Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2025; 17(1): 100130
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.100130
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.100130
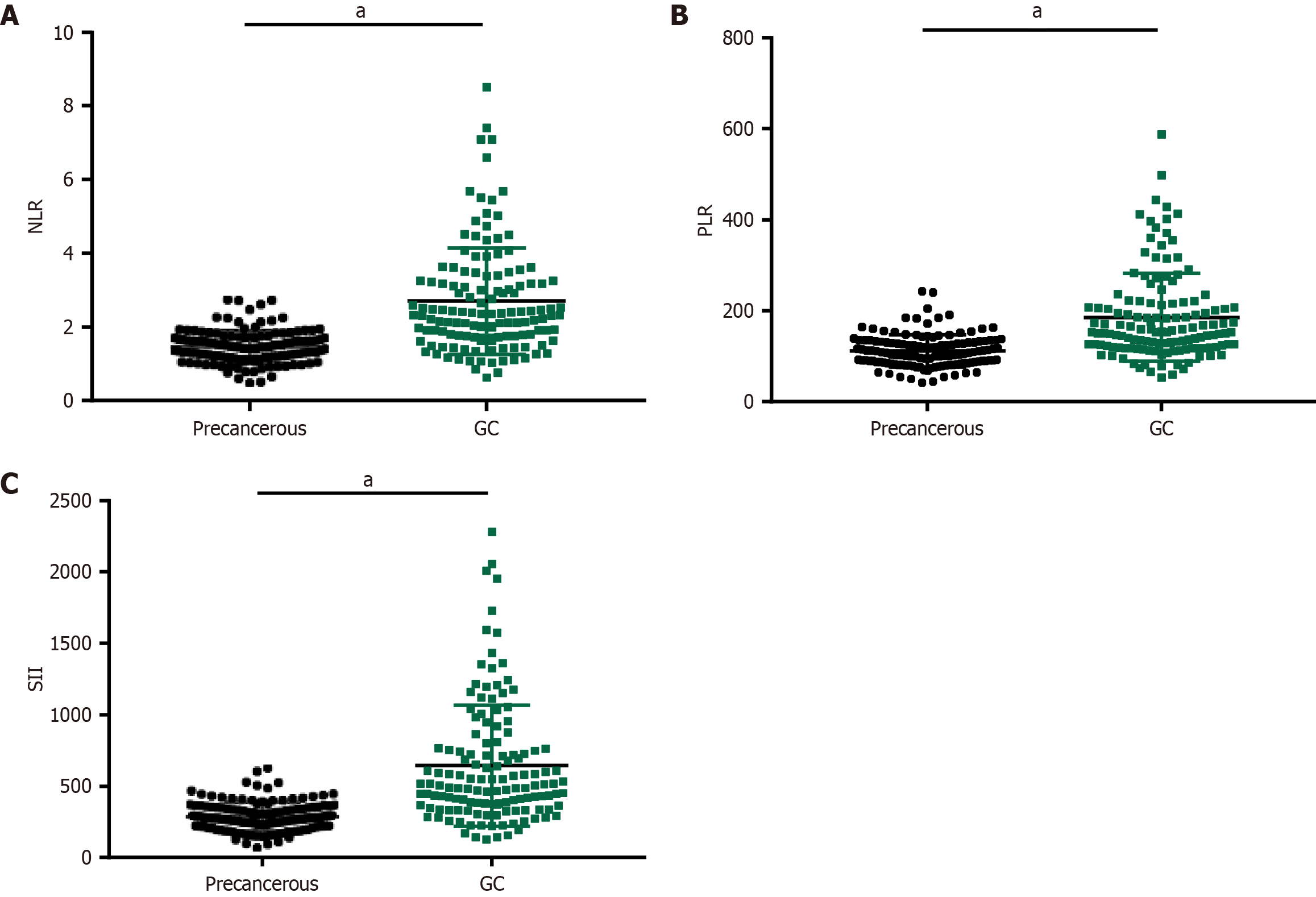
Figure 1 Levels of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and systemic immune-inflammatory index in the gastric carcinoma and precancerous gastric condition groups.
A: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio levels in the two groups; B: Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio levels in the two groups; C: Systemic immune-inflammatory index levels in the two groups. aP < 0.001 in the inter-group comparison. GC: Gastric carcinoma; NLR: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; PLR: Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; SII: Systemic immune-inflammatory index.
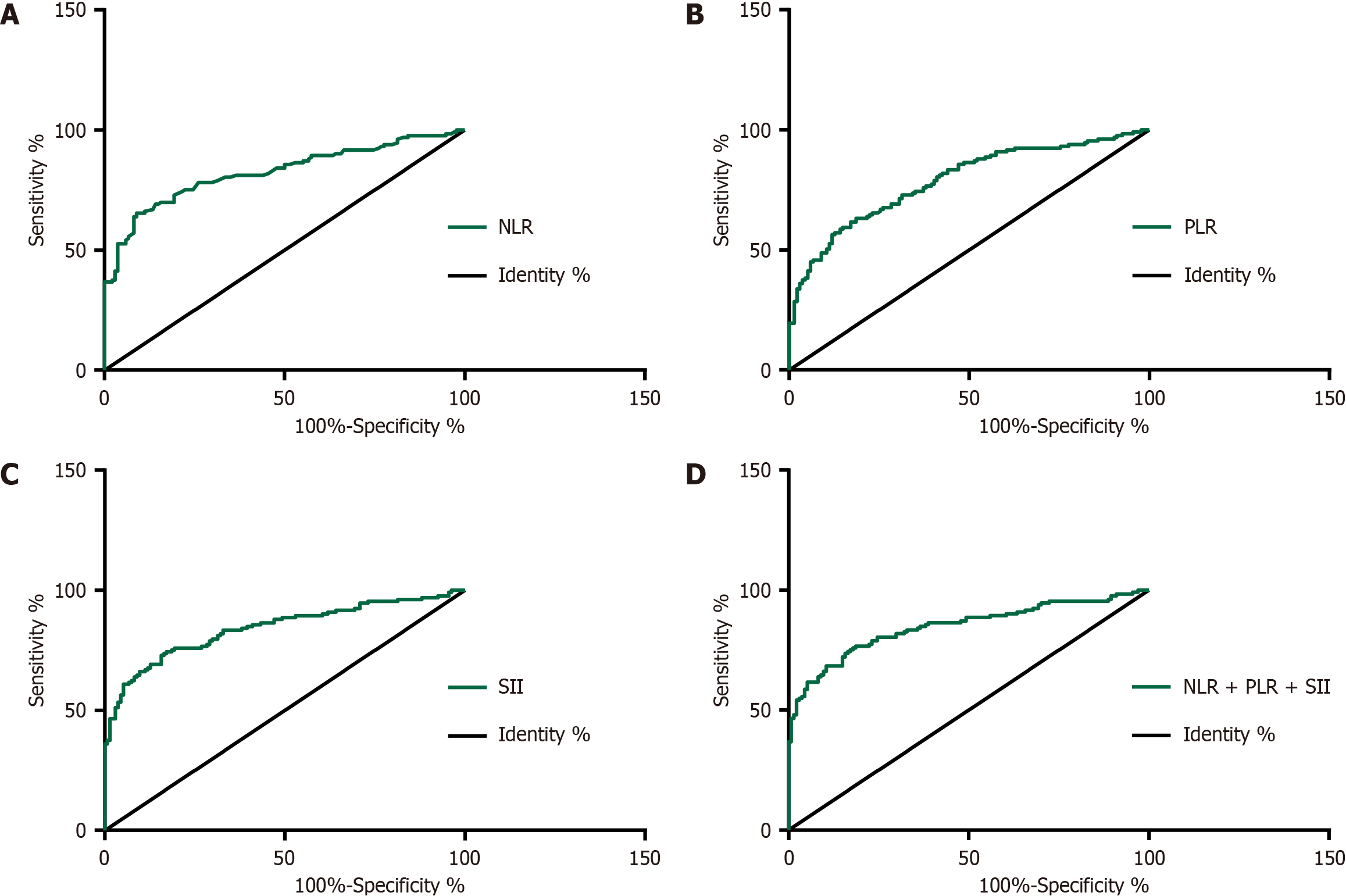
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of the diagnostic implications of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and systemic immune-inflammatory index for gastric carcinoma.
A: The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in the diagnosis of gastric carcinoma (GC); B: The ROC curve of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in the diagnosis of GC; C: The ROC curve of systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) in the diagnosis of GC; D: The ROC curve of NLR + PLR + SII in the diagnosis of GC. NLR: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; PLR: Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; SII: Systemic immune-inflammatory index.
- Citation: Wu HM, Ying XX, Lv LL, Hu JW. Diagnostic implications of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and systemic immune-inflammatory index for gastric carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(1): 100130
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i1/100130.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.100130