©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 107002
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.107002
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.107002
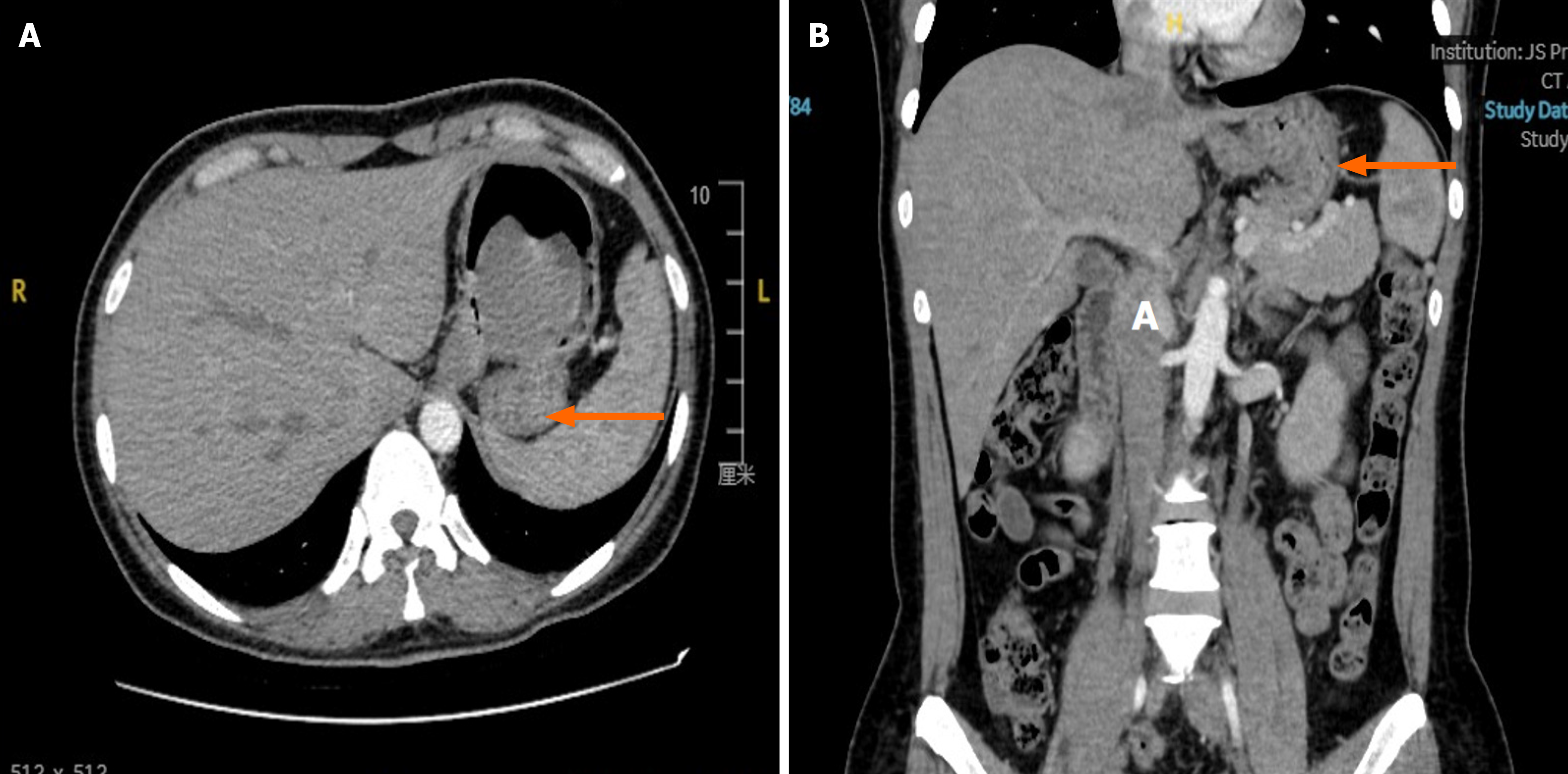
Figure 1 Preoperative radiologic findings: Abdominal computed tomography of Case 1.
A: Case 1 abdominal computed tomography (CT) in the coronal plane. The arrow indicates a gastric stromal tumor; B: Case 1 abdominal CT in the sagittal plane. The arrow indicates a gastric stromal tumor.
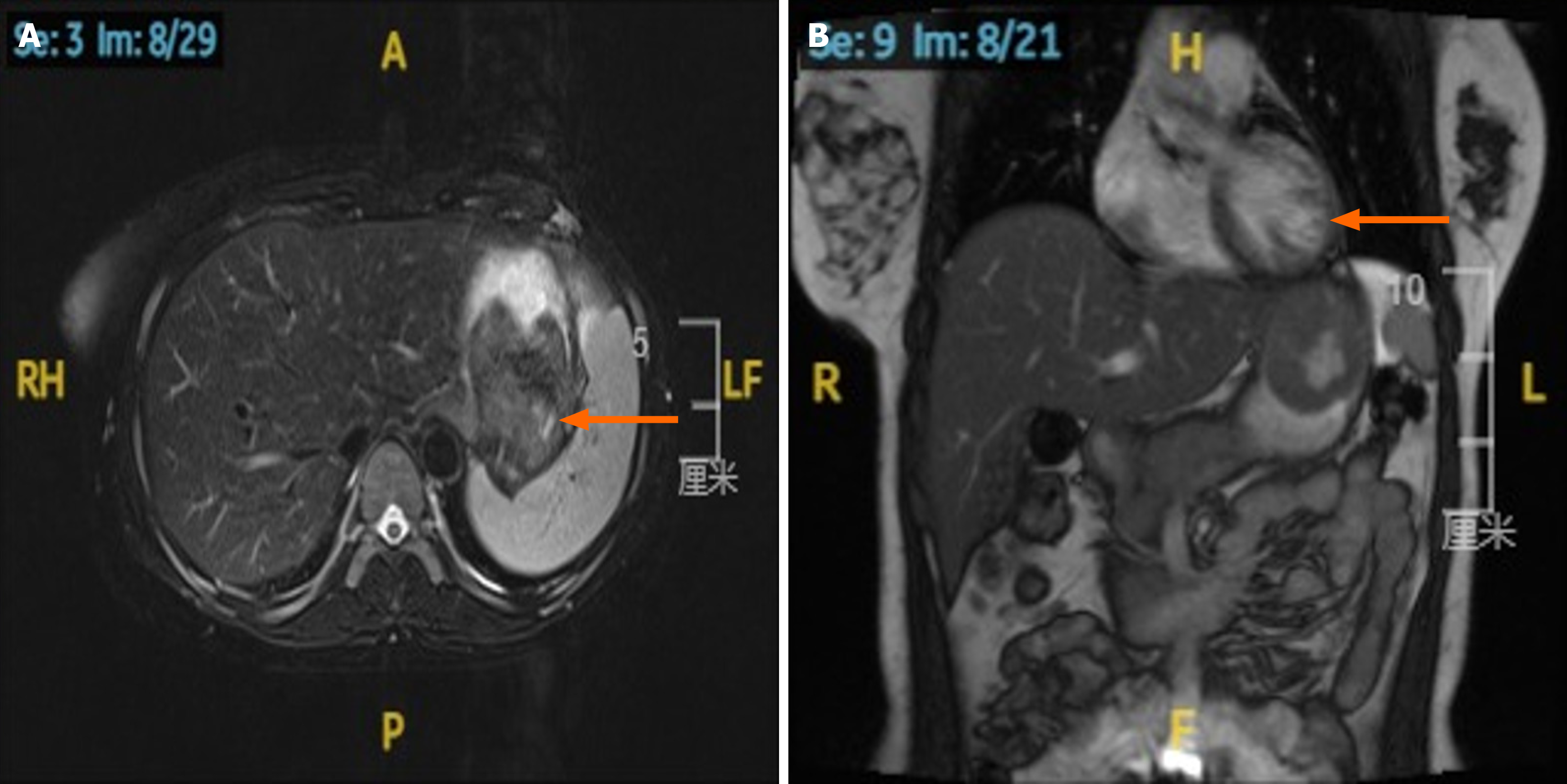
Figure 2 Preoperative radiologic findings: Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging of Case 1.
A: Case 1 abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the coronal plane. The arrow indicates a gastric stromal tumor; B: Case 1 abdominal MRI in the sagittal plane. The arrow indicates a gastric stromal tumor.
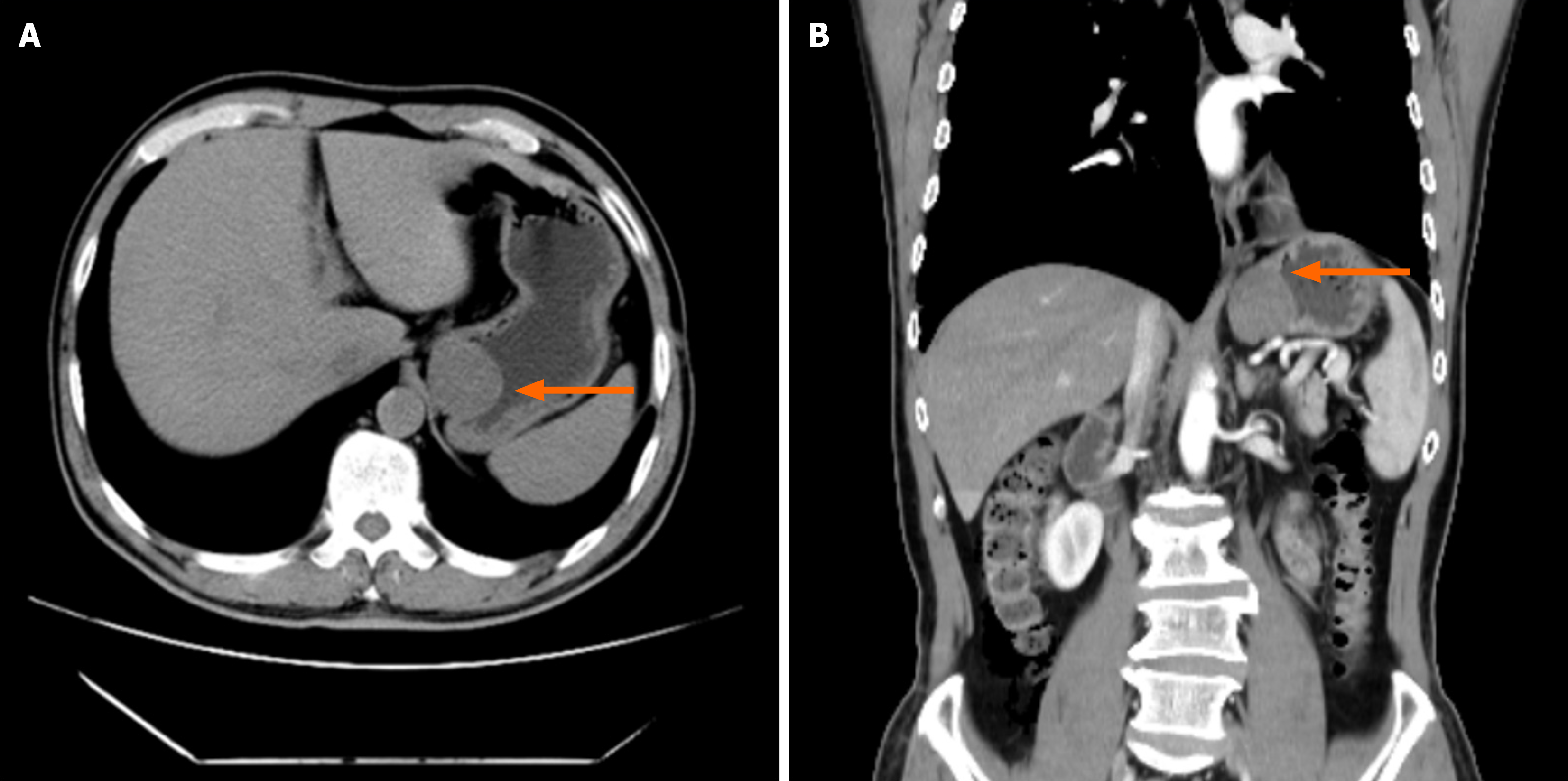
Figure 3 Preoperative radiologic findings: Abdominal computed tomography of Case 2.
A: Case 2 abdominal computed tomography (CT) in the coronal plane. The arrow indicates a gastric stromal tumor; B: Case 2 abdominal CT in the sagittal plane. The arrow indicates a gastric stromal tumor.
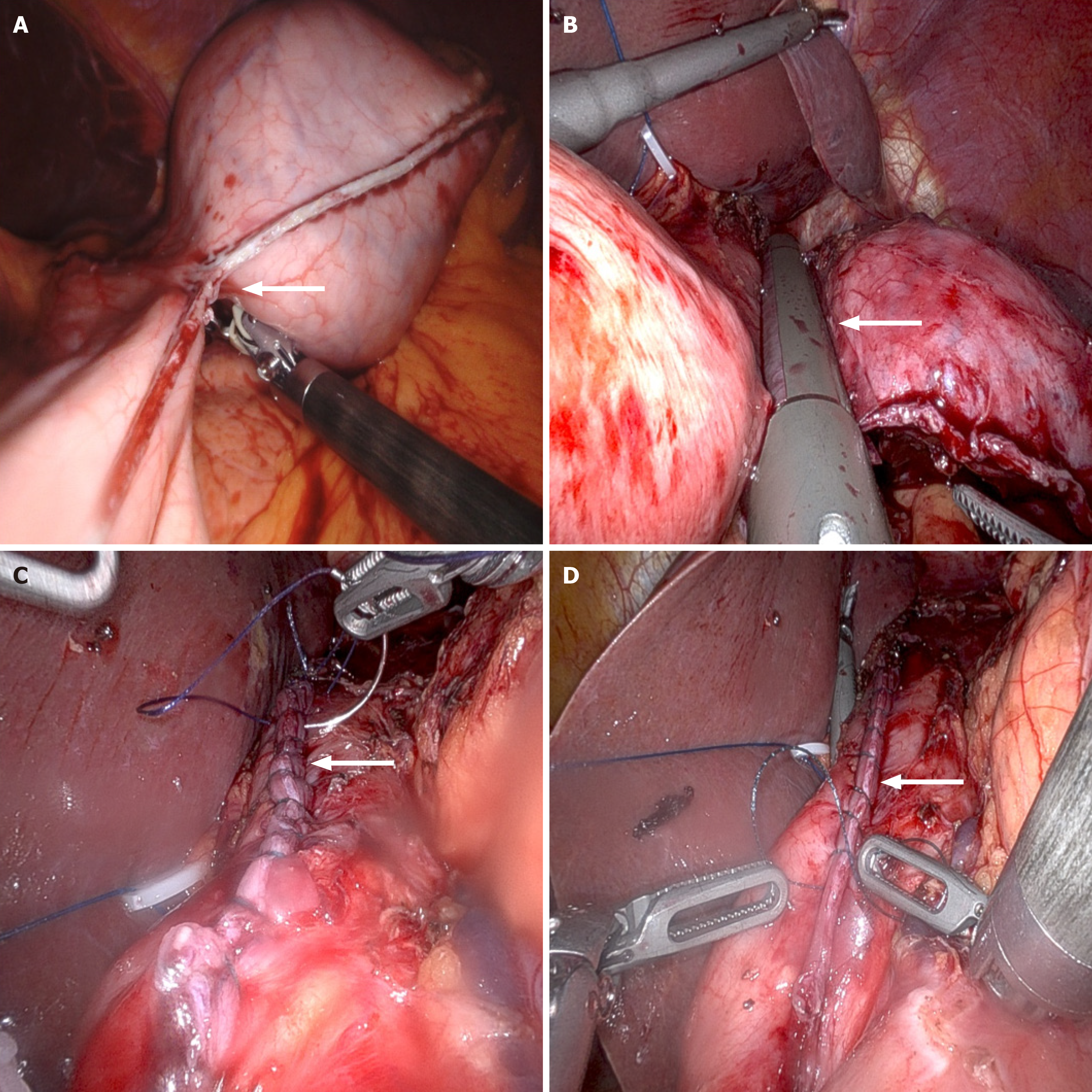
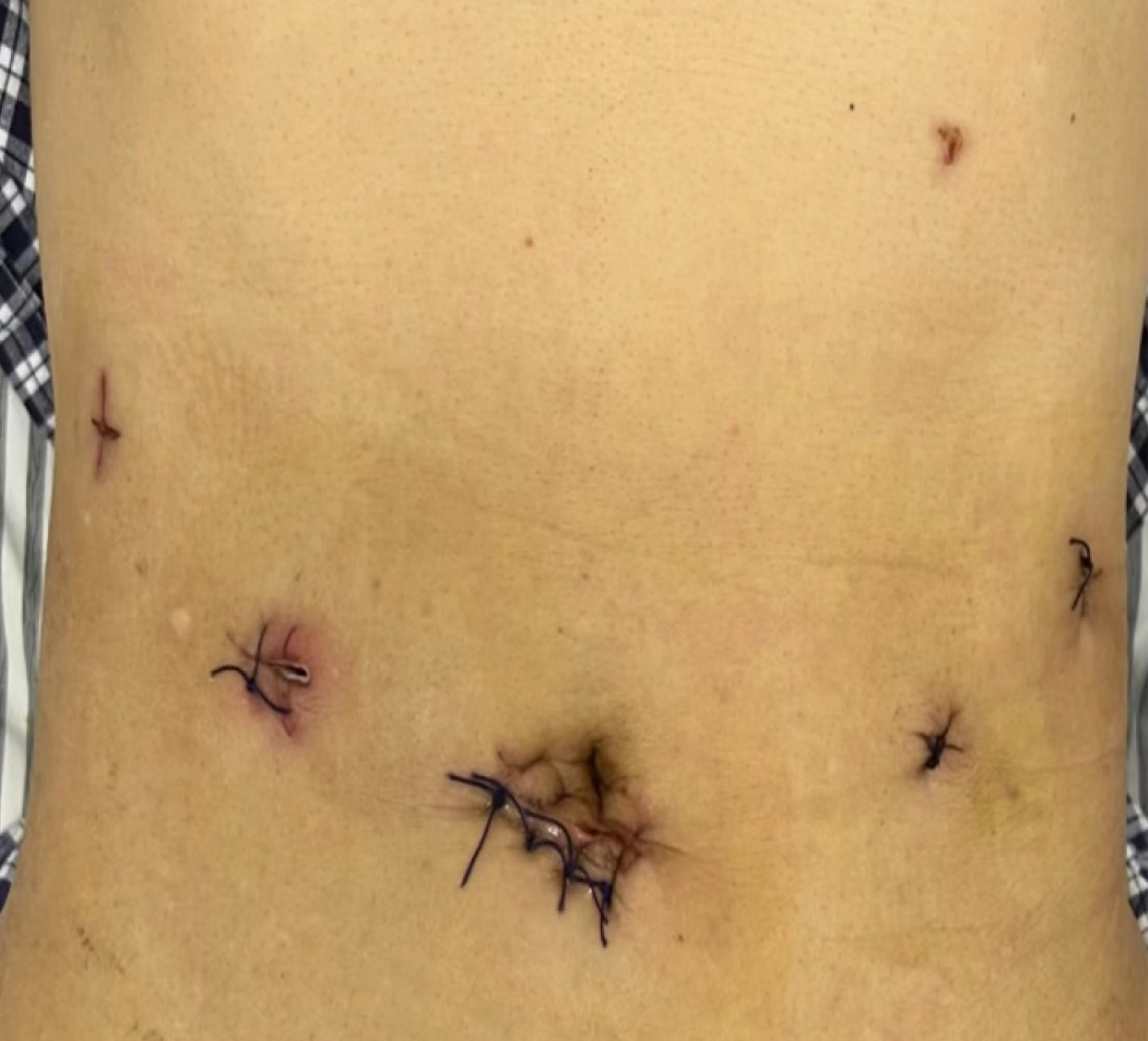
Figure 4 Distribution of trocar sites during the operation.
A and B: Robotic-assisted laparoscopic resection; C and D: Robotic-assisted laparoscopic suturing.
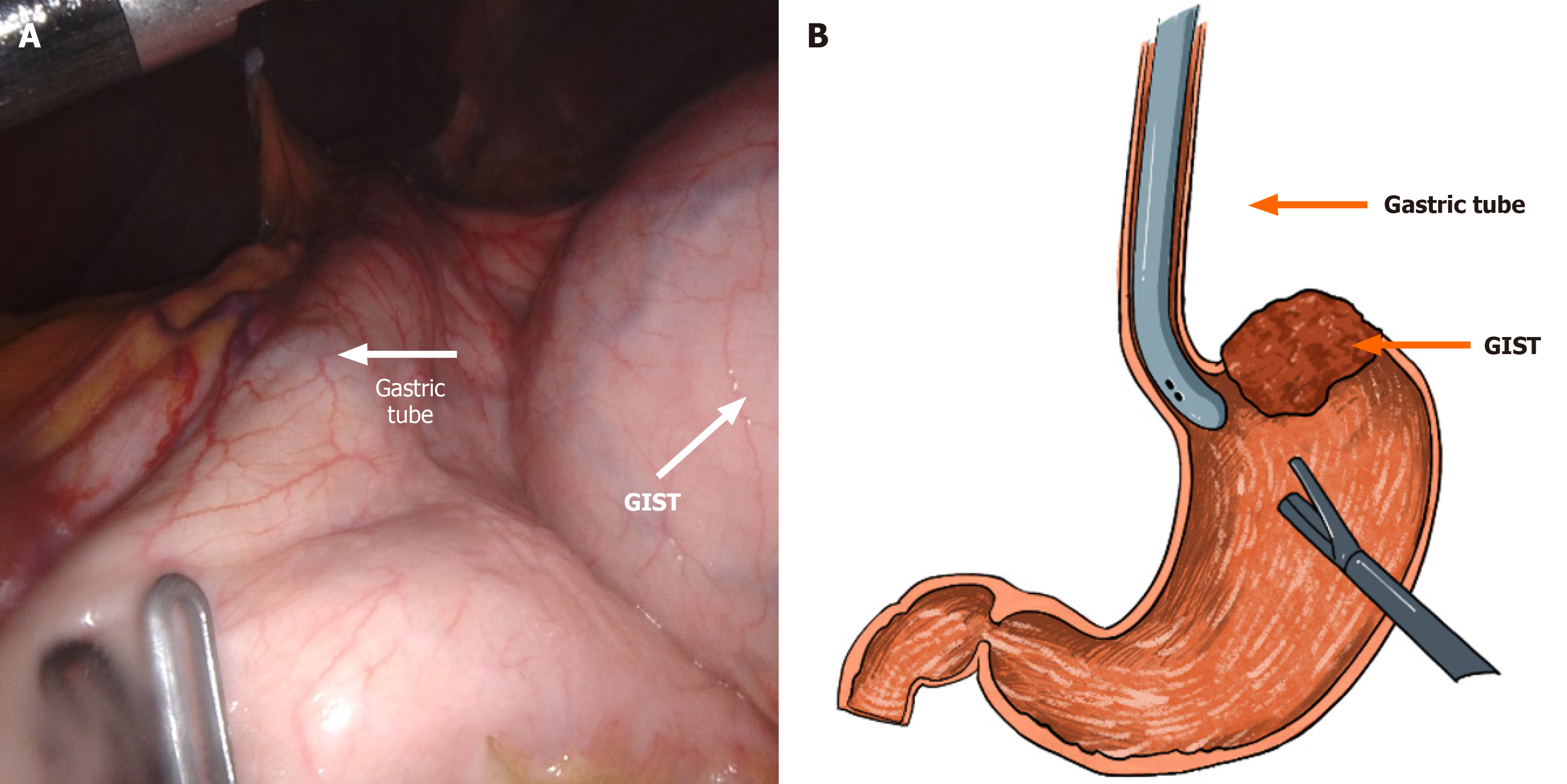
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the use of a gastroscope.
The gastric tube placed during operation is routine used in bariatric surgery. The tube itself is flexible and resilient, with good supporting strength. The tube wall and tip end is smooth to prevent damage to the digestive tract and facilitate the insertion. The tube served as bougie during of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, with a larger diameter of 12 mm. The use of bougie when stapling the incisura angularis will result in decreased incidence of strictures and better preserve the cardiac sphincter function. A: Intraoperative exploration of tumor margins using a gastroscope; B: Schematic diagram of intraoperative exploration of tumor margins using a gastroscope. GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of surgical trocar distribution.
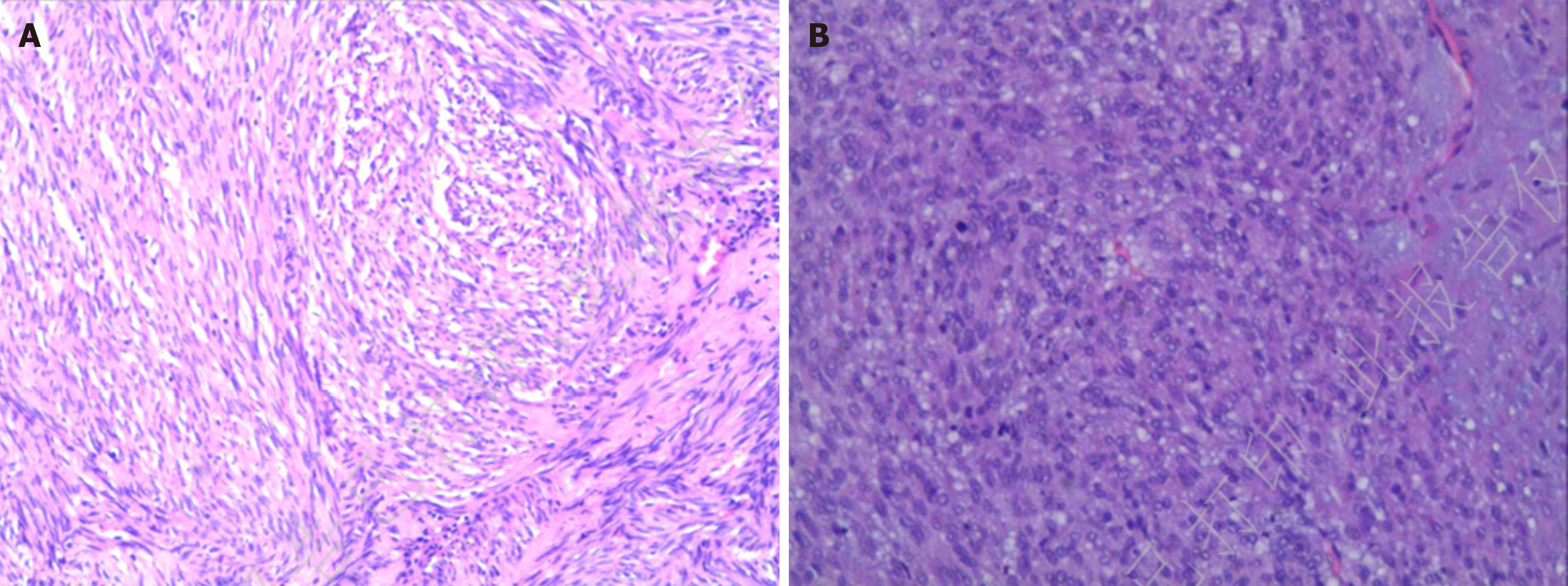
Figure 7 Pathologic finding.
A: Gastric tumor resection specimen gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Postoperative risk stratification: Intermediate. No residual tumor was identified at the resection margins (Case 1); B: Gastric tumor resection specimen GIST (Case 2). Postoperative risk stratification: High. No residual tumor was identified at the resection margins.
- Citation: Su QL, Yuan SL, Chen P, Wang HD, Liu J, Jiang W, Jiang ZW, Dai HS, Liu XX. Gastric tube-guided and robot-assisted laparoscopic resection of gastroesophageal junction stromal tumors: Two case reports. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(7): 107002
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i7/107002.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.107002