©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2021; 13(9): 446-455
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v13.i9.446
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v13.i9.446
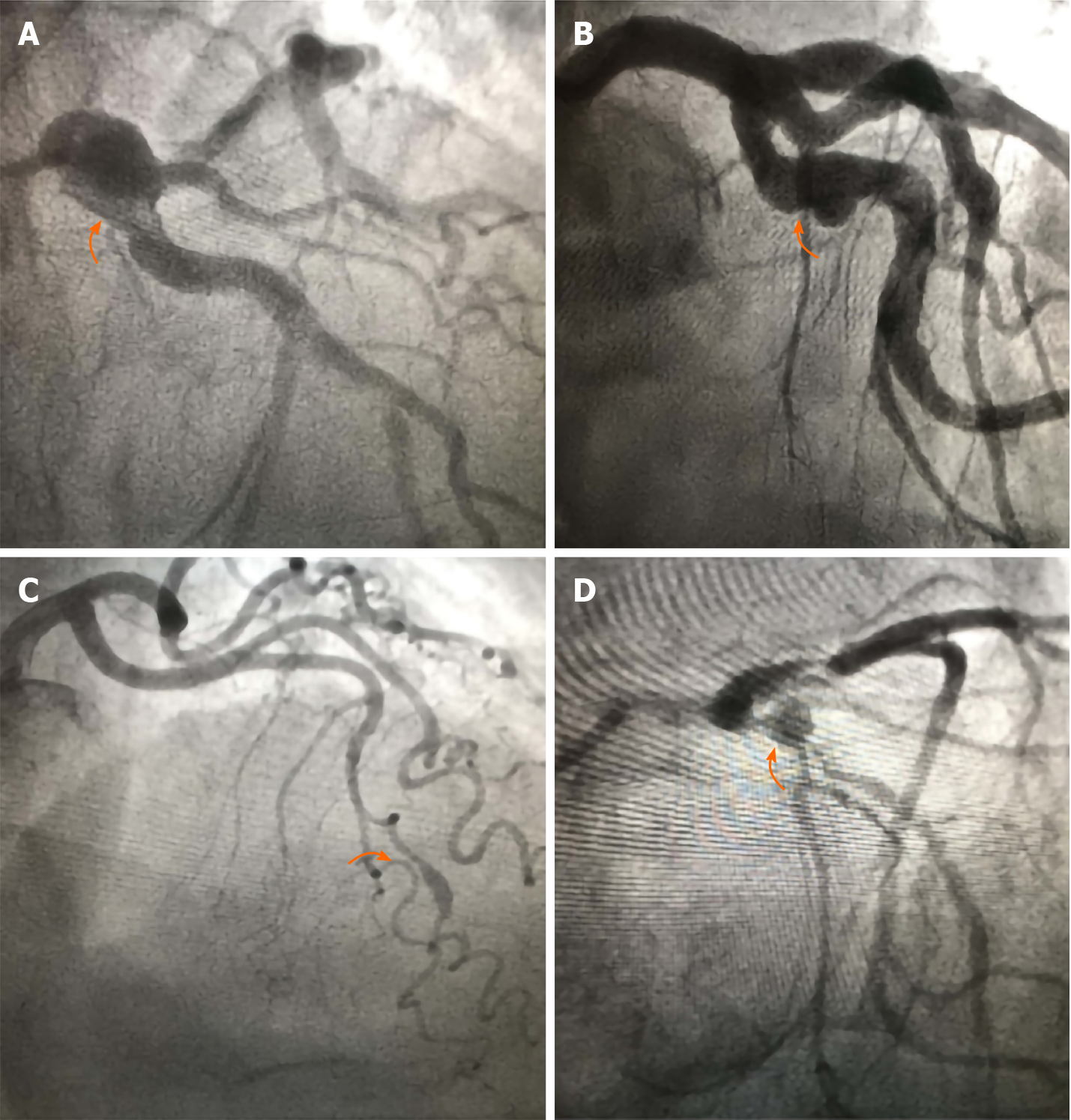
Figure 1
Coronary angiograms showing saccular aneurysm of the left main (A), saccular aneurysm of the left circumflex (B), fusiform aneurysm of the distal left anterior descending (C) and saccular aneurysm of the bifurcation left anterior descending/diagonal (D).
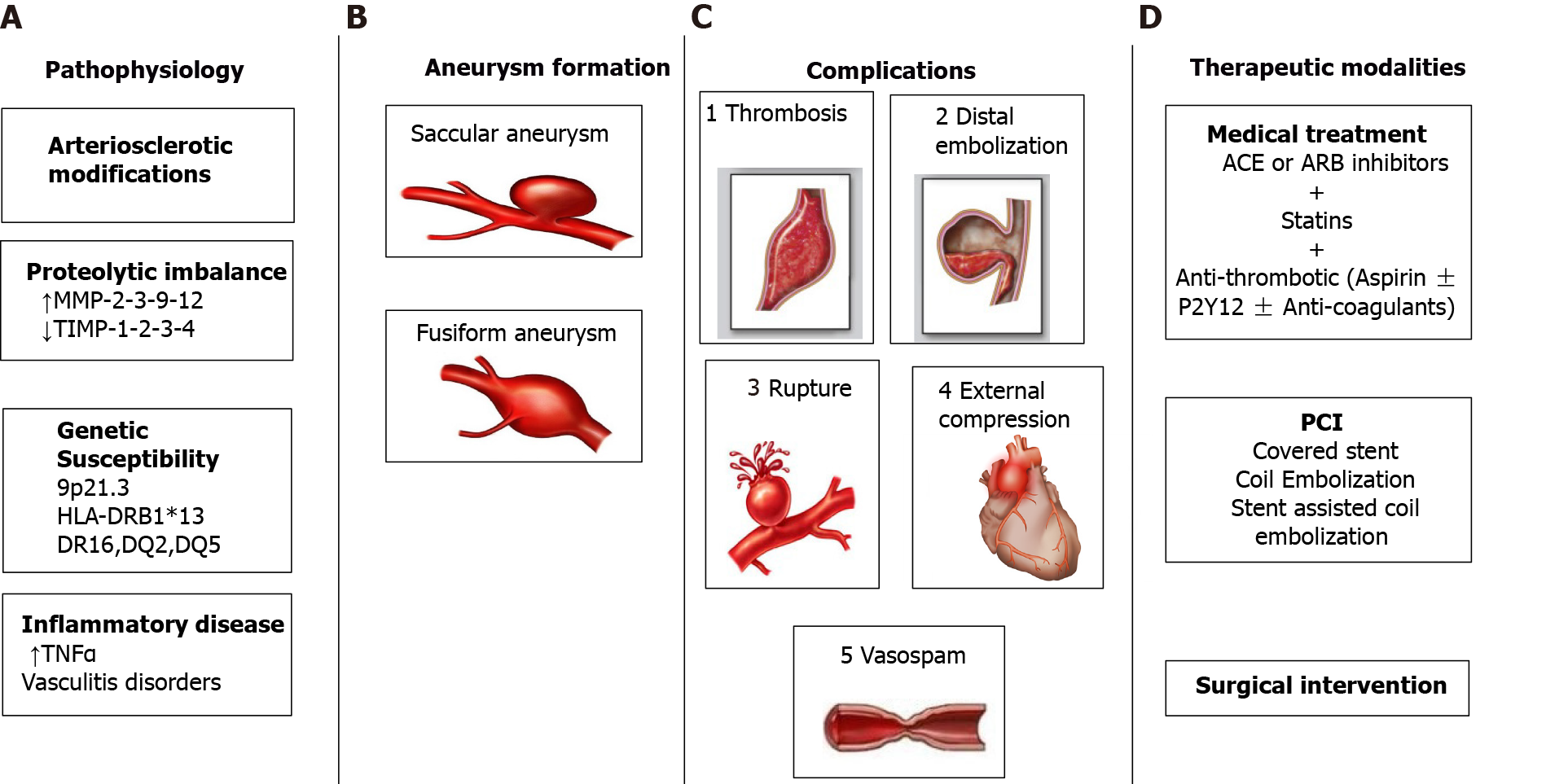
Figure 2 An illustration of the pathophysiology (A), types (B), complications (C) and therapeutic (D) modalities for coronary artery aneurysm.
ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; ARB: Angiotensin II receptor blockers; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinases; PCI: Percutaneous coronary intervention; TIMP: Tissue-specific inhibitors of metalloproteinases; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
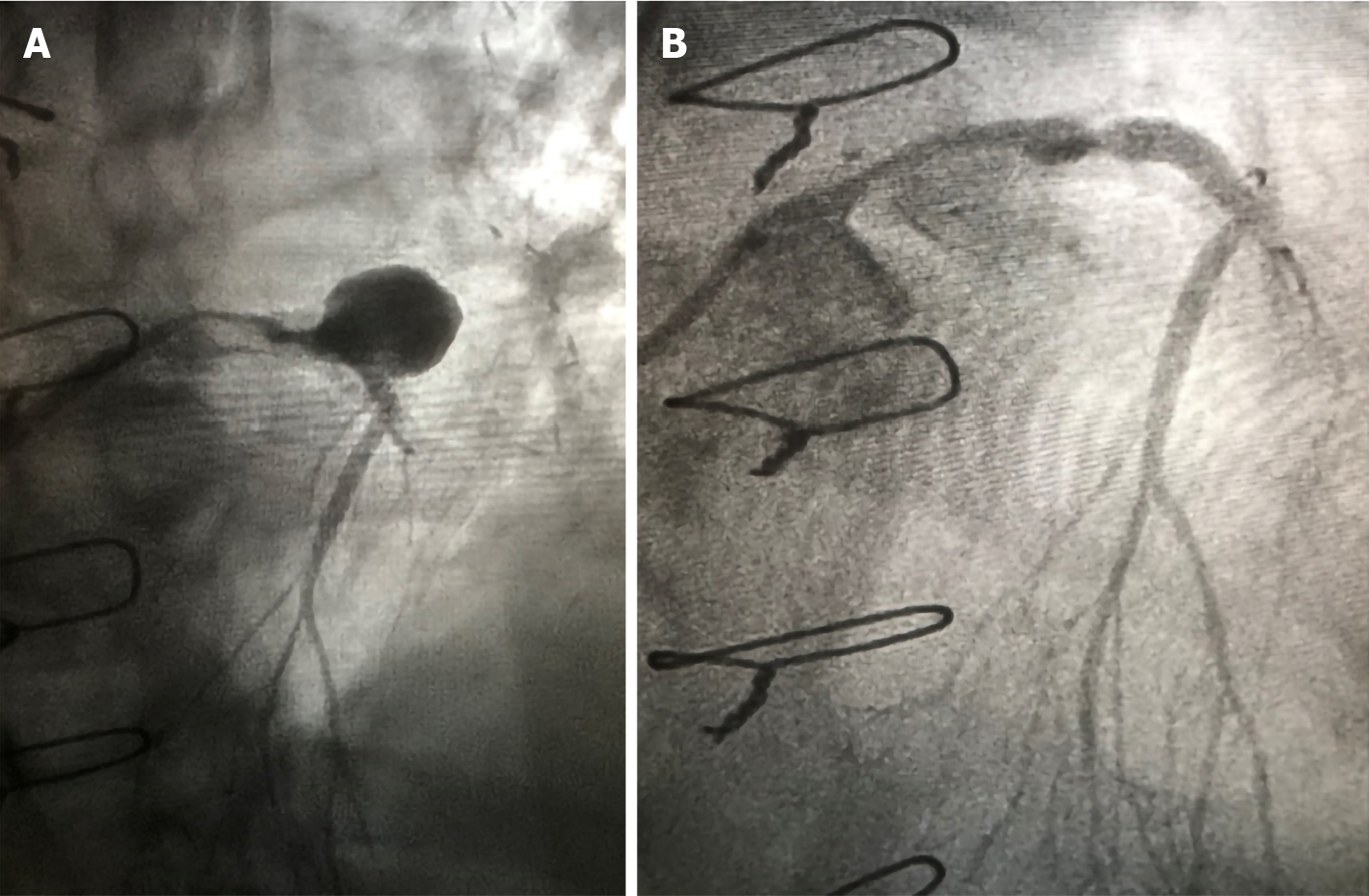
Figure 3
Coronary angiograms showing a giant coronary artery aneurysm of the proximal left anterior descending artery (A) excluded by implanting a bare metal stent with nonsignificant residual stenosis (B).
- Citation: Matta AG, Yaacoub N, Nader V, Moussallem N, Carrie D, Roncalli J. Coronary artery aneurysm: A review. World J Cardiol 2021; 13(9): 446-455
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v13/i9/446.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v13.i9.446