©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Cardiol. Jan 26, 2026; 18(1): 111954
Published online Jan 26, 2026. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v18.i1.111954
Published online Jan 26, 2026. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v18.i1.111954
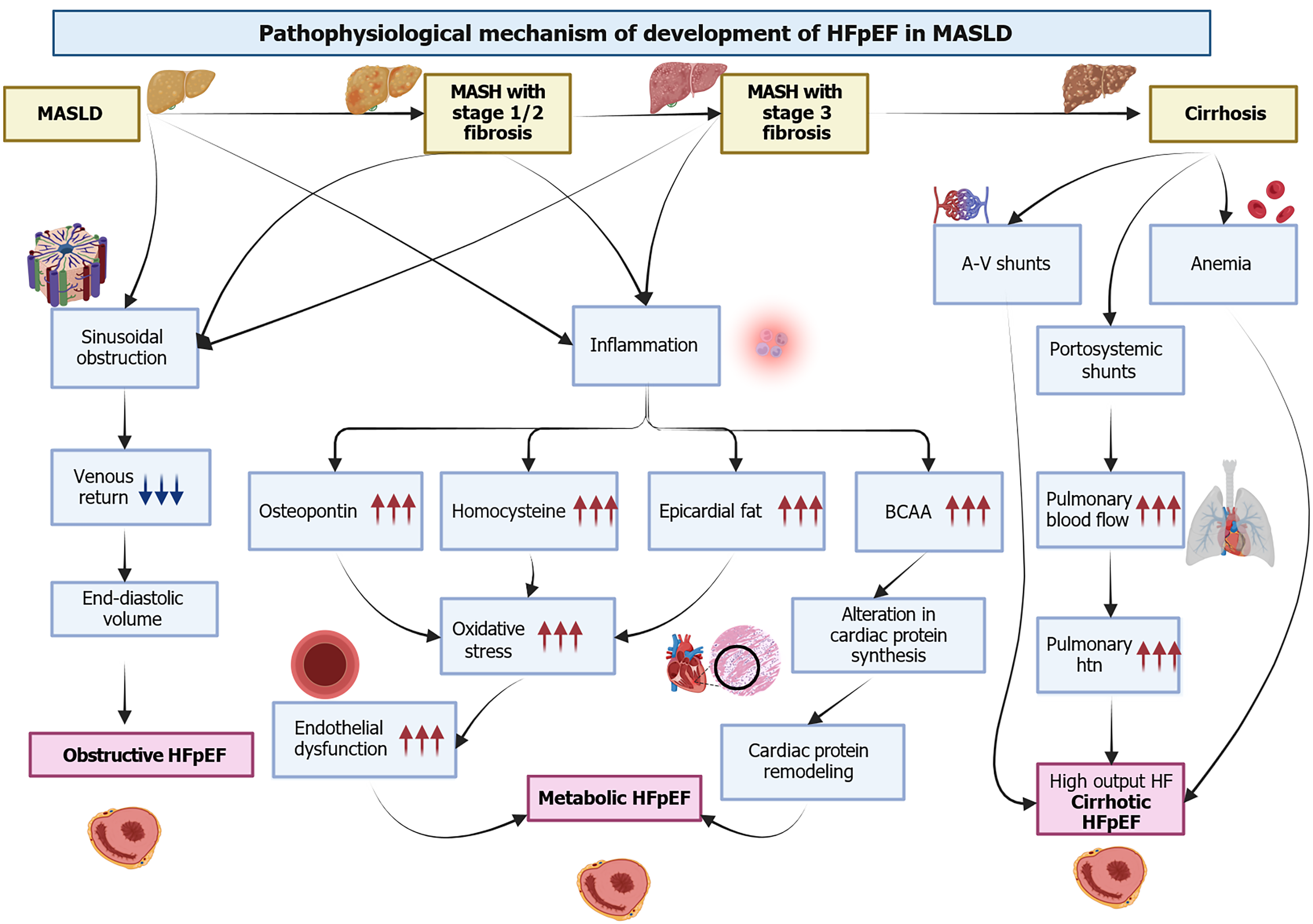
Figure 1 The pathophysiological mechanism of development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease.
HFpEF: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; MASLD: Metabolic-dysfunction associated liver disease; A-V shunt: Arteriovenous shunt; BCAA: Branched-chain amino acid; MASH: Metabolic-associated steatohepatitis.
Figure 2 Complex interplay of risk factors and their effect on metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease pathogenesis and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
HFpEF: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; MASLD: Metabolic-dysfunction associated liver disease; MASH: Metabolic-dysfunction associated steatohepatitis; A-V shunt: Arteriovenous shunt; OSA: Obstructive sleep apnea.
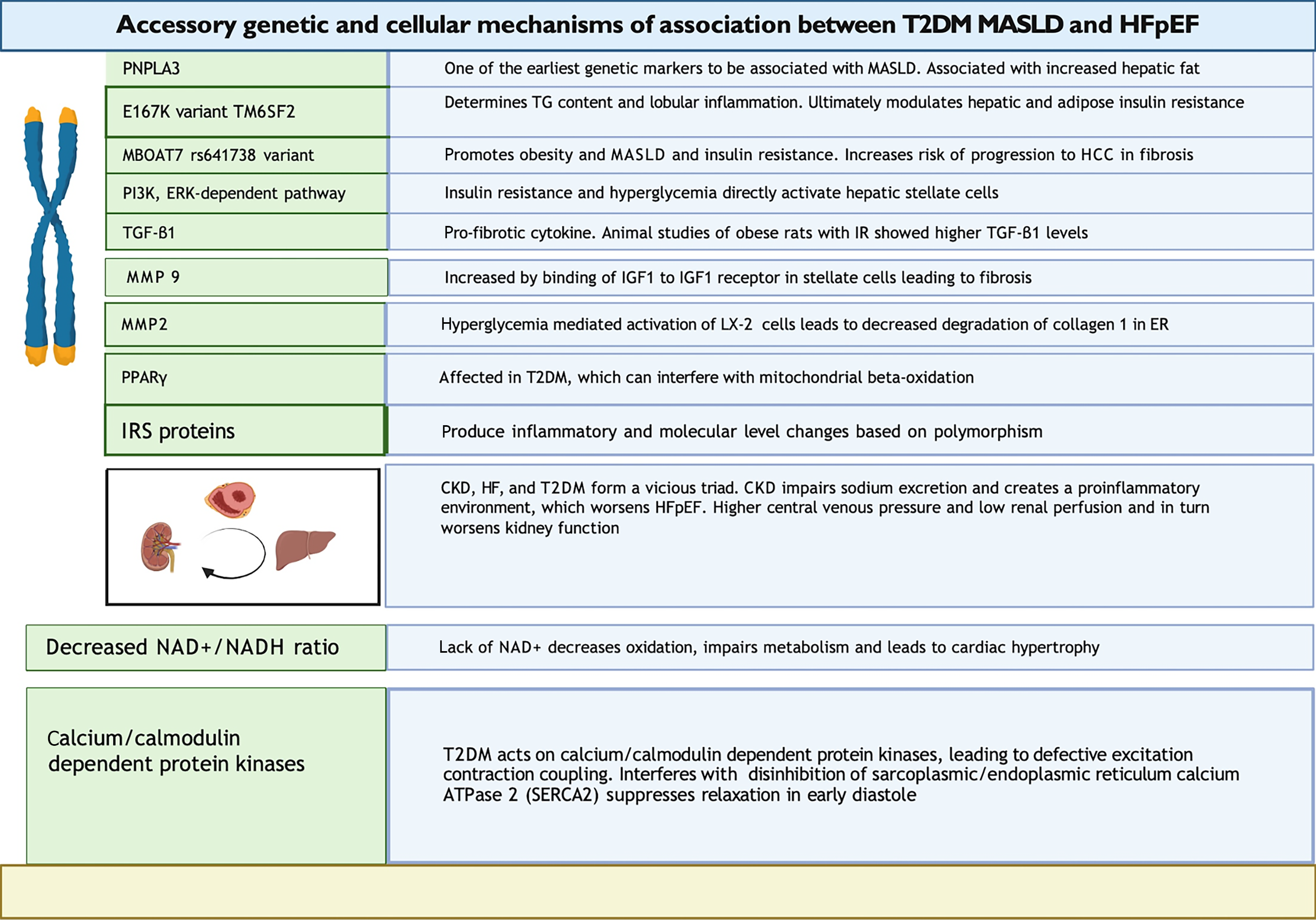
Figure 3 Accessory genetic and cellular association mechanisms between type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; IGF1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; MBOAT7: Membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 7; MMP 2: Matrix metalloproteinase 2; MMP 9: Matrix metalloproteinase 9; PI3K/AKT: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase protein kinase B; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; TGF: Tumor growth factor; TG: Triglycerides; TM6SF2: Transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 gene; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; NAD+/NADH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+/hydrogen; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
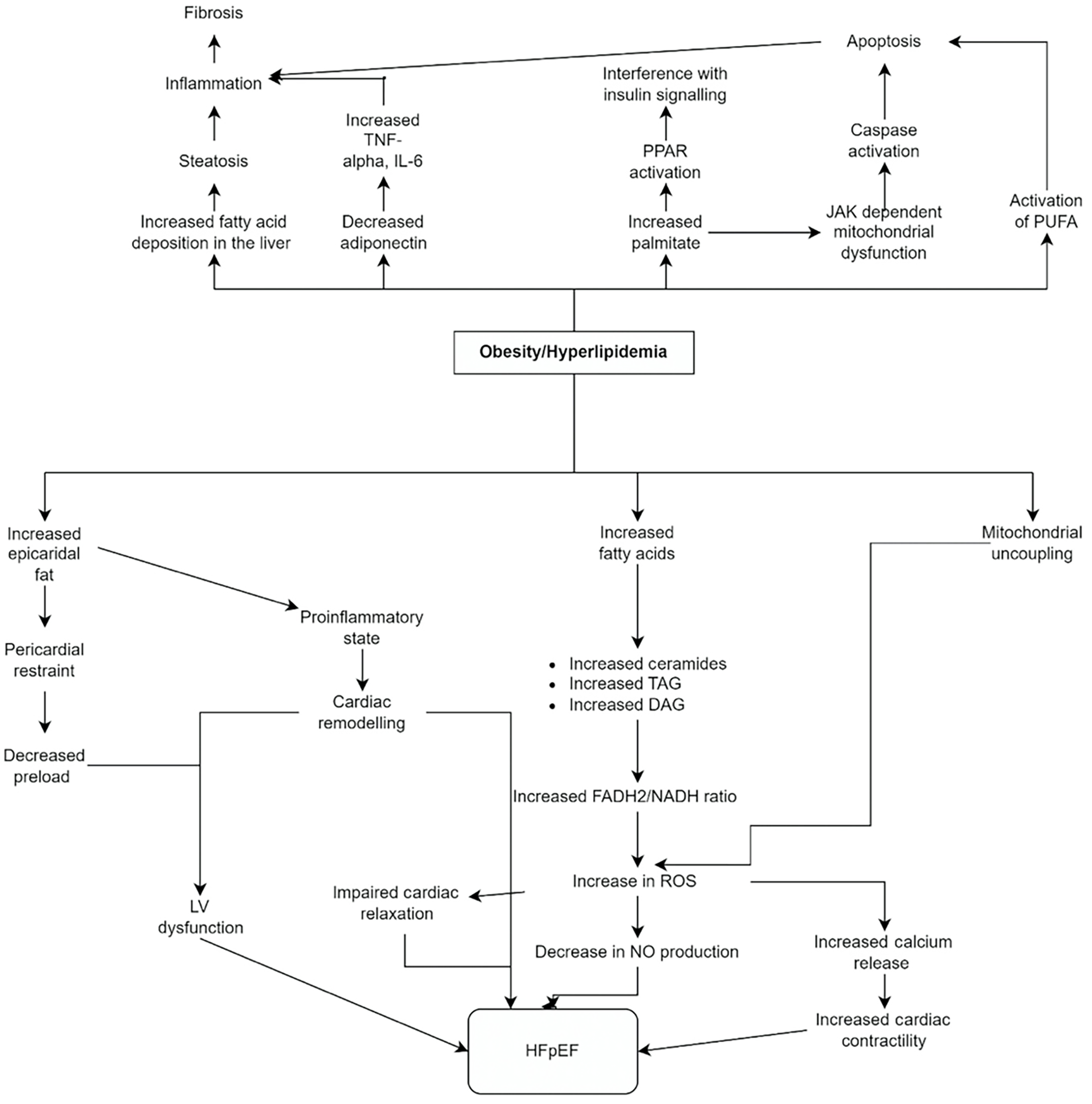
Figure 4 Pathophysiological mechanisms of obesity/hyperlipidemia on the risk of development of metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
DAG: Diacylglycerol; HFpEF: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; IL-6: Interleukin-6; JAK: Janus kinase; LV: Left ventricle; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor; PUFA: Polyunsaturated fatty acid; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TAG: Triacylglycerol.
Figure 5 The key chains of interactions between metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, which serve as pharmacological targets.
HFpEF: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; AGEs: Advance glycation end products: AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ATII: Angiotensin II; ChREPB: Carbohydrate element binding protein; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; FXR: Farnesoid receptor X; H2S: Hydrogen sulfide; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; LXR: Liver X receptor; MAFLD: Metabolic-dysfunction associated fatty liver disease; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; NADPH oxidase: Nicotinamide adeninenucleotide phosphate oxidase; NF-Kb: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer activated B cells; PDGF: Platelet derived growth factor; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; SCD-1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; RhoA: Ras homolog family member A; ROCK: Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase; SGLT-2 inhibitors: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor; SHH: Sonic hedgehog pathway; TG: Triglyceride; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein.
Figure 6 Current pharmacological options, proposed action and their impact on reducing the burden of metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; AGEs: Advance glycation end products; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ATII: Angiotensin II; ChREPB: Carbohydrate element binding protein; CPT1: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; CV: Cardiovascular; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; FA: Fatty acid; FXR: Farnesoid receptor X; H2S: Hydrogen sulfide; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HSC: Hepatic stellate cells; KLF2: Kruppel like factors; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; LSEC: Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; LXR: Liver X receptor; MASH: Metabolic-dysfunction associated steatohepatitis; NADPH oxidase: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase; NF-Kb: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer activated B cells; OSA: Obstructive sleep apnea; PDGF: Platelet derived growth factor; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; RAAS: Renin-aldosterone-angiotensin system; SCD-1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; RhoA: Ras homolog family member A; ROCK: Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase; SGLT-2 inhibitors: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor; SHH: Sonic hedgehog pathway; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; TG: Triglyceride; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein.
- Citation: Brar AS, Khanna T, Sohal A, Hatwal J, Sharma V, Singh C, Batta A, Chandra P, Mohan B. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A state-of-the-art review. World J Cardiol 2026; 18(1): 111954
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v18/i1/111954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v18.i1.111954