©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2013; 5(6): 202-206
Published online Jun 27, 2013. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v5.i6.202
Published online Jun 27, 2013. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v5.i6.202
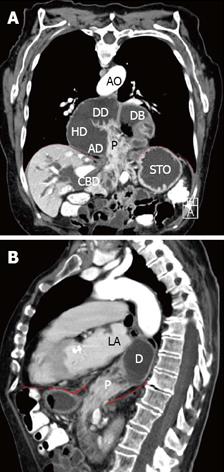
Figure 1 Computed tomographic scan obtained after oral administration of contrast.
A: Frontal plane; B: Sagittal plane. The duodenum (D) lies dorsal to the atrial chambers. The descending duodenum is in immediate proximity to the left atrial (LA) chamber. The diaphragm is pointed out as the red dashed line. P: Head of pancreas; CBD: Common bile duct; STO: Stomach; DB: Duodenal bulb; DD: Descending duodenum; HD: Horizontal duodenum; AD: Ascending duodenum; AO: Aorta. The diaphragm is pointed out as the red dashed line.
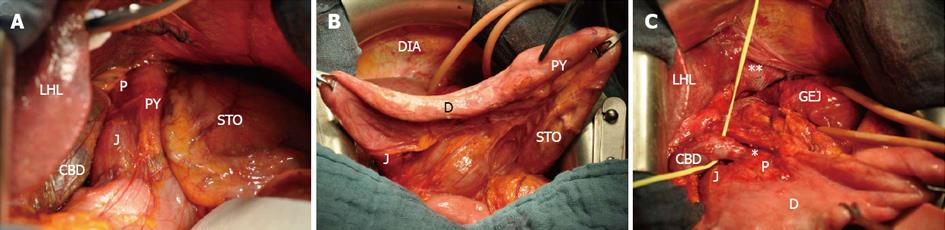
Figure 2 Intraoperative findings.
A: After midline laparotomy; B: After reposition of the hiatal content; C: After closure with non-absorbable mesh. Asterisk indicates constriction of the common bile duct; Asterisks indicate closure of the esophageal hiatus with mesh and non-absorbable sutures. STO: Stomach; PY: Pylorus; J: Jejunum; CBD: Enlarged common bile duct; LHL: Left hepatic lobe; P: Pancreas; D: Duodenum; DIA: Diaphragm; GEJ: Gastroesophageal junction.
- Citation: Jäger T, Neureiter D, Nawara C, Dinnewitzer A, Öfner D, Lamadé W. Intrathoracic major duodenal papilla with transhiatal herniation of the pancreas and duodenum: A case report and review of the literature. World J Gastrointest Surg 2013; 5(6): 202-206
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v5/i6/202.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v5.i6.202