©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2025; 17(12): 114628
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.114628
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.114628
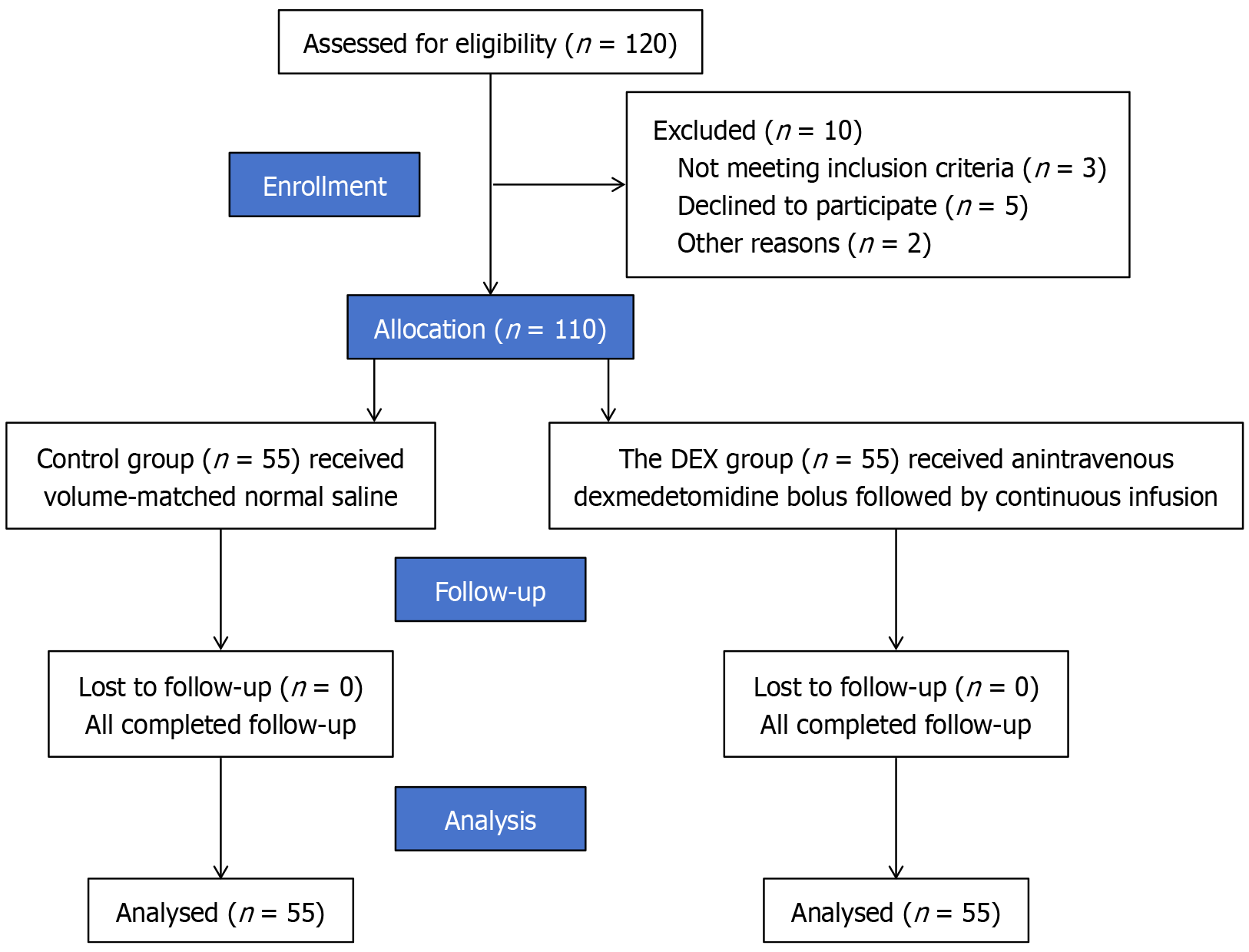
Figure 1 CONSORT flowchart.
DEX: Dexmedetomidine.
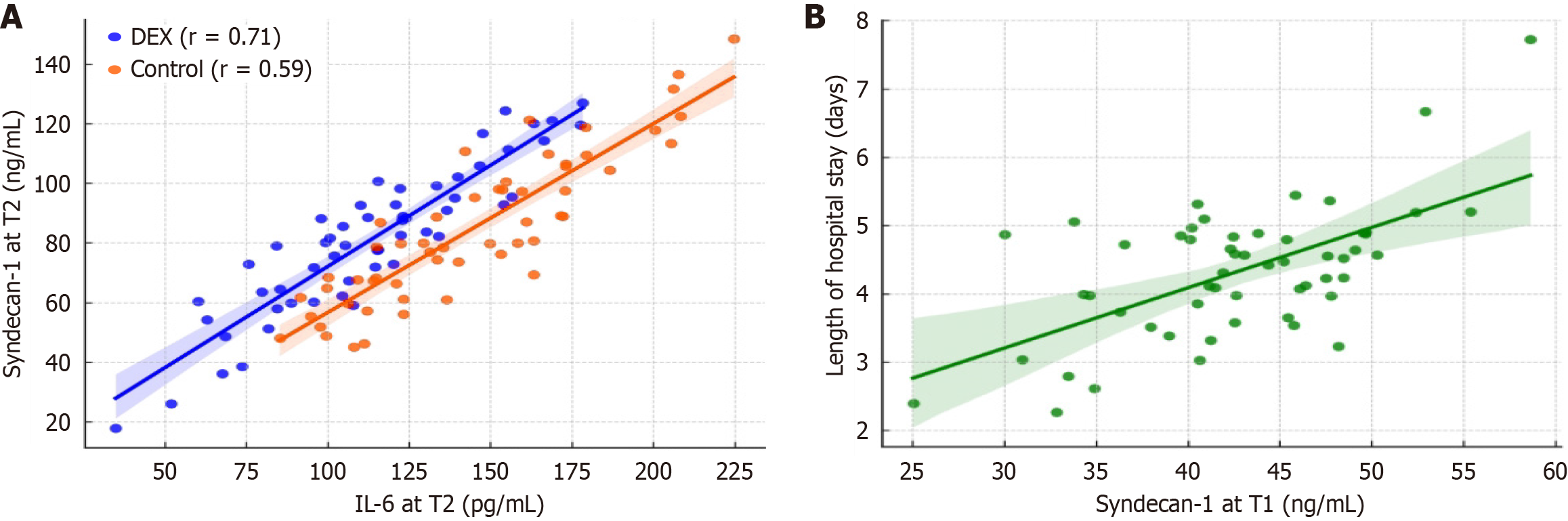
Figure 2 Correlation analyses of syndecan-1.
A: Correlation between syndecan-1 and interleukin-6 levels at T2 (24 hours postoperatively); B: Correlation between syndecan-1 at T1 and length of hospital stay in the dexmedetomidine group. IL-6: Interleukin-6; DEX: Dexmedetomidine.
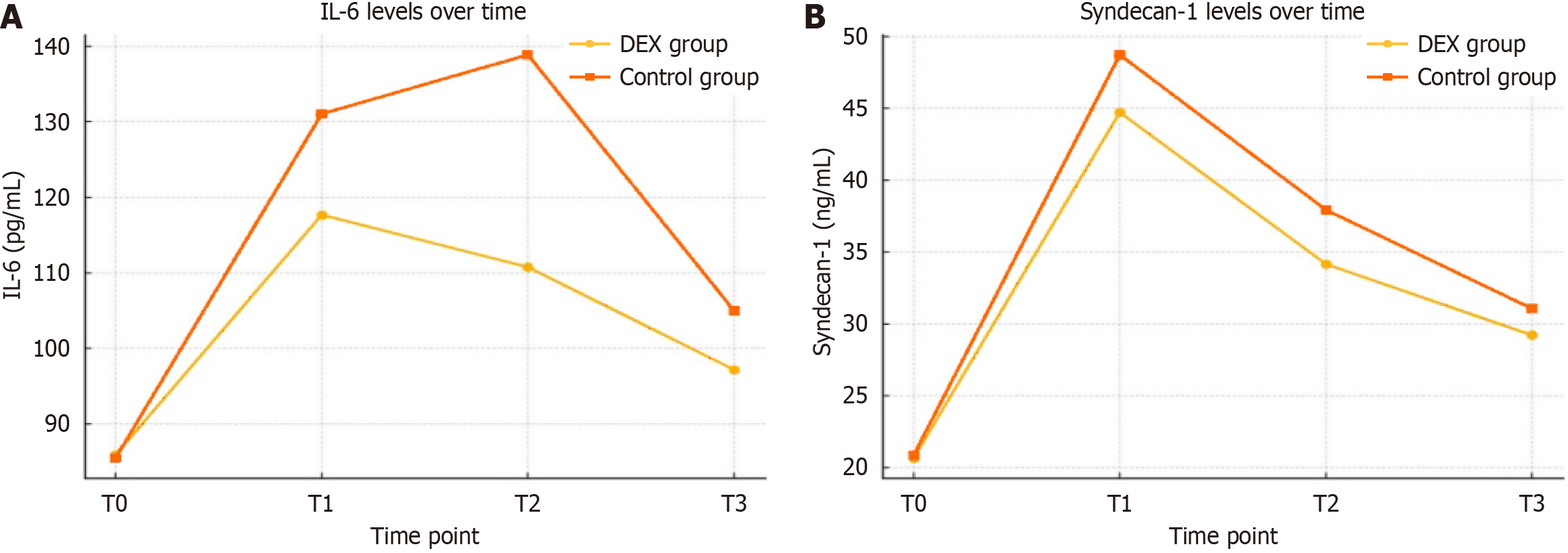
Figure 3 Interleukin-6 and syndecan-1 levels over time.
A: Interleukin-6; B: Syndecan-1. IL-6: Interleukin-6; DEX: Dexmedetomidine.
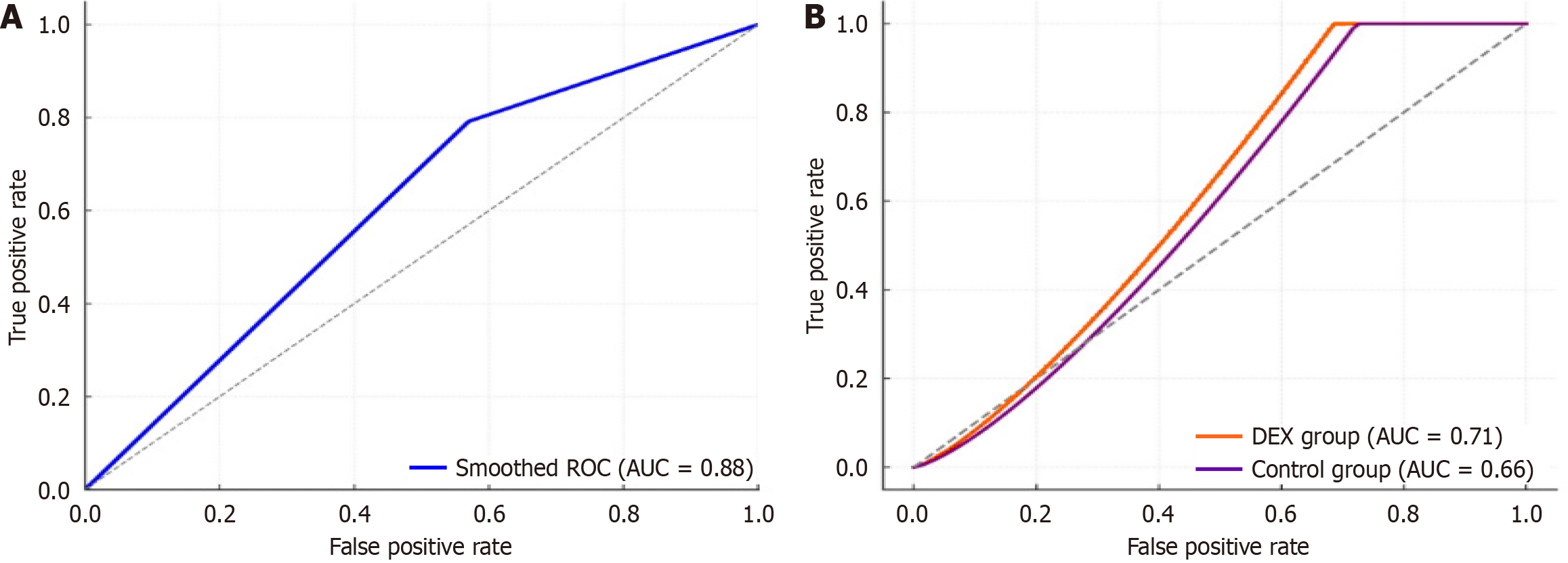
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic curves for syndecan-1 levels at abdominal closure (T1) in predicting postoperative complications.
A: Overall cohort: A threshold of > 45 ng/mL yielded an area under the curve of 0.68 (95%CI: 0.59-0.76), with 79.2% sensitivity and 43.0% specificity; B: Subgroup analyses: In the dexmedetomidine group, the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.71 (95%CI: 0.60-0.82; sensitivity 77.8%, specificity 48.0%), while in the control group the AUC was 0.66 (95%CI: 0.55-0.77; sensitivity 80.0%, specificity 42.9%). AUC: Area under the curve; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic curve; DEX: Dexmedetomidine.
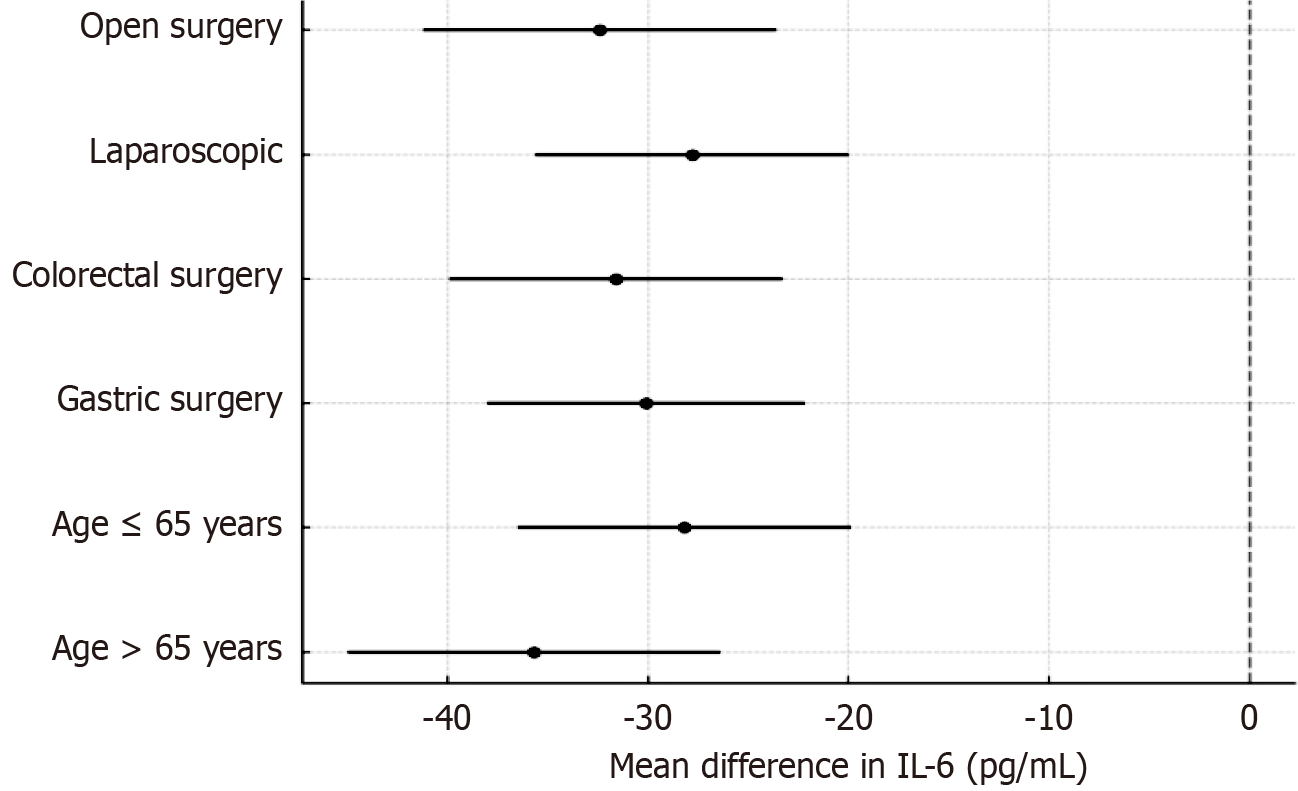
Figure 5 Subgroup analysis: Interleukin-6 reduction at T2 (dexmedetomidine vs control).
IL-6: Interleukin-6.
- Citation: Zeng R, Tang CL, Zhao Y, Wang RX, Fang Y, Hu XW. Dexmedetomidine enhances recovery after gastrointestinal cancer surgery by protecting the endothelial glycocalyx: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(12): 114628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i12/114628.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i12.114628