©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2024; 16(12): 740-750
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.740
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.740
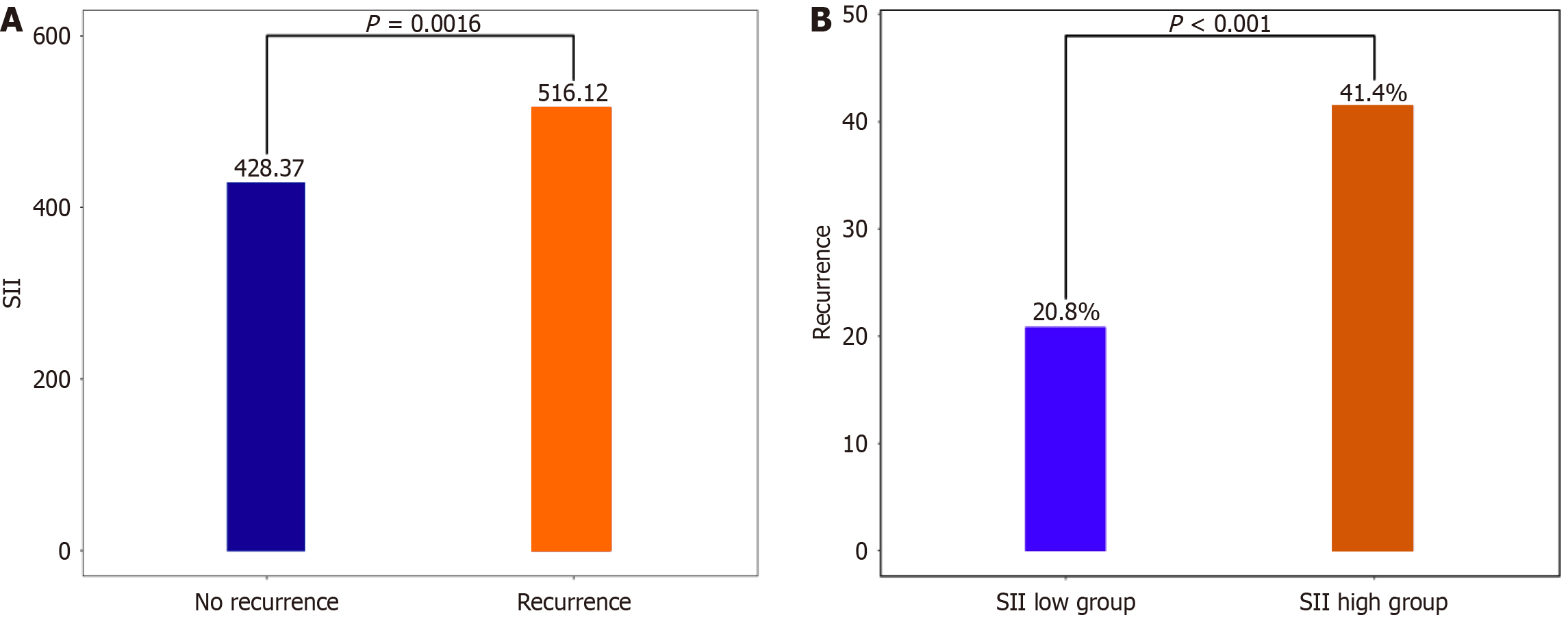
Figure 1 Comparison of variables between two groups.
A: Comparison of systemic immune inflammation index level; B: The patients developing atrial fibrillation recurrence post-ablation divided into the low group and the high group by the optimal cut-off value of pre-ablation systemic immune inflammation index level.
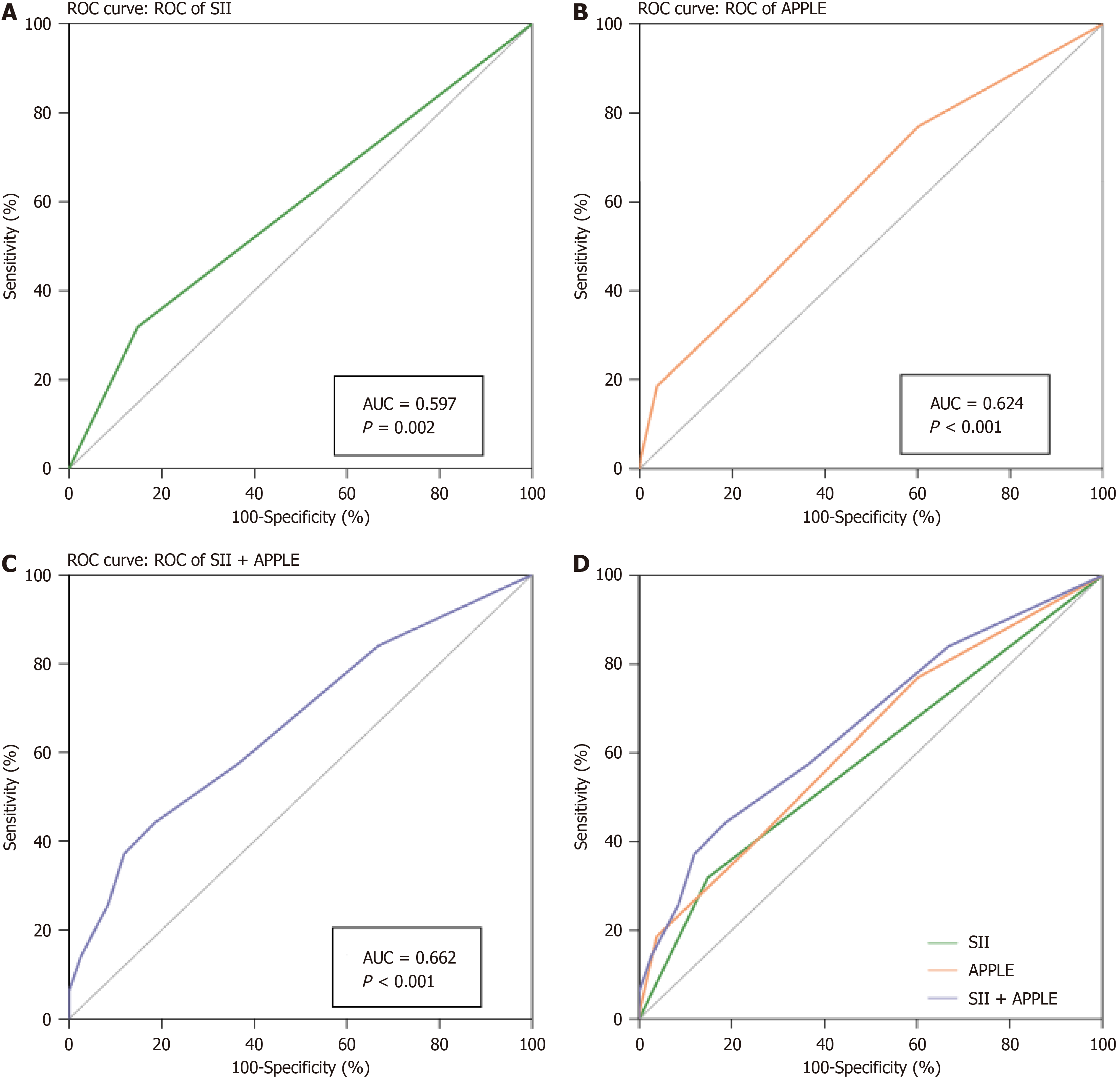
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curves and comparison of various variables.
A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) of systemic immune inflammation index (SII) for predictor of recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF) after radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA); B: ROC of APPLE score for predictor of recur-rence of AF after RFCA; C: ROC of the combined model for predictor of recurrence of AF after RFCA; D: ROC of SII, APPLE score, and the combined model for predictor of recurrence of AF after RFCA. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; SII: Systemic immune inflammation index.
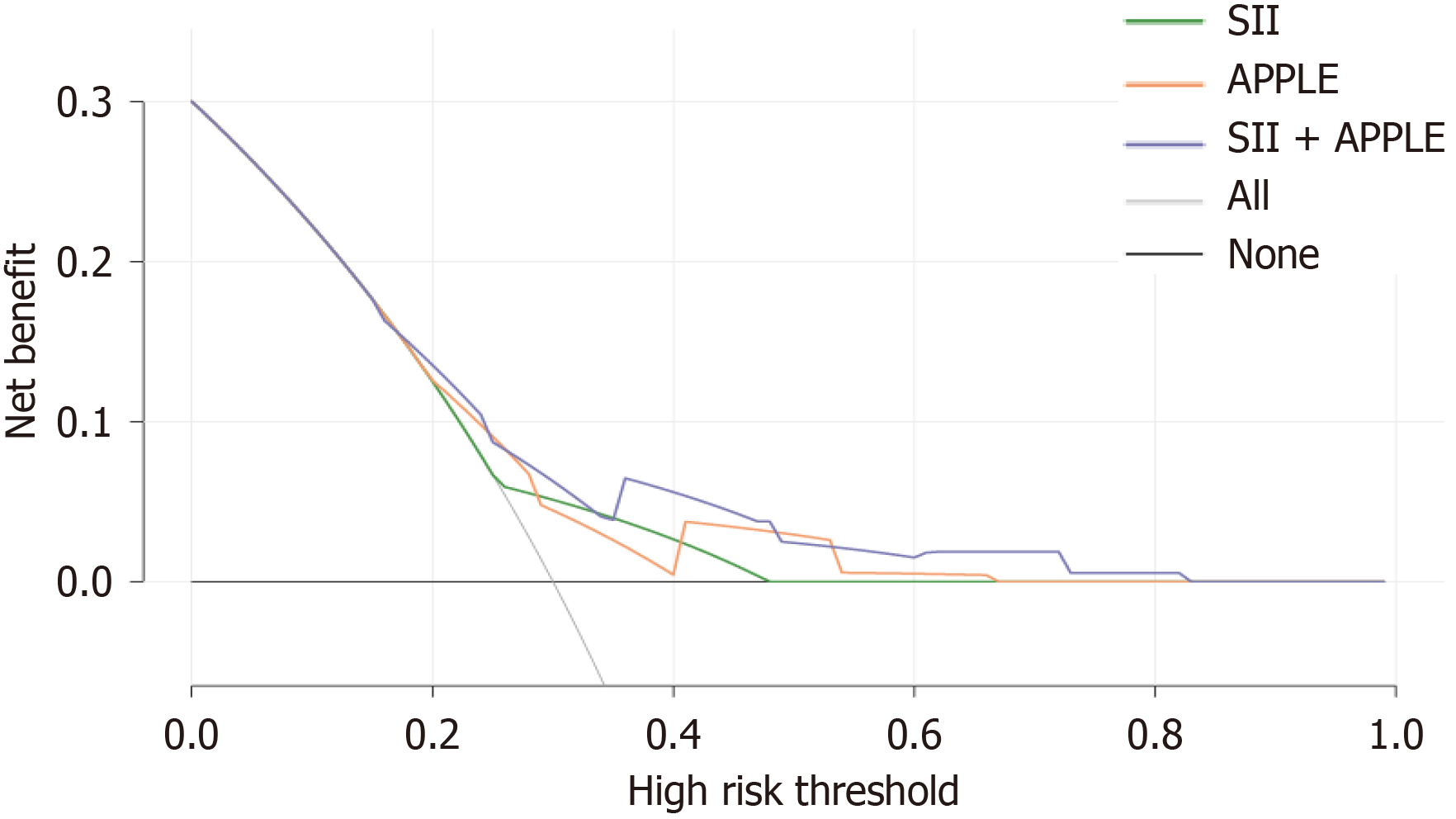
Figure 3 Decision curve analysis of the systemic immune inflammation index, APPLE score and combined model.
SII: Systemic immune inflammation index.
- Citation: Wang YJ, Liu KS, Meng XJ, Han XF, Nie LJ, Feng WJ, Chen YB. Role of a new inflammation predictor in predicting recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(12): 740-750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i12/740.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.740