©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 102133
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.102133
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.102133
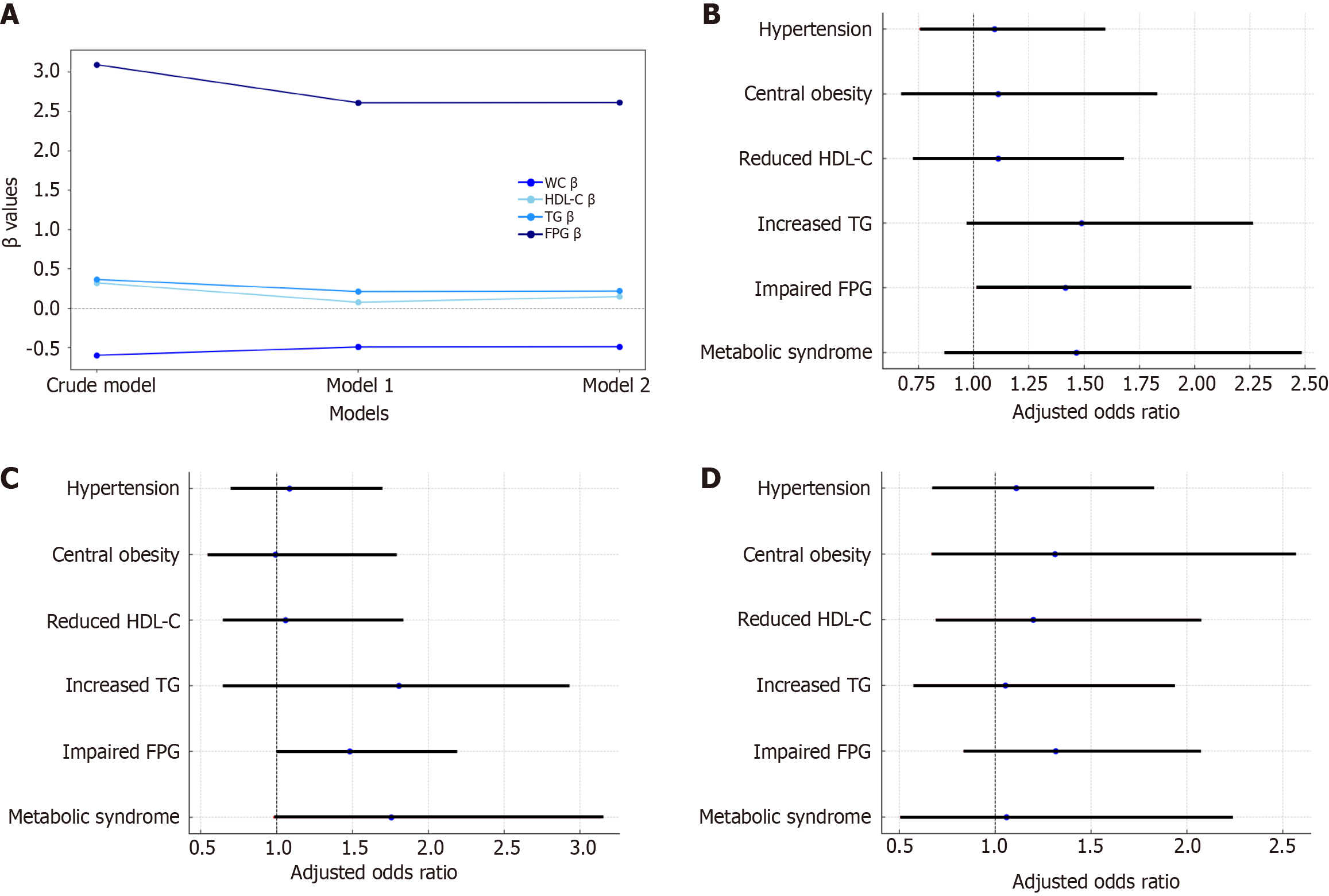
Figure 1 The study presented detailed tables illustrating the associations between night duty frequency and various metabolic markers.
A: Regression analysis of metabolic syndrome biomarkers. Data are presented as standardized β and P value using linear regression analysis. Model 1: Age, sex, alcohol drinking, betel nut chewing, cigarette smoking adjustments, model 2: Age, sex, alcohol drinking, betel nut chewing, cigarette smoking, body mass index and time for a run adjustment; B: The Relationship between night sentry duty frequency and metabolic syndrome and its associated characteristics, night duty ≥ 1/month; C: The relationship between night sentry duty frequency and metabolic syndrome and its associated characteristics, night duty 1-2/month; D: The relationship between night sentry duty frequency and metabolic syndrome and its associated characteristics, night duty ≥ 3/month. WC: Waist circumference; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: Serum triglycerides; FPG: Fasting plasma glucose.
- Citation: Byeon H. Impact of night sentry duties on cardiometabolic health in military personnel. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(4): 102133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i4/102133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.102133