction. World J Cardiol 2017; 9(4): 304-311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i4/304.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i4.304