©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 98585
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.98585
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.98585
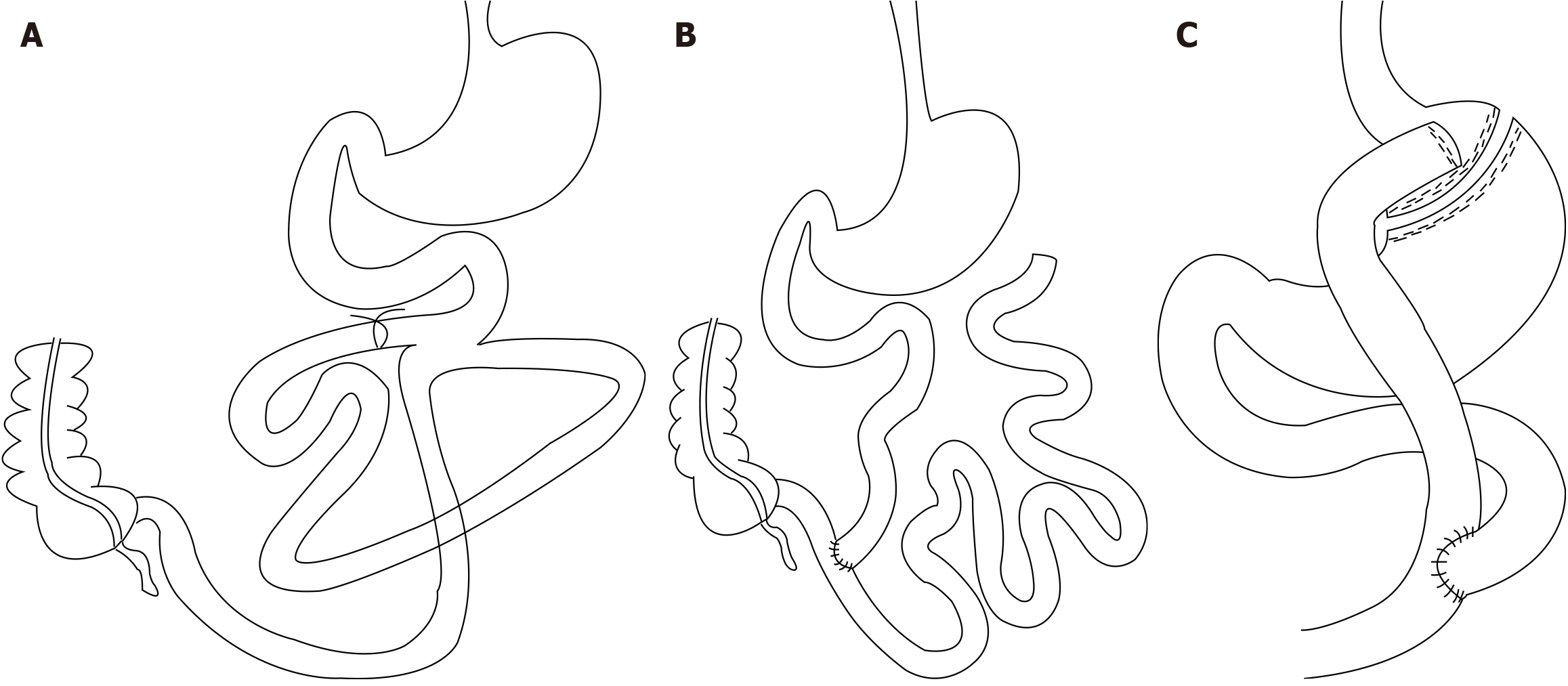
Figure 1 Surgical model.
A: Proximal small intestinal bypass (absence of approximately 60% of the proximal small intestine); B: Jejunoileal bypass (absence of approximately 85% of the small intestine); C: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
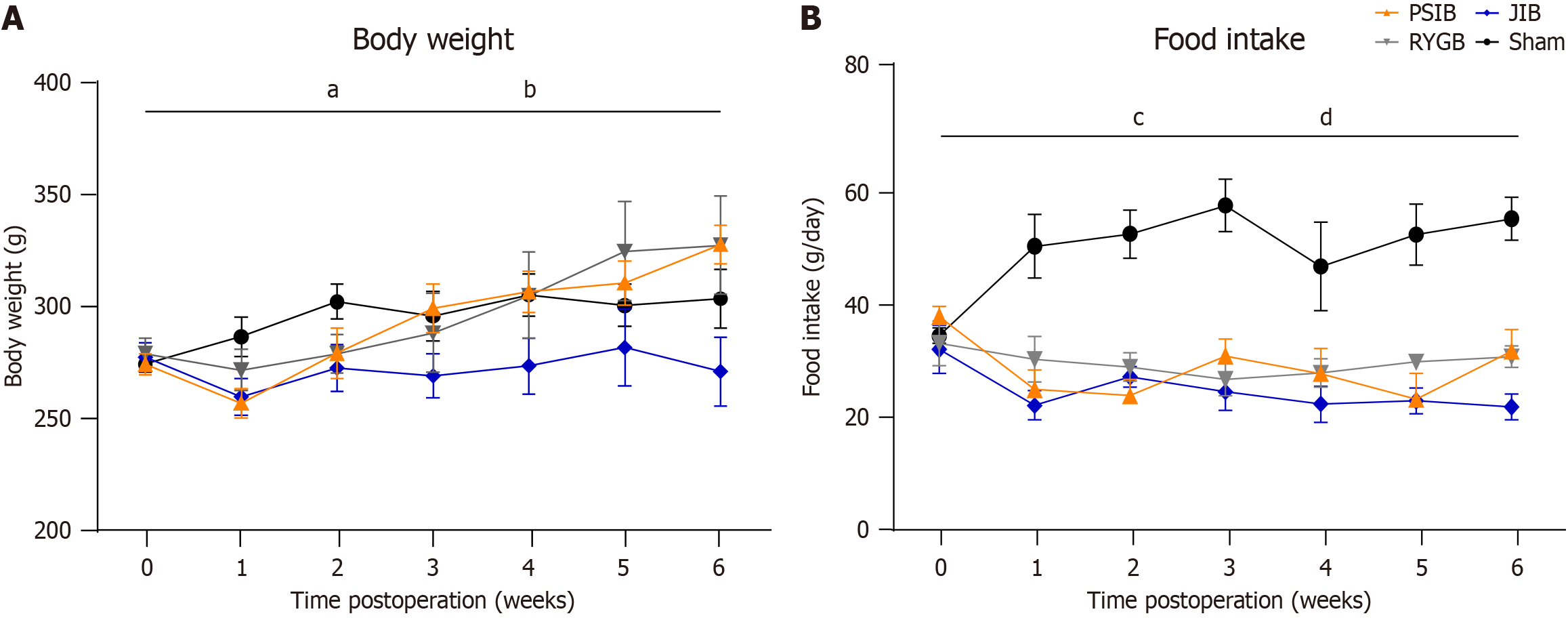
Figure 2 Body weight and food intake.
A: Body weight postoperatively; B: Food intake postoperatively. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.01, jejunoileal bypass vs sham; bP < 0.05, jejunoileal bypass vs Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; cP < 0.01, proximal small intestinal bypass, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, and jejunoileal bypass vs sham; dP < 0.05, jejunoileal bypass vs proximal small intestinal bypass and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. PSIB: Proximal small intestinal bypass; RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; JIB: Jejunoileal bypass.
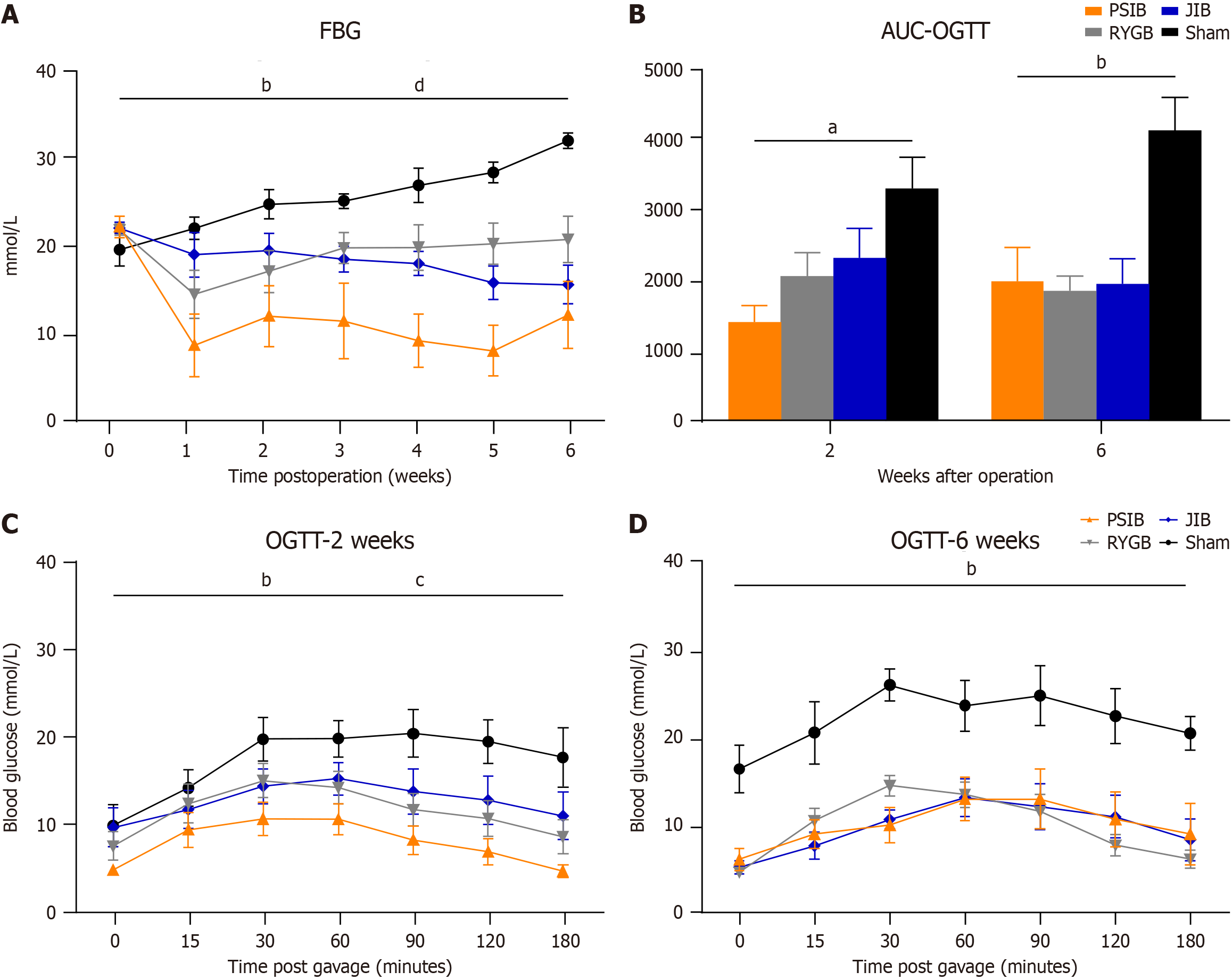
Figure 3 Fasting blood glucose and oral glucose tolerance test.
A: Mean fasting blood glucose levels postoperatively; B: Area under the curve of oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) values; C: OGTT at 2 weeks postoperatively; D: OGTT at 6 weeks postoperatively. Data are presented as means ± SE. aP < 0.05, proximal small intestinal bypass vs sham; bP < 0.01, proximal small intestinal bypass, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, and jejunoileal bypass vs sham; cP < 0.05, proximal small intestinal bypass vs Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and jejunoileal bypass; dP < 0.01, proximal small intestinal bypass vs Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and jejunoileal bypass. FBG: Fasting blood glucose; AUC-OGTT: Area under the oral glucose tolerance test curve; OGTT: Oral glucose tolerance test; PSIB: Proximal small intestinal bypass; RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; JIB: Jejunoileal bypass.
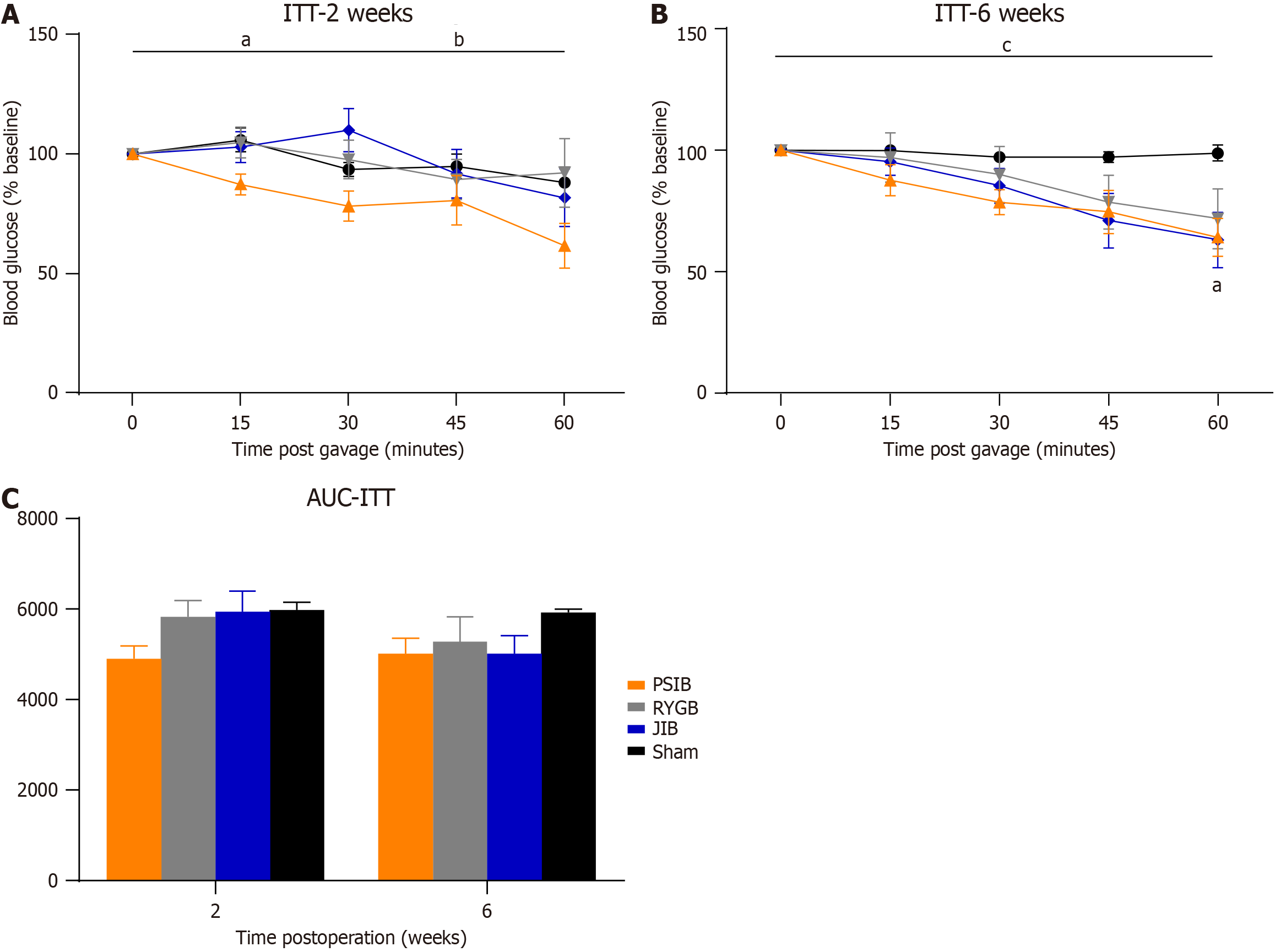
Figure 4 Insulin tolerance test.
A: Insulin tolerance test (ITT) at 2 weeks postoperatively; B: ITT at 6 weeks postoperatively; C: Area under the curve of ITT values. Data are presented as means ± SE. aP < 0.05, proximal small intestinal bypass vs sham; bP < 0.05, proximal small intestinal bypass vs Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and jejunoileal bypass; cP < 0.05, proximal small intestinal bypass and jejunoileal bypass vs sham. ITT: Insulin tolerance test; AUC-ITT: Area under the insulin tolerance test curve; PSIB: Proximal small intestinal bypass; RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; JIB: Jejunoileal bypass.
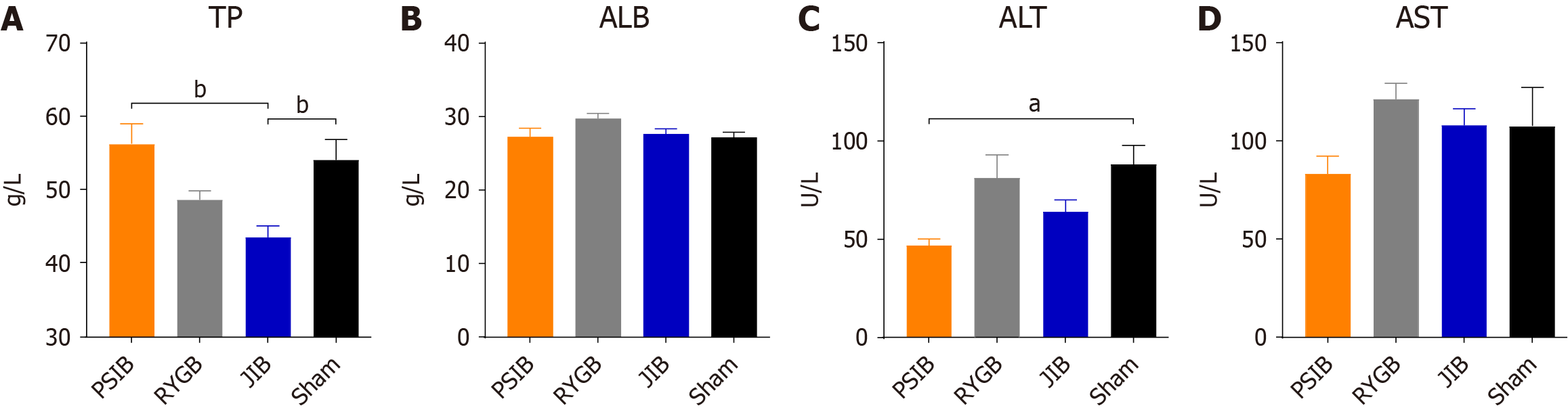
Figure 5 The levels of serum proteins and liver enzymes in each group were assessed at 6 weeks postoperatively.
A: Total protein; B: Albumin; C: Alanine aminotransferase; D: Aspartate aminotransferase. Data are presented as means ± SE. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. TP: Total protein; PSIB: Proximal small intestinal bypass; RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; JIB: Jejunoileal bypass; ALB: Albumin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
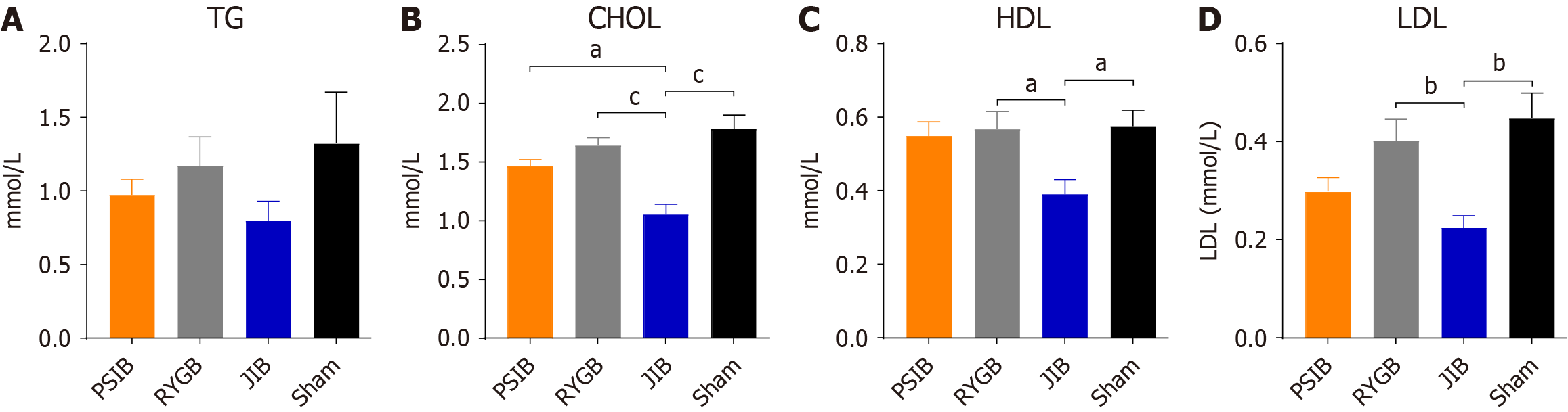
Figure 6 Lipid profiles of all groups at 6 weeks postoperatively.
A: Triglycerides; B: Cholesterol; C: High-density lipoprotein; D: Low-density lipoprotein. Data are presented as means ± SE. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. TG: Triglycerides; PSIB: Proximal small intestinal bypass; RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; JIB: Jejunoileal bypass; CHOL: Cholesterol; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein.
- Citation: Xu CY, Tan C, Luo X, Yang K, Wu RR, Lin L, Liu GL, Duan JY. Proximal small intestinal bypass outperforms Roux-en-Y and jejunoileal bypass in glucose regulation in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(2): 98585
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i2/98585.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.98585