©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jan 26, 2025; 17(1): 101491
Published online Jan 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i1.101491
Published online Jan 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i1.101491
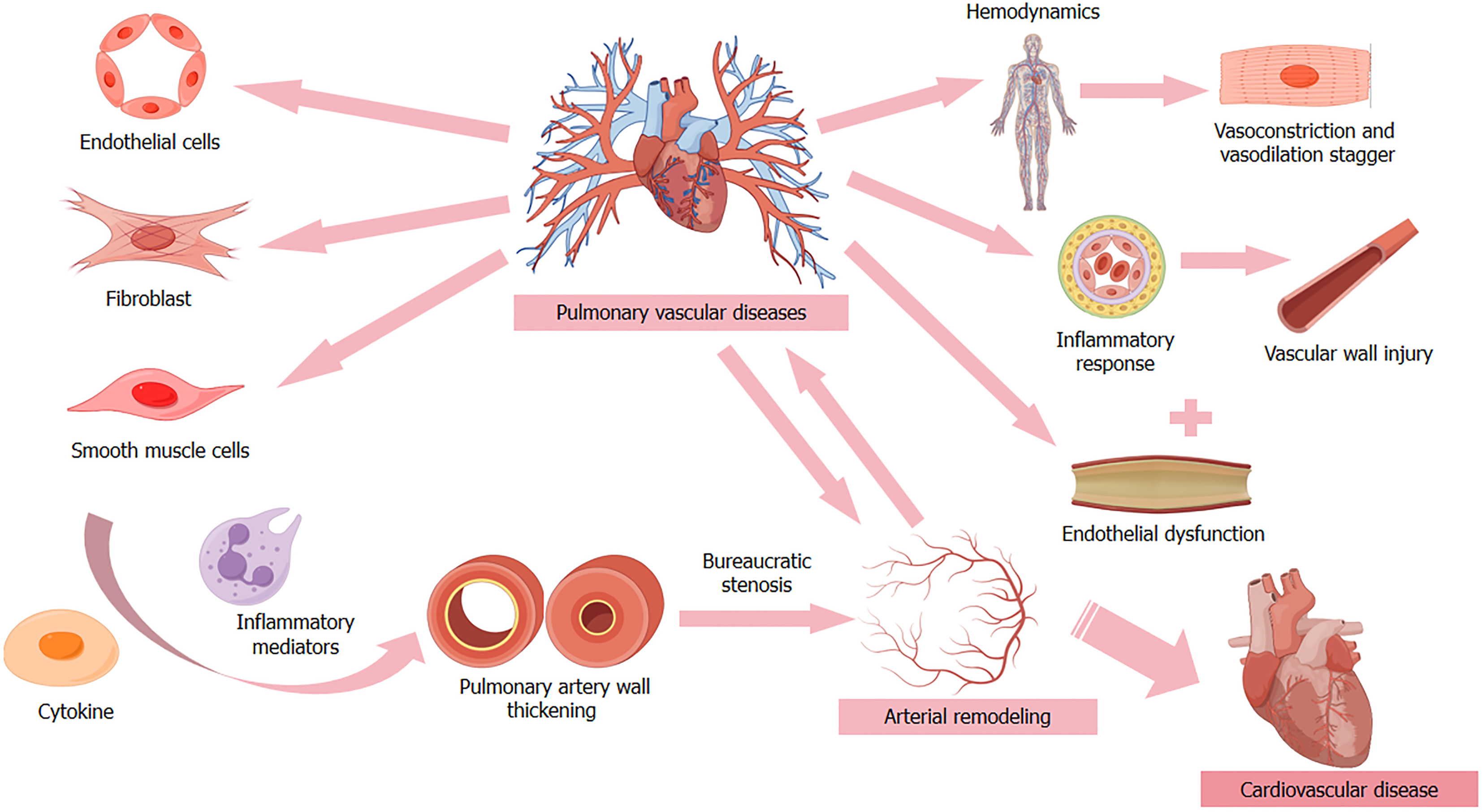
Figure 1
Relationship between pulmonary vascular cells and cardiovascular disease.
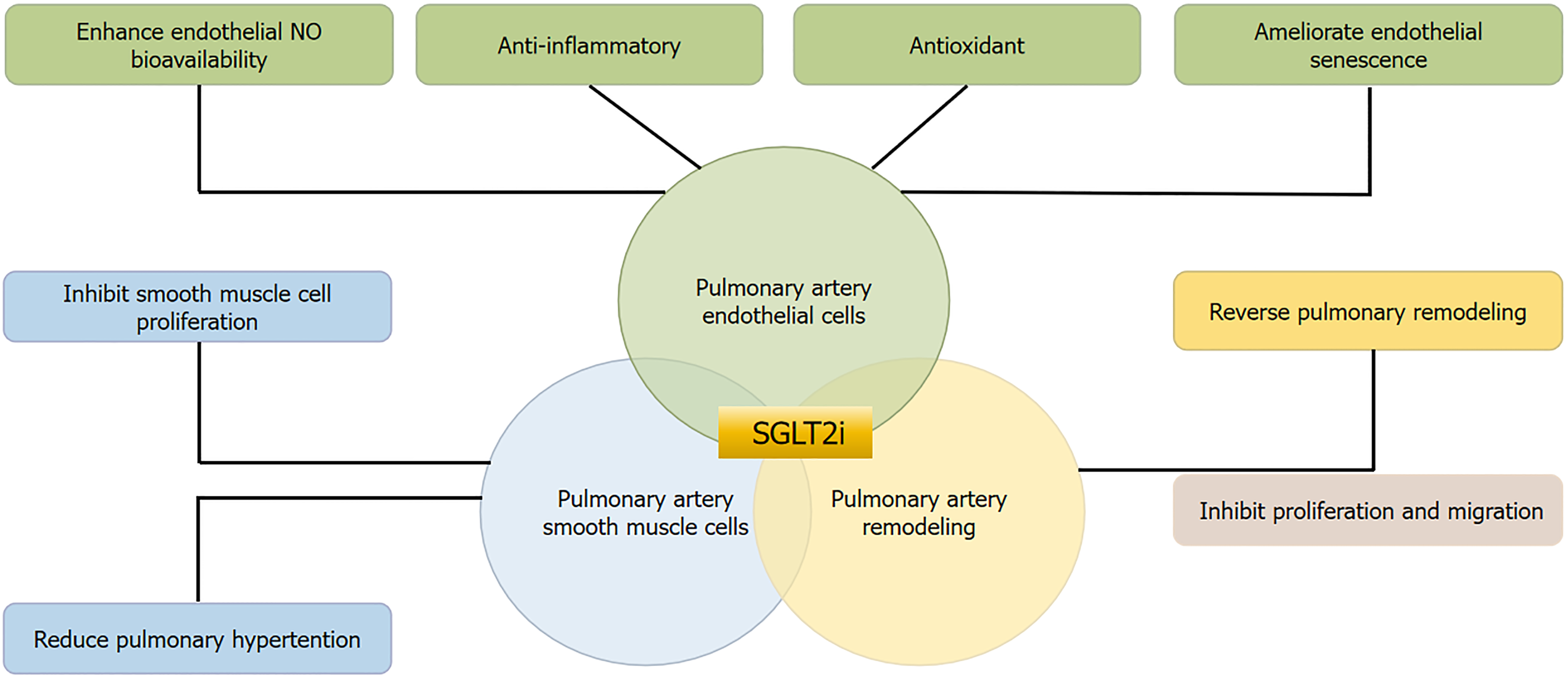
Figure 2 Impacts of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on pulmonary vascular cell function and pulmonary artery remodeling.
NO: Nitric oxide; SGLT2i: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor.
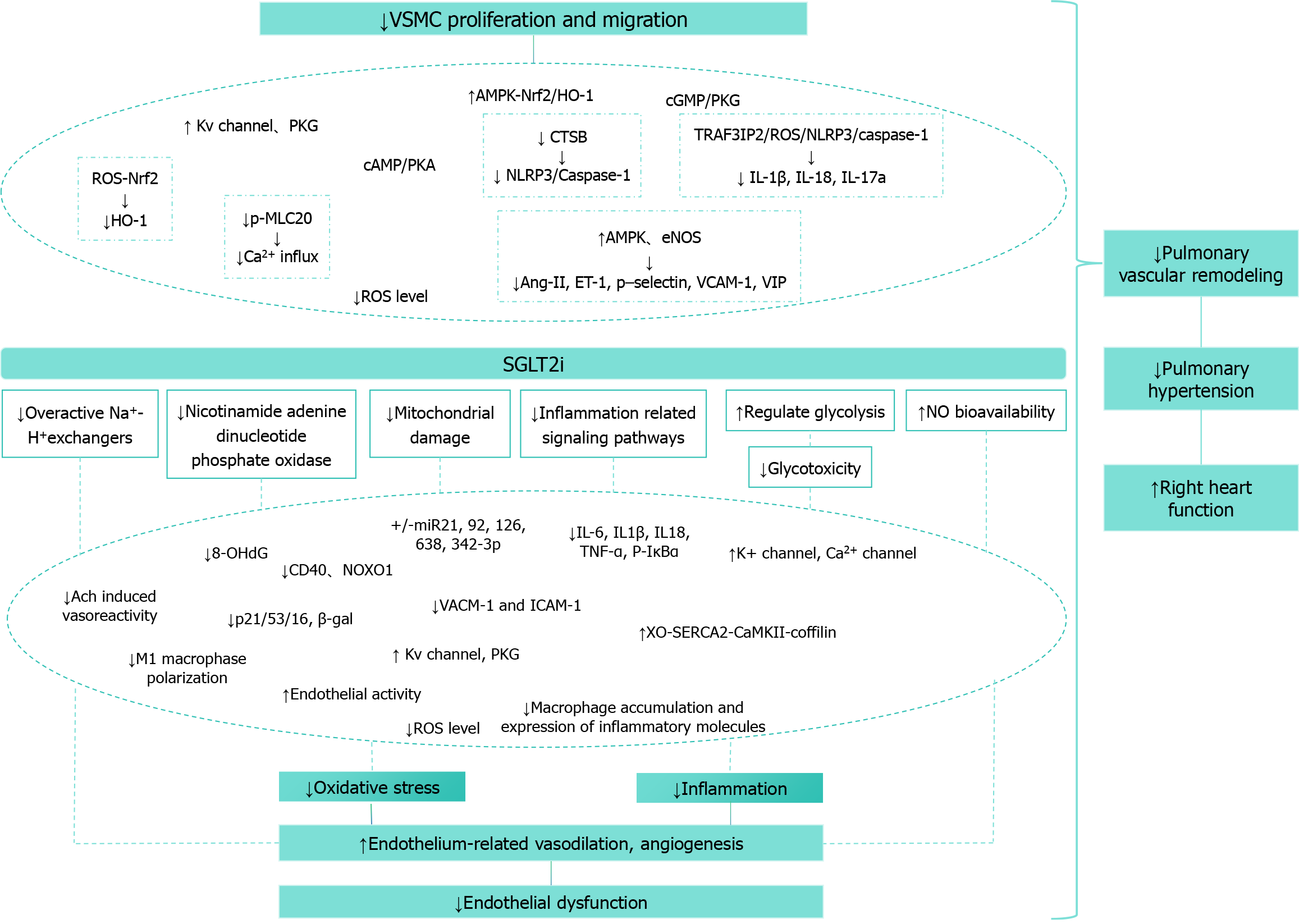
Figure 3 Mechanisms through which sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors modulate pulmonary vascular cell function and pulmonary artery remodeling.
VSMC: Vascular smooth muscle cells; Kv channel: Voltage-gated potassium channels; PKG: Protein kinase G; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine 3’,5’-monophosphate; PKA: Protein kinase A; CTSB: Cathepsin B; NLRP3: Nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; p-MLC20: Phospho-myosin light chain 20; TRAF3IP2: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 interacting protein 2; IL: Interleukin; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Ang-II: Angiotensin II; ET-1: Endothelin-1; VACM-1: Vasopressin-activated calcium-mobilizing-1; VIP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide; SGLT-2i: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor; NO: Nitric oxide; 8-OHdG: 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine; p-IκBα: Phosphorylated-IkappaBalpha; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; miRNA: MicroRNA; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; XO-SERCA2-CaMKII-cofilin: Xanthine oxidase-sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase 2-calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II-cofilin.
- Citation: Zhang JJ, Ye XR, Liu XS, Zhang HL, Qiao Q. Impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on pulmonary vascular cell function and arterial remodeling. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(1): 101491
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i1/101491.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i1.101491