©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Apr 27, 2025; 17(4): 103696
Published online Apr 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i4.103696
Published online Apr 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i4.103696
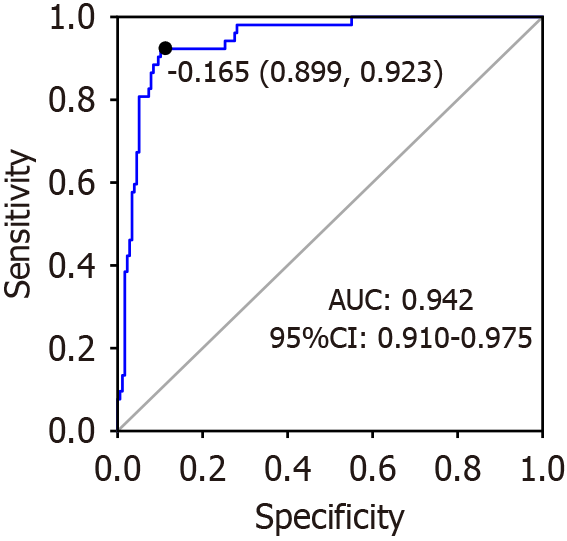
Figure 1 Receiver operating characteristic curve of the model to predict the risk of postoperative death in patients who underwent abdominal surgery.
AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CI: Confidence interval.
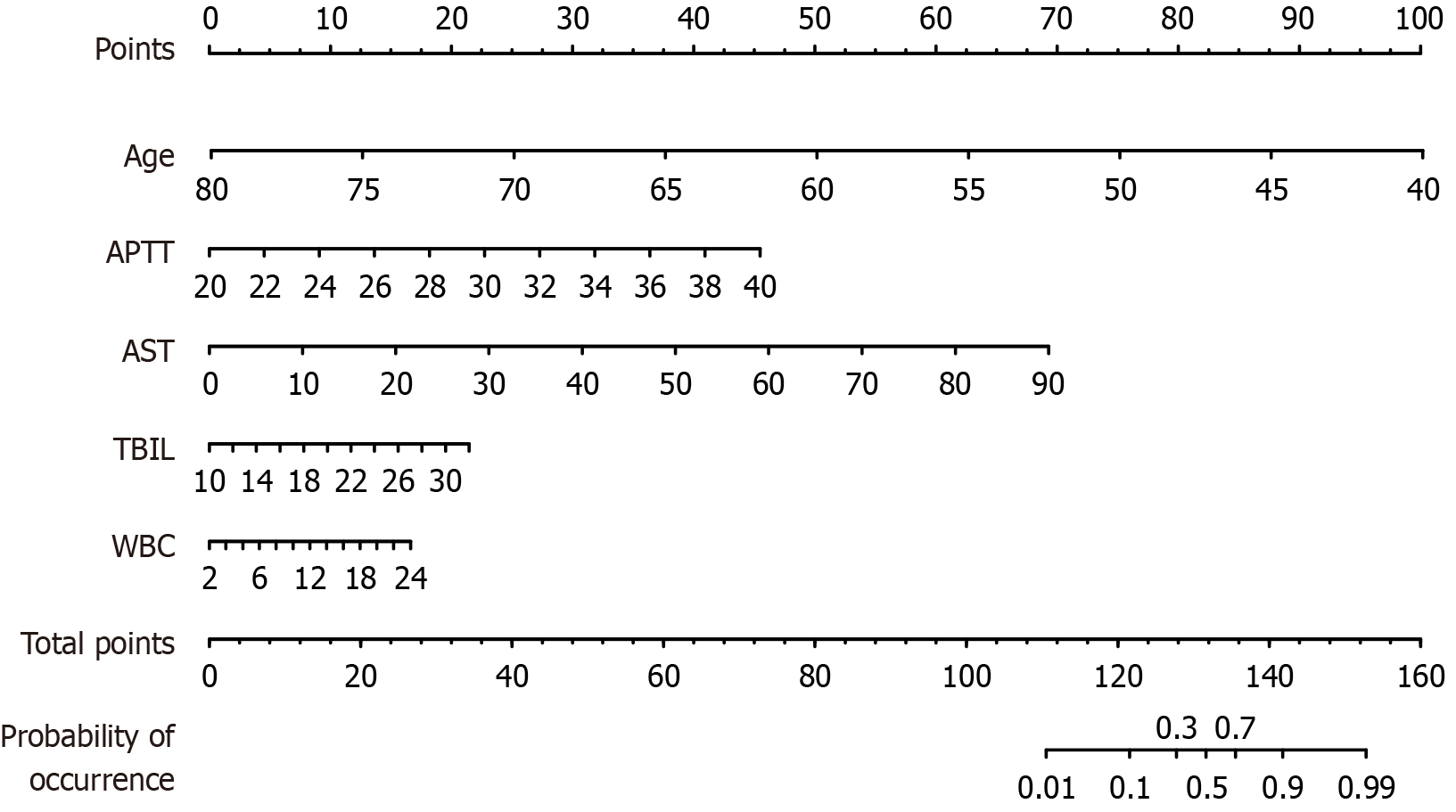
Figure 2 Nomogram for the risk of postoperative death in patients who underwent abdominal surgery.
The independent influencing factors used in the process of establishing the model were derived from the multivariate logistic regression analysis. APTT: Activated partial thromboplastin time; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; WBC: White blood cell.
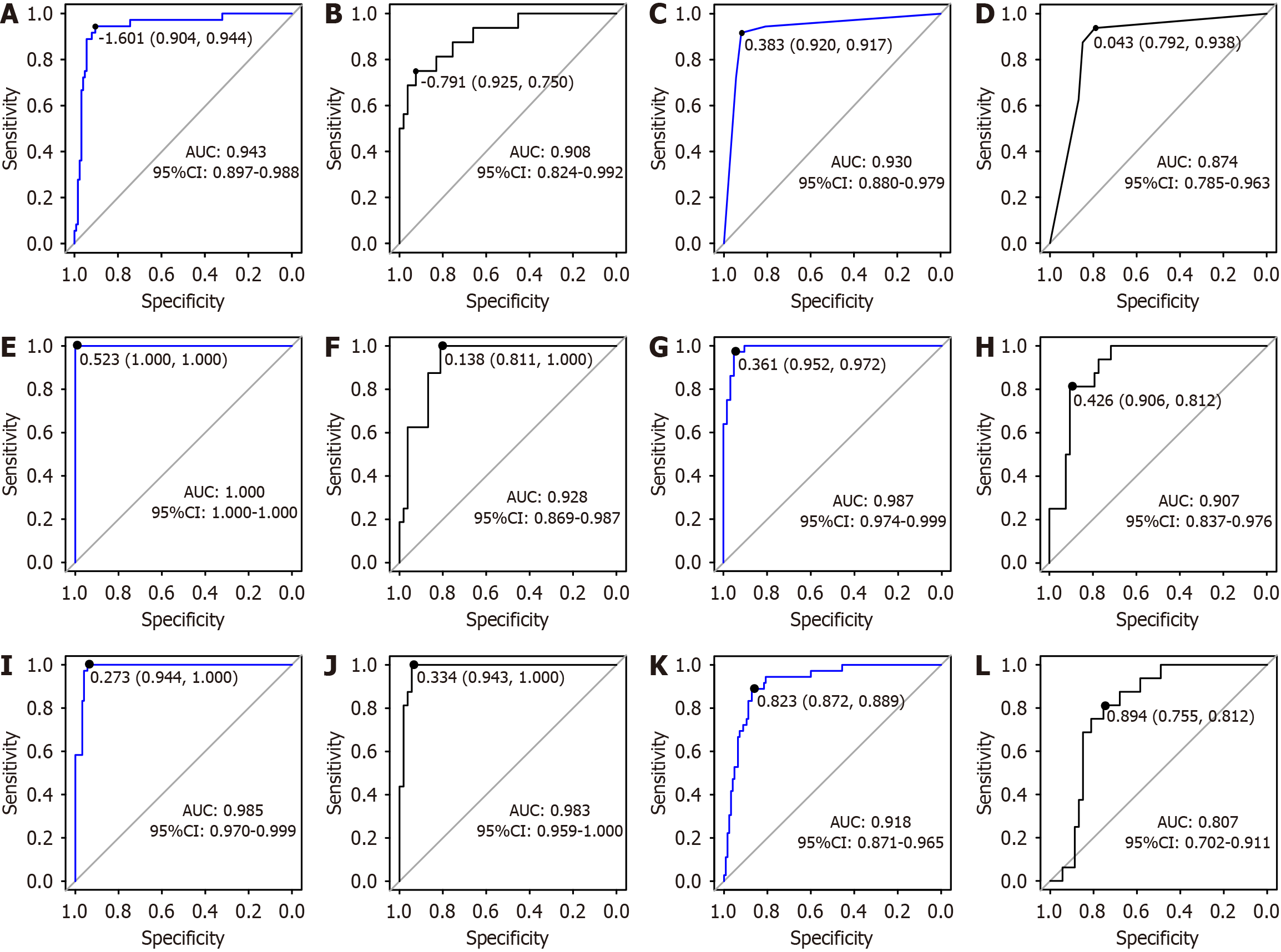
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curves to predict postoperative death in patients who underwent abdominal surgery.
A: The nomogram (training cohort); B: The nomogram (validation cohort); C: The decision-tree model (training cohort); D: The decision-tree model (validation cohort); E: The random-forest model (training cohort); F: The random-forest model (validation cohort); G: The gradient-boosting tree model (training cohort); H: The gradient-boosting tree model (validation cohort); I: The support vector machine model (training cohort); J: The support vector machine model (validation cohort); K: The naive Bayesian model (training cohort); L: The naive Bayesian model (validation cohort). AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CI: Confidence interval.
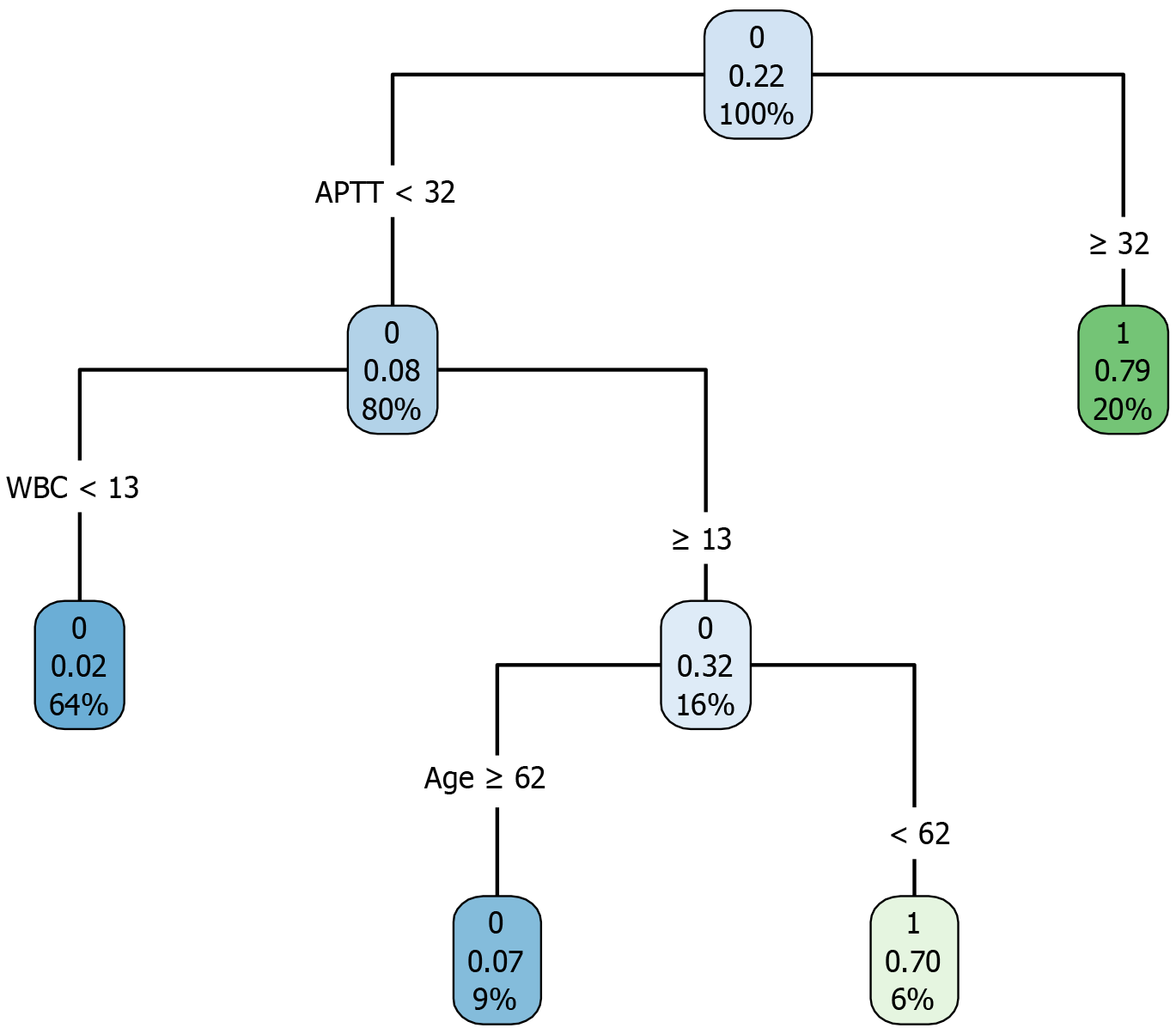
Figure 4 Decision-tree prediction model for the risk of postoperative death in patients who underwent abdominal surgery.
The independent influencing factors used in the process of establishing the model were derived from the multivariate logistic regression analysis. APTT: Activated partial thromboplastin time; WBC: White blood cell.
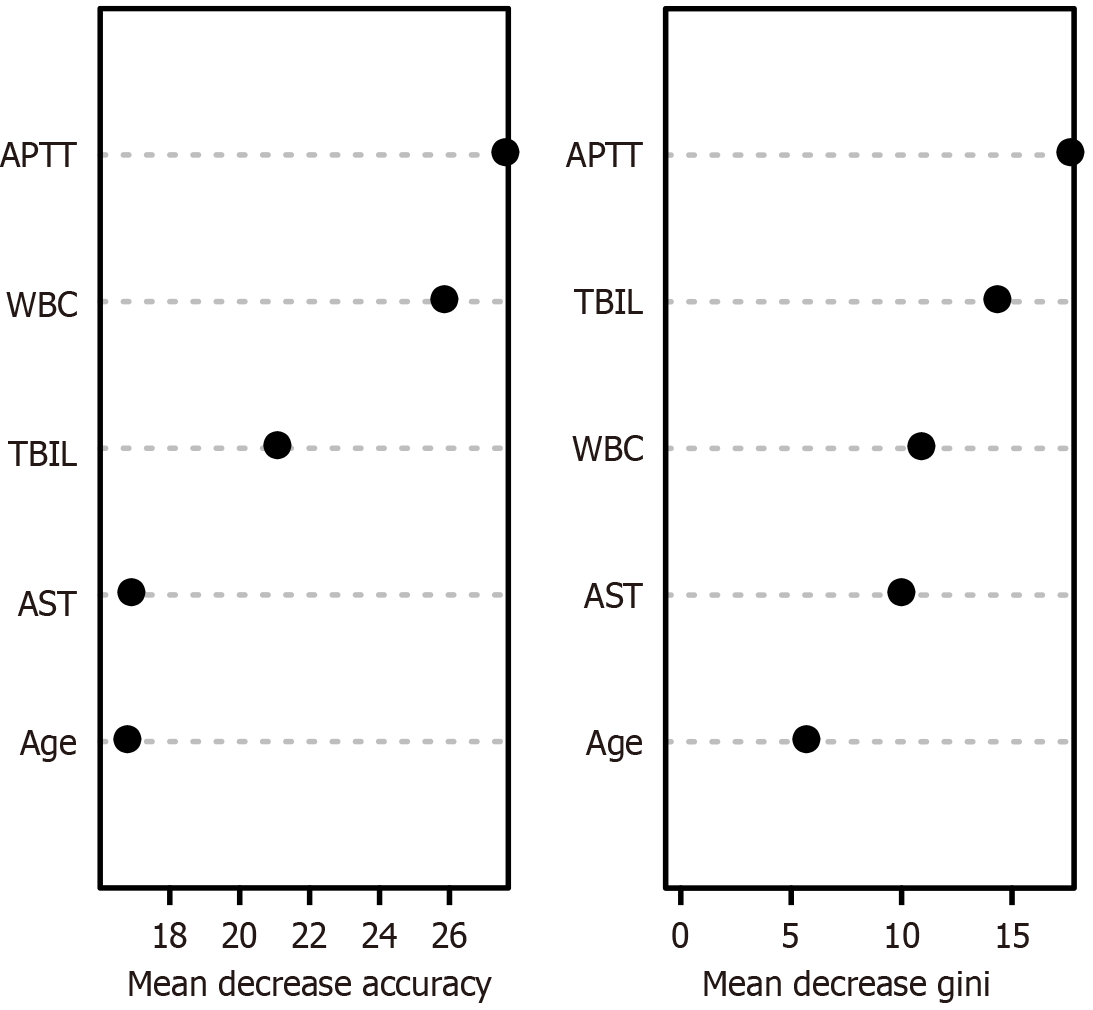
Figure 5 Random-forest prediction model for the risk of postoperative death in patients who underwent abdominal surgery.
The independent influencing factors used in the process of establishing the model were derived from the multivariate logistic regression analysis. APTT: Activated partial thromboplastin time; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; WBC: White blood cell.
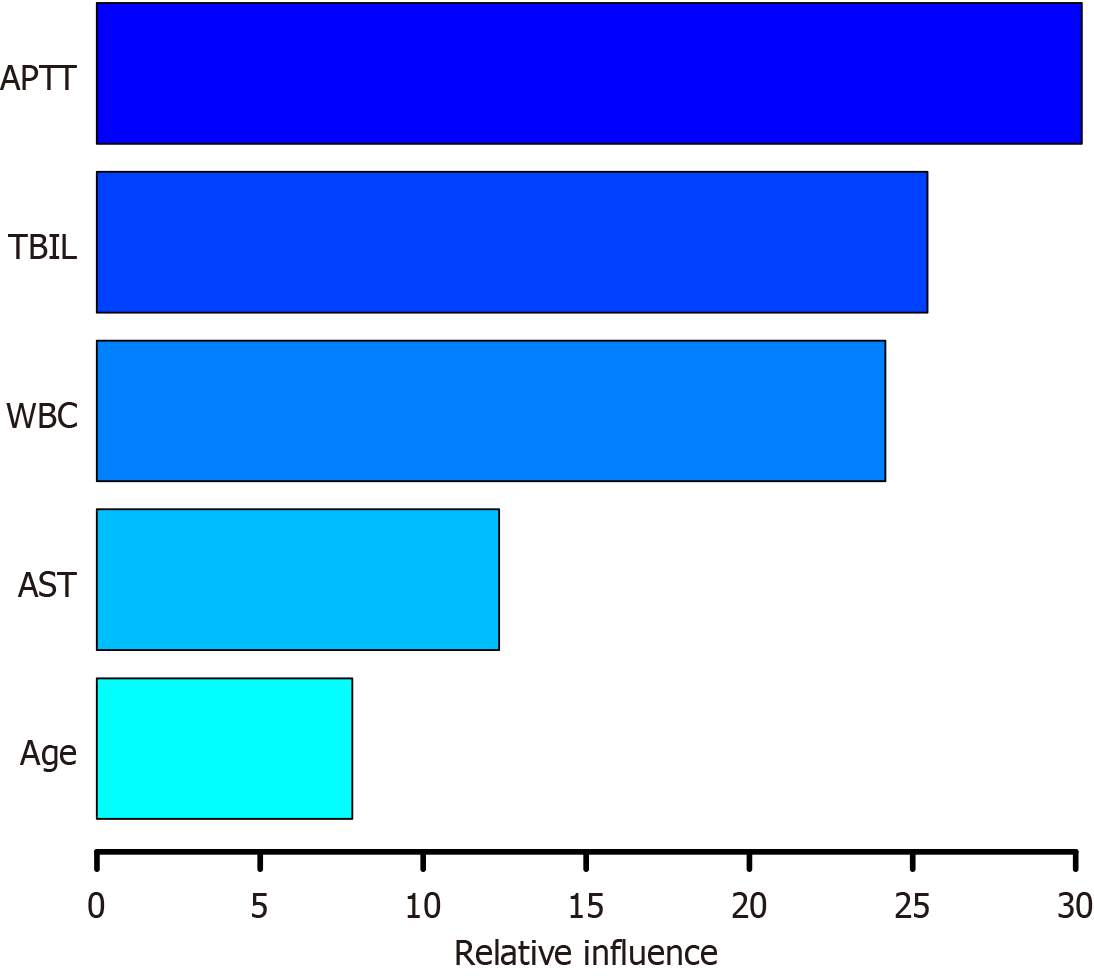
Figure 6 Gradient-boosting tree model for the risk of postoperative death in patients who underwent abdominal surgery.
The independent influencing factors used in the process of establishing the model were derived from the multivariate logistic regression analysis. APTT: Activated partial thromboplastin time; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; WBC: White blood cell.
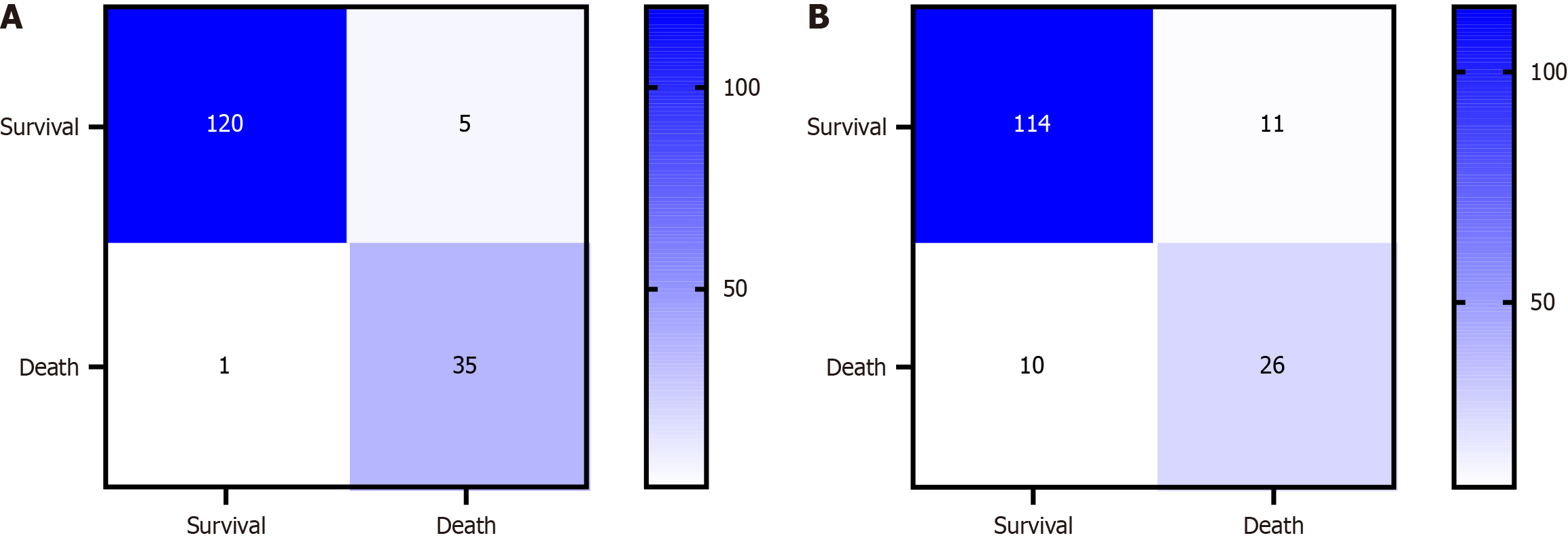
Figure 7 Confusion matrix for the risk of postoperative death in patients who underwent abdominal surgery.
A: The support vector machine model; B: The naive Bayesian model. The independent influencing factors used in the process of establishing the model were derived from the multivariate logistic regression analysis.
- Citation: Yuan JH, Jin YM, Xiang JY, Li SS, Zhong YX, Zhang SL, Zhao B. Machine learning-based prediction of postoperative mortality risk after abdominal surgery. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(4): 103696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i4/103696.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i4.103696