©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2014; 6(7): 122-128
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v6.i7.122
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v6.i7.122
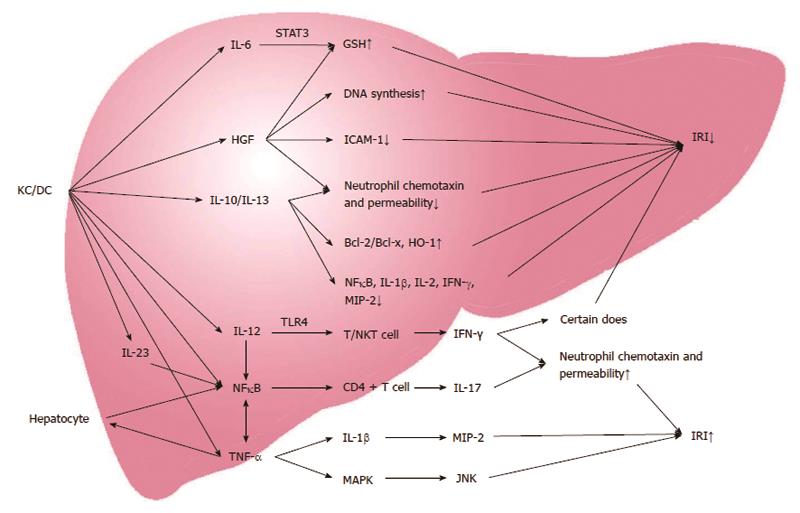
Figure 1 Cytokine network on the regulation of liver ischemia-reperfusion injury.
IRI: Ischemia-reperfusion injury; IL: Interleukin; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; MIP: Macrophage inflammatory protein; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; NF: Nuclear factor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
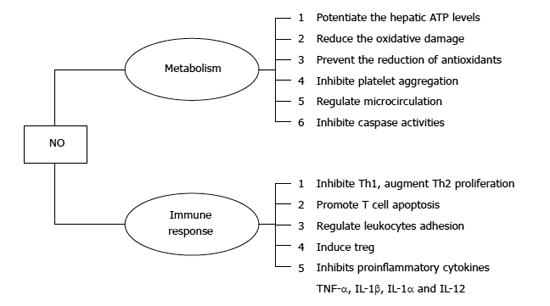
Figure 2 The protective effects of nitric oxide on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; IL: Interleukin.
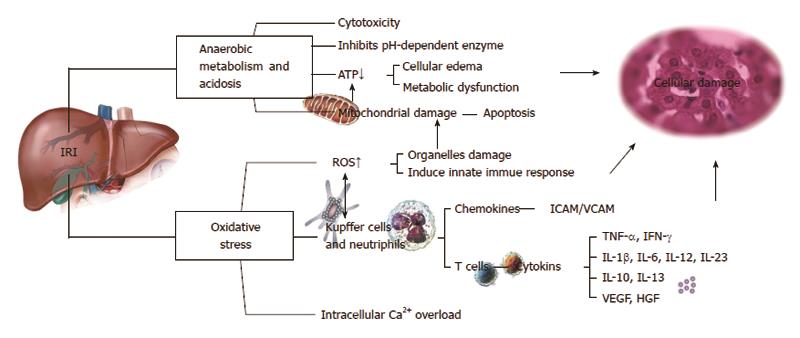
Figure 3 Mechanisms of hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; IL: Interleukin; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; IRI: Ischemia-reperfusion injury; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Guan LY, Fu PY, Li PD, Li ZN, Liu HY, Xin MG, Li W. Mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and protective effects of nitric oxide. World J Gastrointest Surg 2014; 6(7): 122-128
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v6/i7/122.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v6.i7.122