©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2014; 6(6): 117-121
Published online Jun 27, 2014. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v6.i6.117
Published online Jun 27, 2014. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v6.i6.117
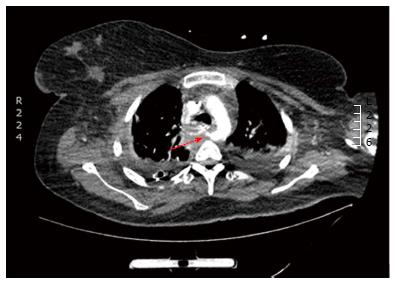
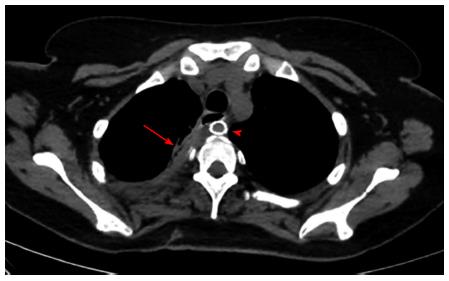
Figure 1 Computed tomography angiography showing a retroesophageal right suclavian artery with a pseudoaneurysm (arrow) around 1cm from its takeoff.
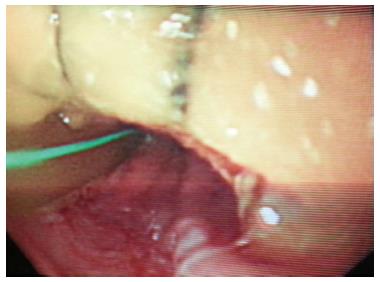
Figure 2 Upper endoscopy showing a 2 cm × 3 cm Teflon patch 22 cm from the incisor.
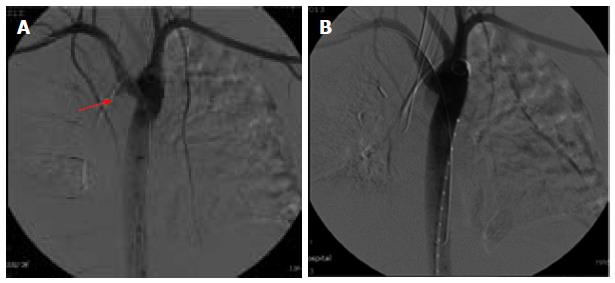
Figure 3 Thoracic aortic angiography.
A: Showing the pseudoaneurysm (arrow); B: Angiography after stent deployment.
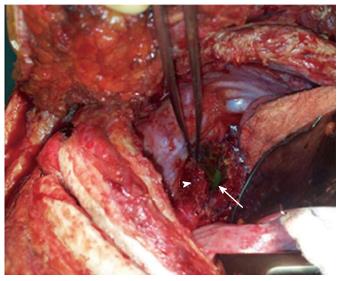
Figure 4 Thoracotomy with the Teflon patch (arrowhead) and nasogastric tube (arrow) visible through the esophagotomy.
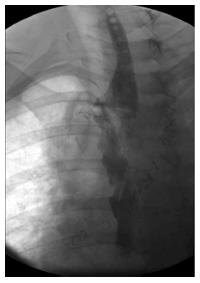
Figure 5 Gastrografin swallow performed postoperatively showing no evidence of a contrast leak at the site of the esophageal repair.
Figure 6 Computed tomography scan with oral contrast done after removal of the T-Tube with both the remnant tract of the T-tube (arrow) and the subclavian artery stent (arrowhead) seen.
- Citation: Hosn MA, Haddad F, El-Merhi F, Safadi B, Hallal A. Repair of an aberrant subclavian arterioesophageal fistula following esophageal stent placement. World J Gastrointest Surg 2014; 6(6): 117-121
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v6/i6/117.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v6.i6.117