©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Sep 27, 2016; 8(9): 656-659
Published online Sep 27, 2016. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i9.656
Published online Sep 27, 2016. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i9.656
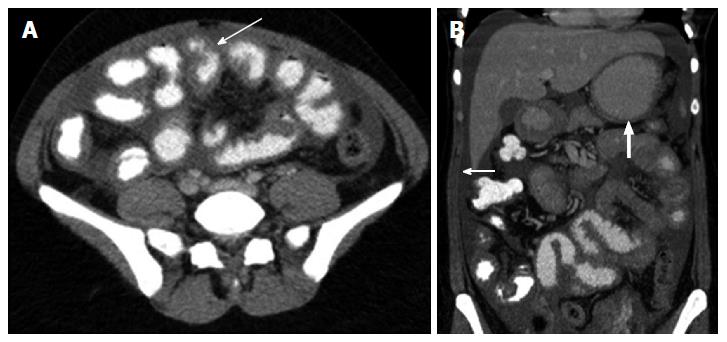
Figure 1 Findings on contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography.
A: Sagittal section demonstrates thickened loops of small bowel (arrow); B: Coronal image demonstrates free peritoneal fluid (arrow), thickened loops of small bowel and circumferential mural thickening of the distal stomach (heavy arrow).
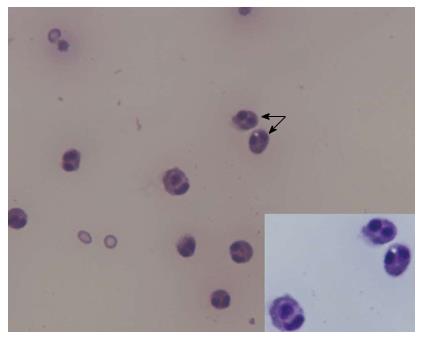
Figure 2 Diagnostic paracentesis demonstrates ascitic fluid rich in eosinophils (arrow), magnification 10 ×.
Inset, eosinophils in ascitic fluid, May Grunwald Giemsa, magnification 100 ×.
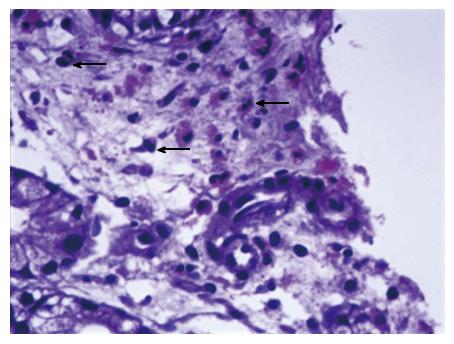
Figure 3 Endoscopic biopsy of gastric mucosa demonstrates scattered eosinophils (arrows) in the lamina propria.
Hematoxylin and eosin, magnification 40 ×.
- Citation: Agrawal S, Vohra S, Rawat S, Kashyap V. Eosinophilic ascites: A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. World J Gastrointest Surg 2016; 8(9): 656-659
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v8/i9/656.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v8.i9.656