©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Mar 27, 2025; 17(3): 100185
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i3.100185
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i3.100185
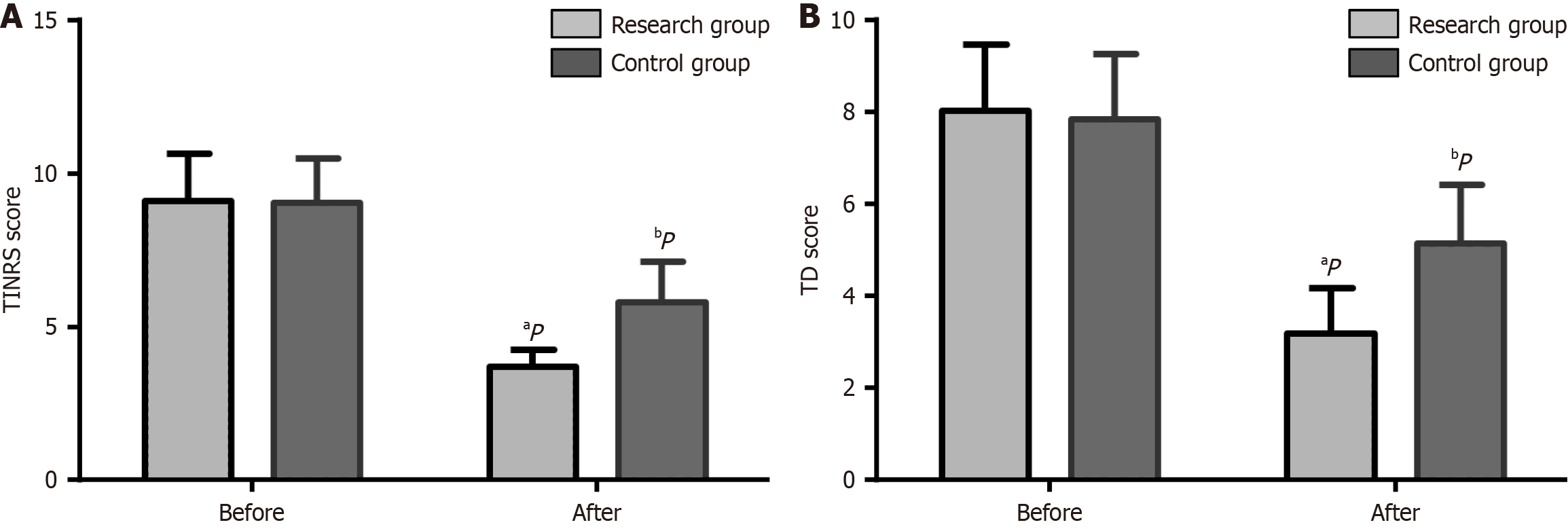
Figure 1 Evaluation of thirst intensity numerical rating scale and thirst distress scores before and after care in both groups.
A: The thirst intensity numerical rating scale (TINRS) scores of both groups were markedly reduced following the nursing intervention, and the TINRS score of the research group was significantly lower than that of the control group after the nursing care; B: The thirst distress (TD) scores of both groups also manifested a significant reduction following the nursing procedures, and likewise, the TINRS score of the research group was considerably lower than that of the control group in the post-nursing phase. The TINRS scale is employed to evaluate the level of thirst, while the TD scale is utilized to assess the degree of distress induced by thirst. The scoring range for both scales spans from 0 to 10, with a higher score indicating a more severe degree of thirst or a more intense sense of distress due to thirst. aP < 0.01 vs before care; bP < 0.05 vs control. TD: Thirst distress; TINRS: Thirst intensity numerical rating scale.
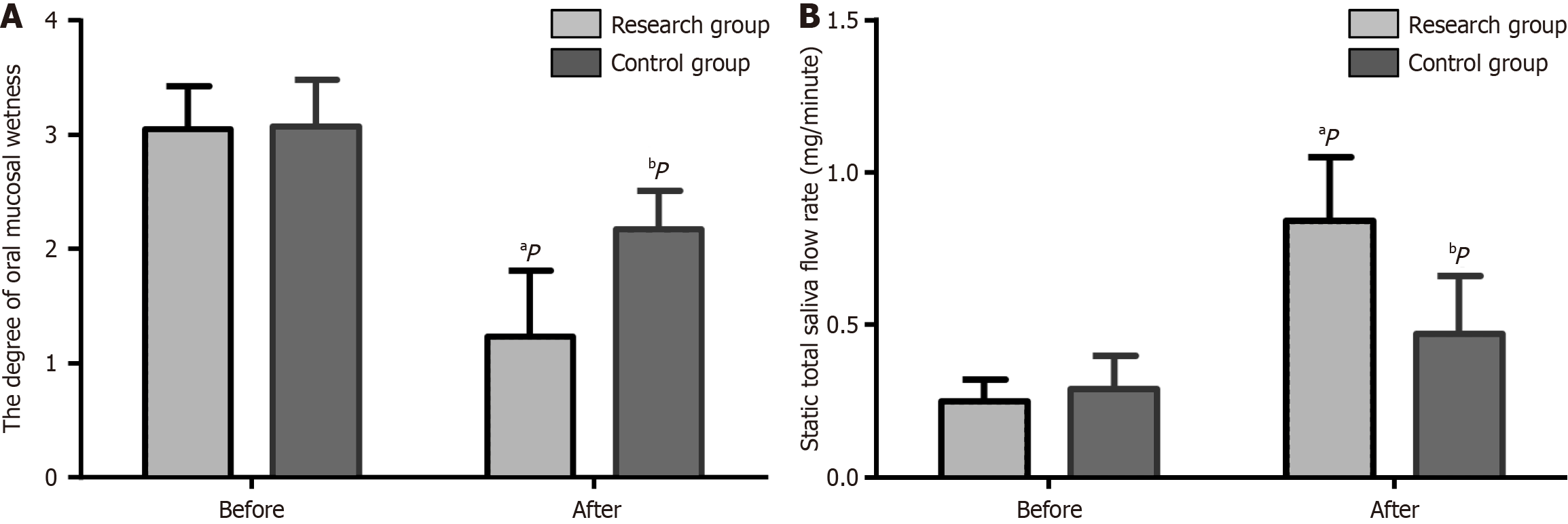
Figure 2 Evaluation of the oral mucosal wetness scores and the unstimulated whole salivary flow rate before and after nursing.
A: The oral mucosal wetness scores. The oral mucosal wetness score of both groups was statistically decreased after the execution of the nursing measures, with that of the research group being significantly lower compared to the control group after nursing care. The scoring range of oral mucosal wetness degree is from 1 to 4, with a higher score signifying a reduced level of oral mucosal wetness; B: The unstimulated whole salivary flow rate. The unstimulated whole salivary flow rate of both groups was significantly increased after nursing, with a more significant increase in the research group vs the control group. The unstimulated whole salivary flow rate was measured by the cotton swab method. aP < 0.01 vs before care; bP < 0.05 vs control.
- Citation: Chen L, Li BX, Gan QZ, Guo RG, Chen X, Shen X, Chen Y. Enhanced recovery after surgery-based evidence-based care plus ice stimulation for thirst management in convalescent patients following digestive surgery under general anesthesia. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(3): 100185
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i3/100185.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i3.100185