©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 106560
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.106560
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.106560
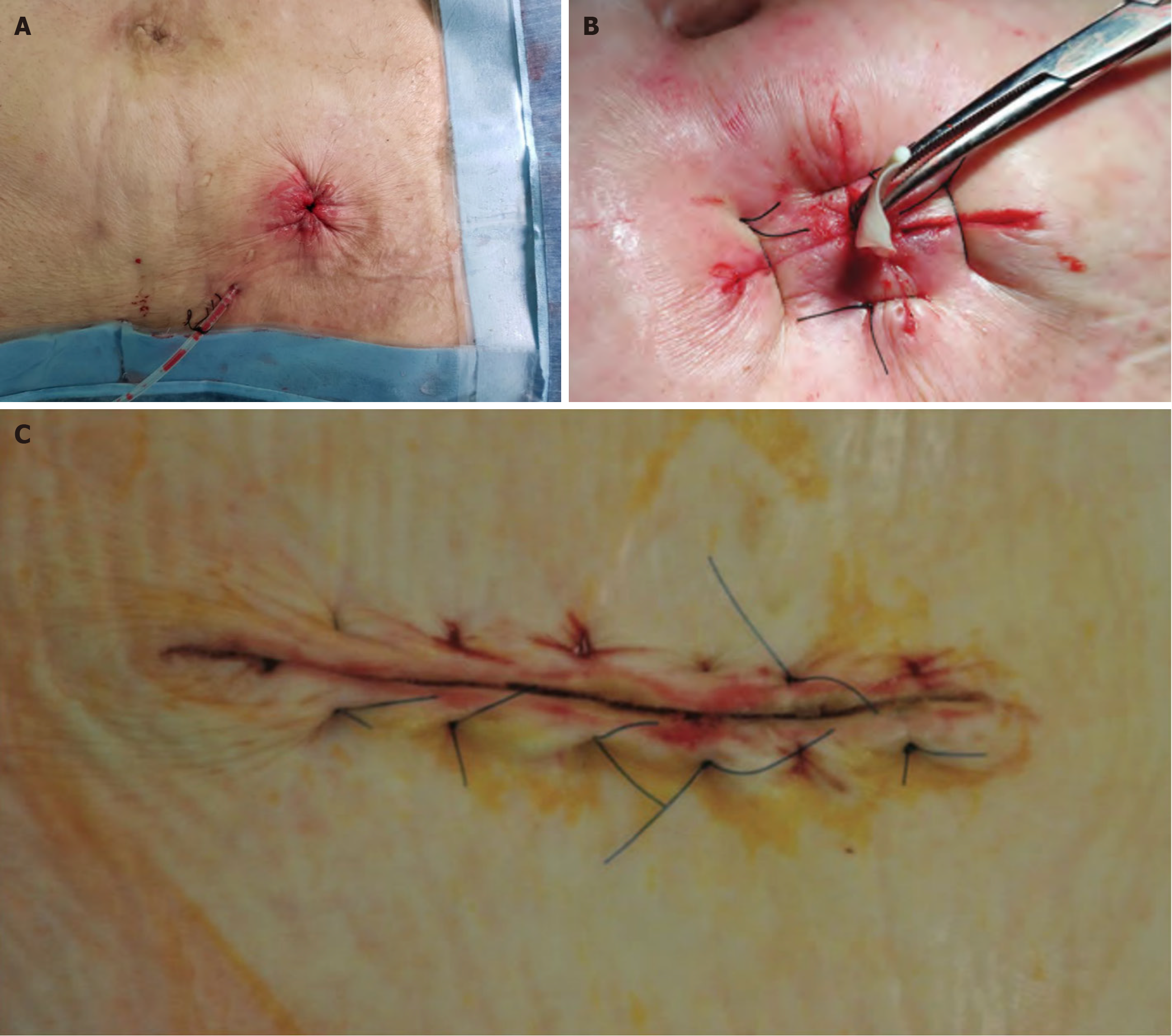
Figure 1 Illustration of operation method.
A: After tightening and knotting the suture, a residual opening of 0.3-0.5 cm in diameter remained in the skin; B: After tightening and knotting the suture, a residual cross-suture opening of 0.5-1 cm in diameter remained. Subsequently, 2-3 vertical interrupted sutures were applied to the skin surface with 3-0 Monocryl (Ethicon); C: After tightening and knotting the suture, a residual cross-suture opening of 0.5-1 cm in diameter remained.
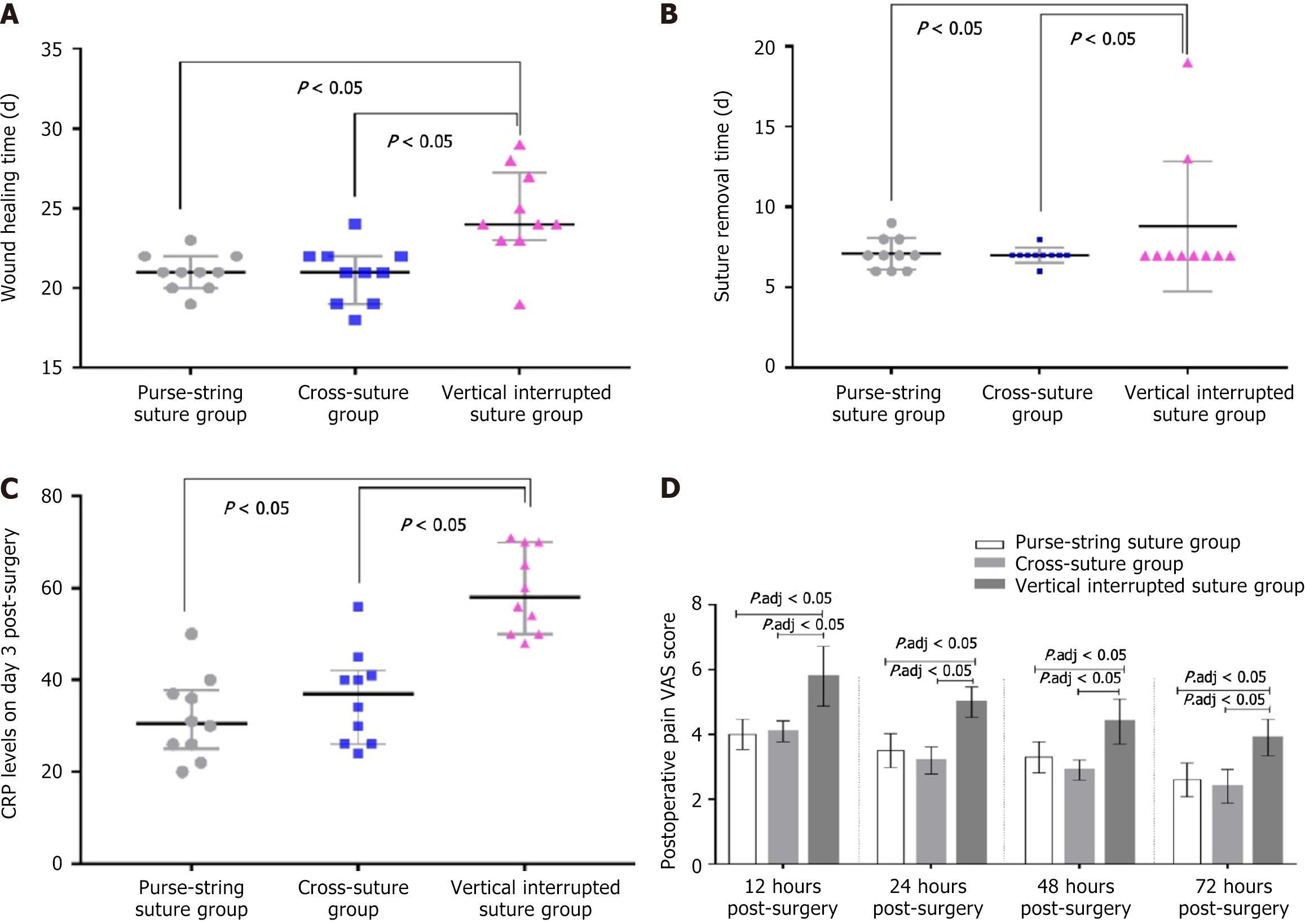
Figure 2 Comparison of intraoperative indicators, postoperative recovery indicators, and postoperative visual analog scale pain scores among the three groups.
A: Wound healing time among three groups, compared with the traditional vertical interrupted suture, cross-stitch suturing and purse-string can shorten the healing time; B: Suture removal time among three groups, compared with the traditional vertical interrupted suture, cross-stitch suturing and purse-string can shorten the suture removal time; C: C-reactive protein levels on day 3 post-surgery among three groups, compared with the traditional vertical interrupted suture, cross-stitch suturing and purse-string have lower C-reactive protein levels; D: Postoperative visual analog scale pain scores among three groups, compared with the traditional vertical interrupted suture, cross-stitch suturing and purse-string have mild pain.
- Citation: Gao YB, Wang L, Shi LN, Wu X, Miao W. Impact of different skin suturing methods on patient prognosis after ileostomy closure. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(7): 106560
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i7/106560.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.106560