©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2021; 13(7): 183-203
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v13.i7.183
Published online Jul 26, 2021. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v13.i7.183
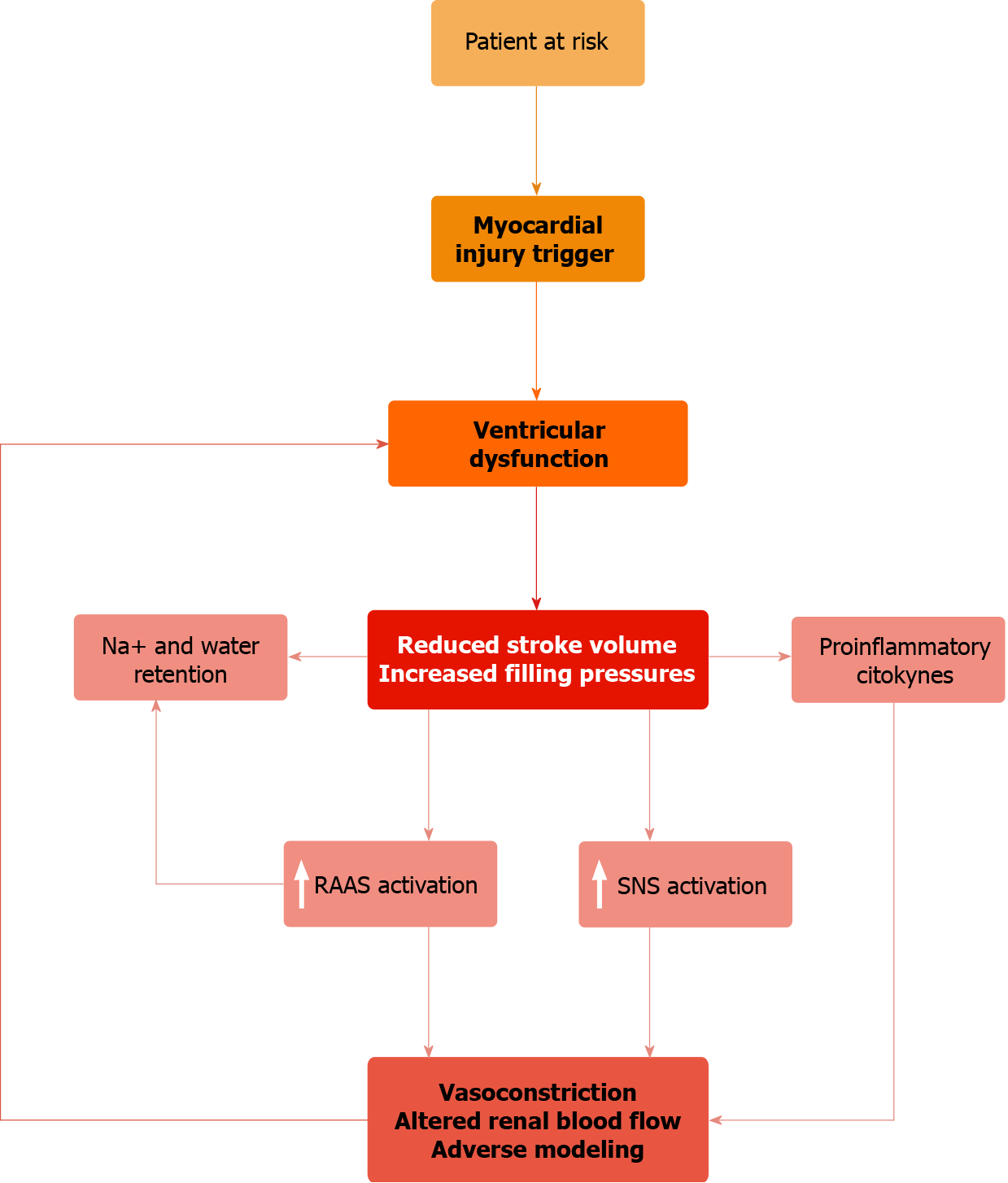
Figure 1 Pathophysiological mechanisms in chronic heart failure (data from[3]).
RAAS: Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System; SNS: Sympathetic nervous systems.
Figure 2 Heart failure – classification and criteria in diagnosis (data from[1,15]).
HFrEF: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HFmrEF: Heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction; HFpEF: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; LVH: Left ventricular hypertrophy; LAE: Left atrial enlargement; BNP: B-type natriuretic peptide; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide; LV: Left ventricle; TR: Tricuspid regurgitation; GLS: Global longitudinal strain; LAVI: Left atrial volume index; LVMI: Left ventricular mass index; RWT: Relative wall thickness; ECHO: Echocardiography.
Figure 3 Heart failure medication therapy (data from[1,51]).
HFrEF: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; ACEi: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB: Angiotensin receptor blocker; MRA: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; ARNI: Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction.
- Citation: Sopek Merkaš I, Slišković AM, Lakušić N. Current concept in the diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of patients with congestive heart failure. World J Cardiol 2021; 13(7): 183-203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v13/i7/183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v13.i7.183