©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Apr 27, 2025; 17(4): 103136
Published online Apr 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i4.103136
Published online Apr 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i4.103136
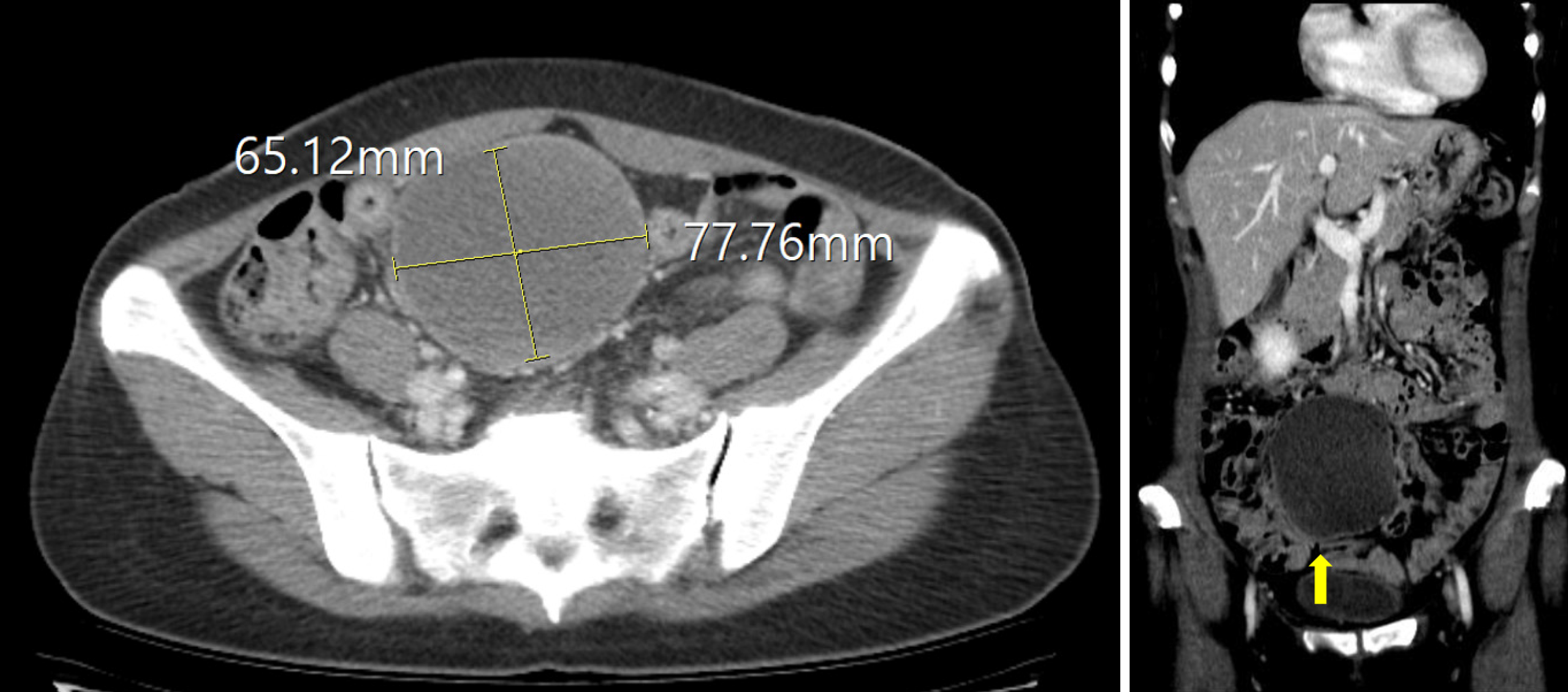
Figure 1 Preoperative radiologic findings.
A 6.5 cm × 7.8 cm × 8.5 cm well-defined cystic mass with internal fatty attenuation and a fluid-fluid level was identified in the right adnexa, without enhancement. The differential diagnoses includes extragonadal teratoma, ovarian teratoma, and, less likely, myxoid liposarcoma. The absence of clear continuity with the ovary suggests an extragonadal teratoma, although an ovarian teratoma cannot be excluded if continuity is obscured by the scan slice thickness.
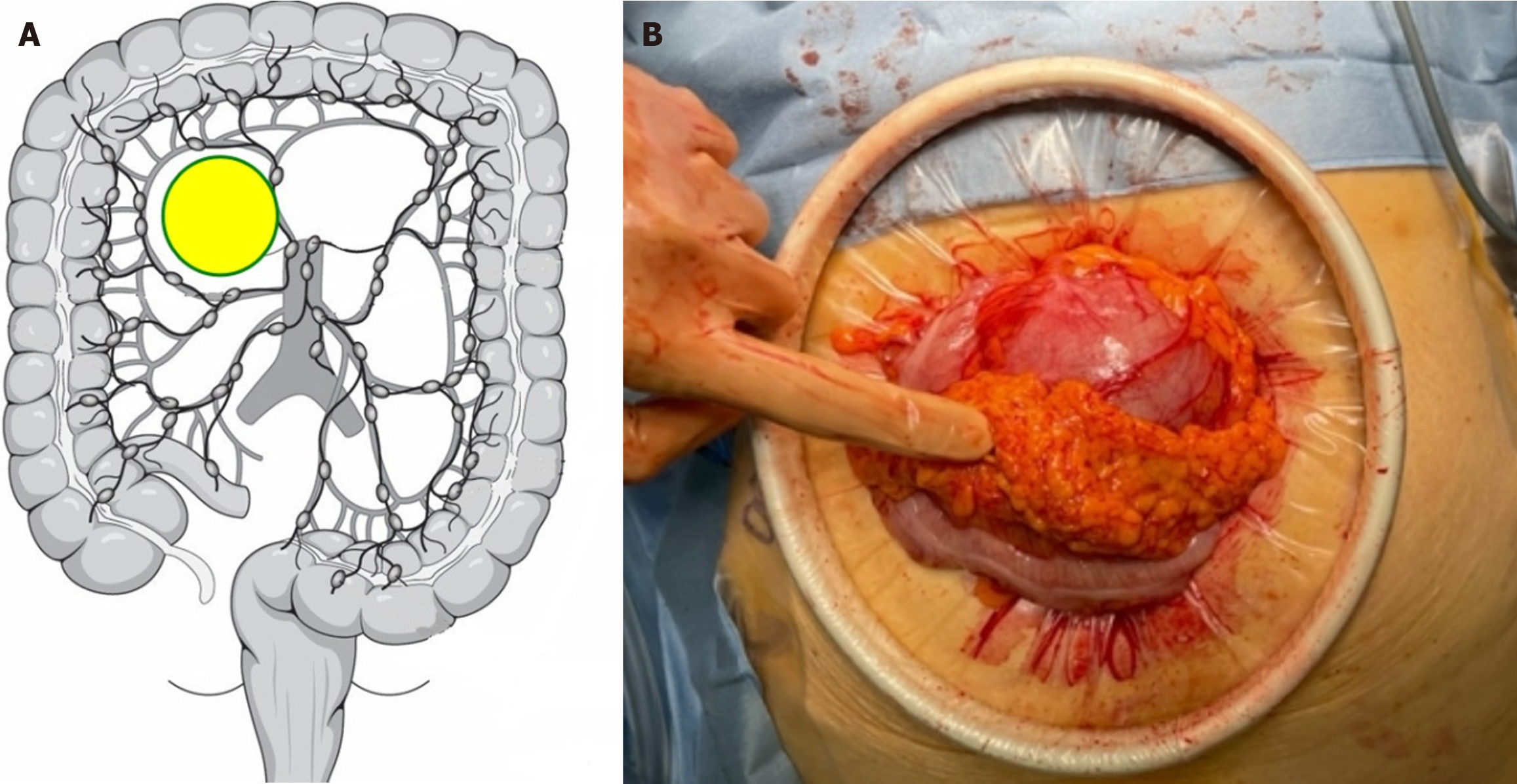
Figure 2 Colonic duplication location.
A: Intraoperative findings of colonic duplication; B: Following mini-laparotomy, colonic duplication was observed adjacent to the colon and attached to the omentum.
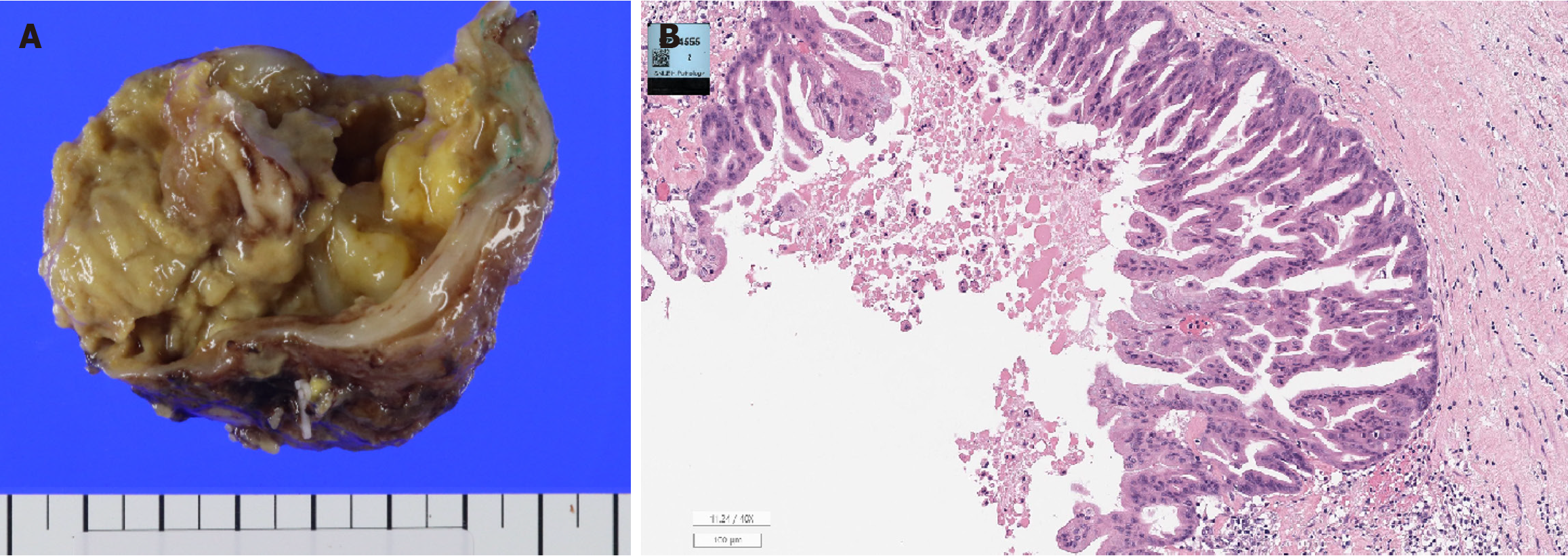
Figure 3 Gross pathologic finding.
A: A cystic tumor section encased in a serosal layer revealed an internal cavity filled with mucinous-like material. Histological and pathological findings; B: The cyst wall was lined with epithelium resembling the intestinal mucosa, with mucin occupying the lumen, and mild inflammatory cell infiltration was observed in the surrounding stroma.
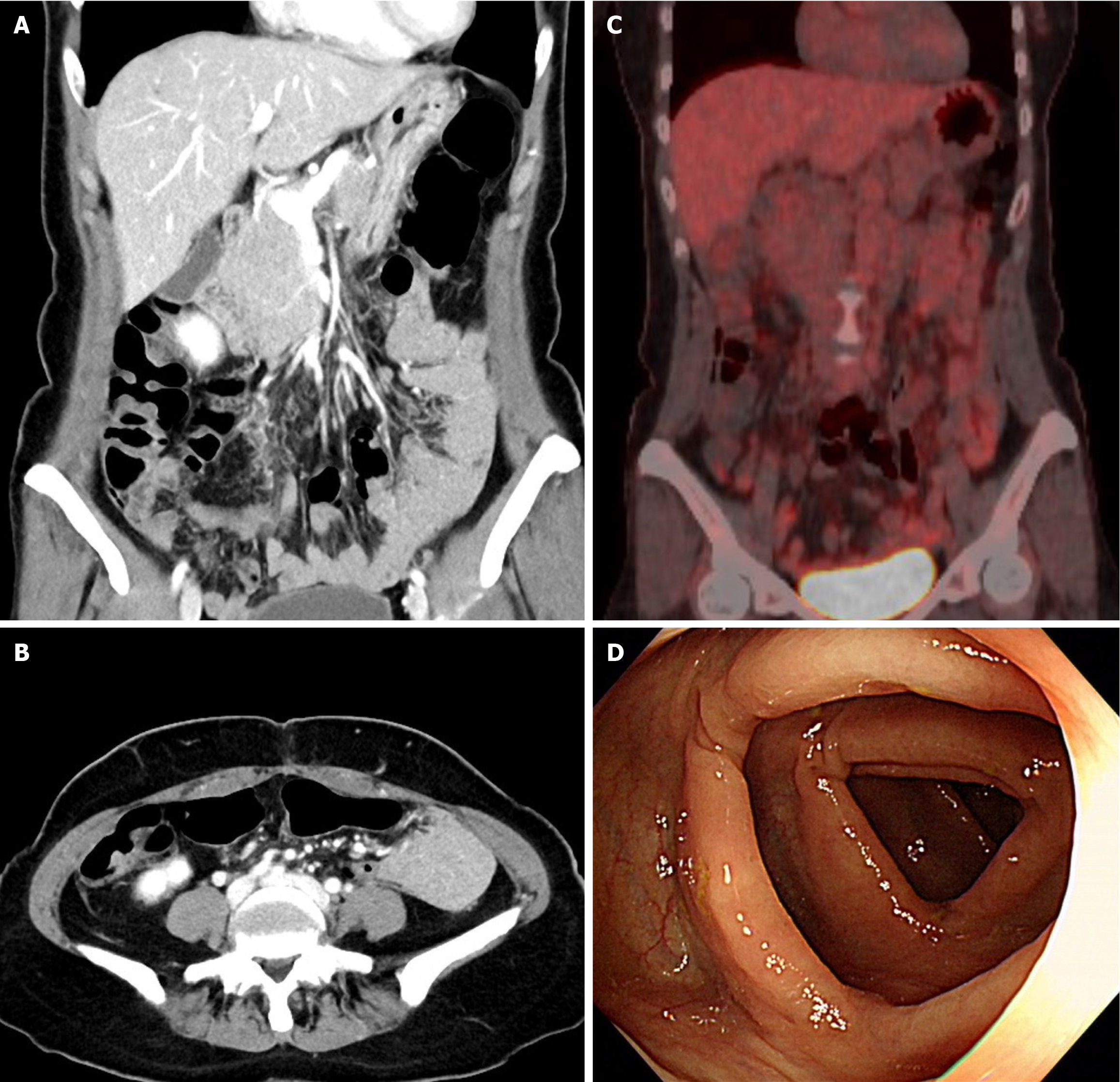
Figure 4 Postoperative imaging and endoscopy findings.
A and B: Postoperative abdominal-pelvic computed tomography scans show no detectable intra-abdominal masses; C: Postoperative positron emission computed tomography-computed tomography reveals no abnormal hypermetabolic lesions suggestive of malignancy; D: Postoperative colonoscopy demonstrates no abnormal lesions in the colon.
- Citation: Lee J, Suh JW. Adenocarcinoma originating from a colonic duplication cyst: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(4): 103136
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i4/103136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i4.103136