Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2024; 16(7): 2054-2064
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i7.2054
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i7.2054
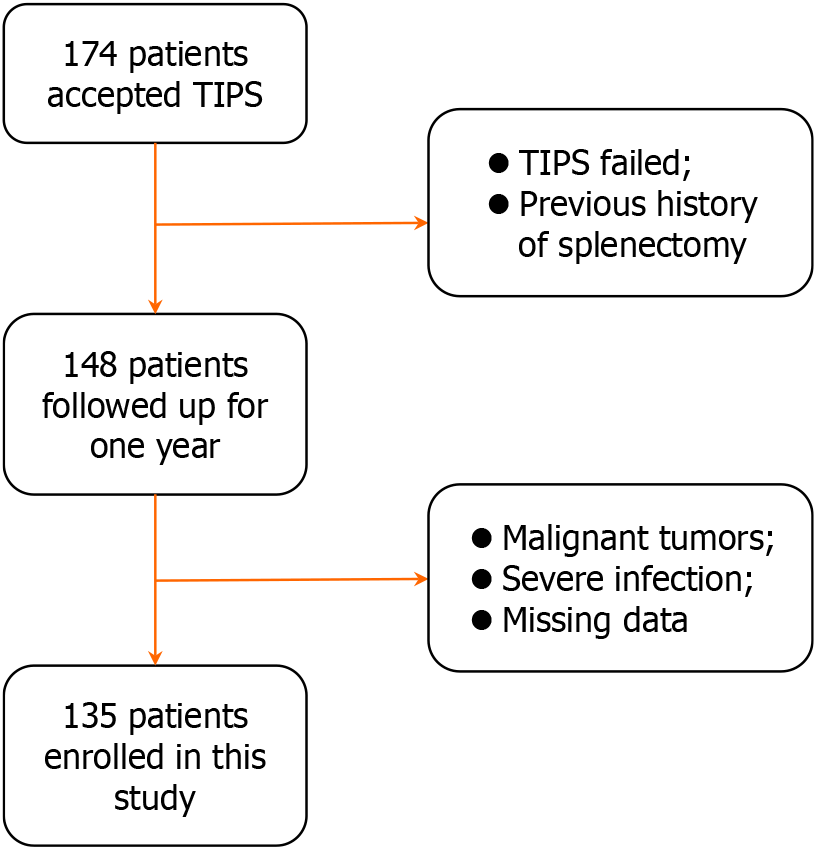
Figure 1 Flow diagram of patient inclusion.
TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
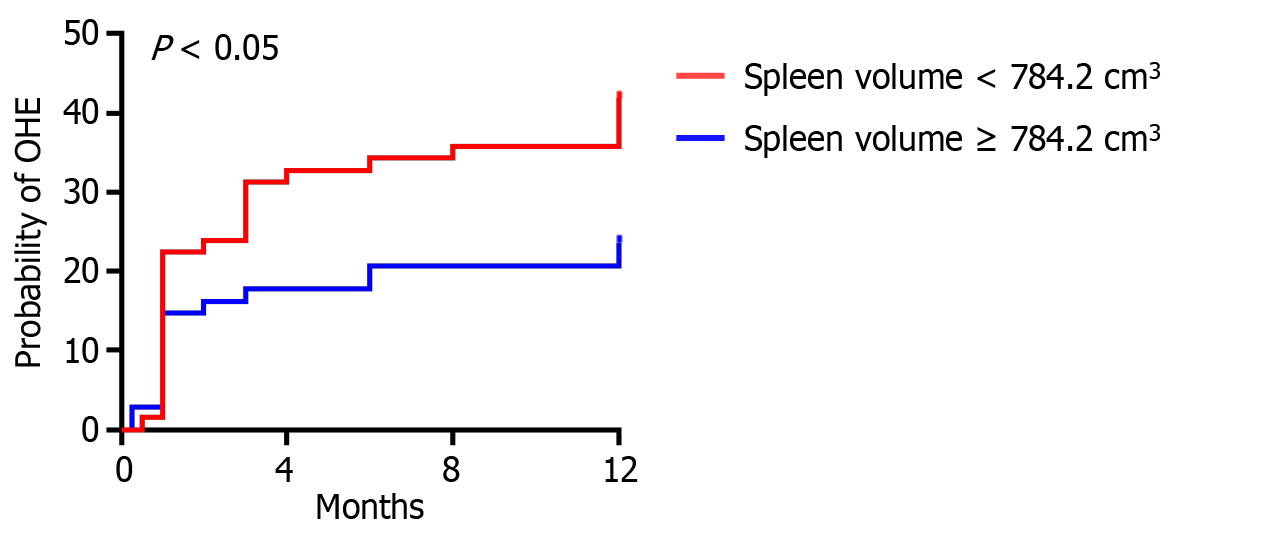
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier curves for cumulative incidence of overt hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt stratified by spleen volume.
The patients was divided into two groups based on the median splenic volume (784.2 cm3). Log-rank test was used to compare the cumulative incidence of overt hepatic encephalopathy between the two groups. OHE: Overt hepatic encephalopathy.
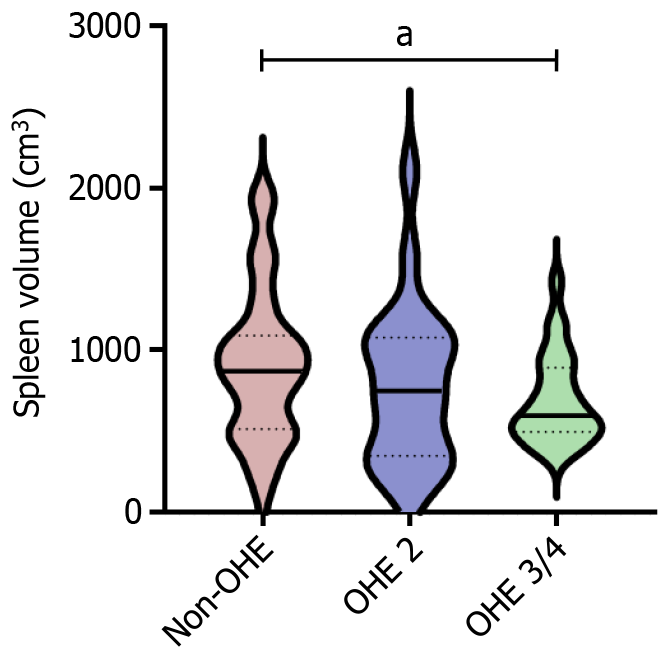
Figure 3 Comparison of spleen volumes among patients with different overt hepatic encephalopathy grades.
The patients were divided in three groups based on overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) grade: Non-OHE (n = 99), OHE 2 (n = 18), and OHE 3/4 (n = 19). Quantitative data are presented as median (interquartile range). Mann-Whitney U test, aP < 0.05. OHE: Overt hepatic encephalopathy.
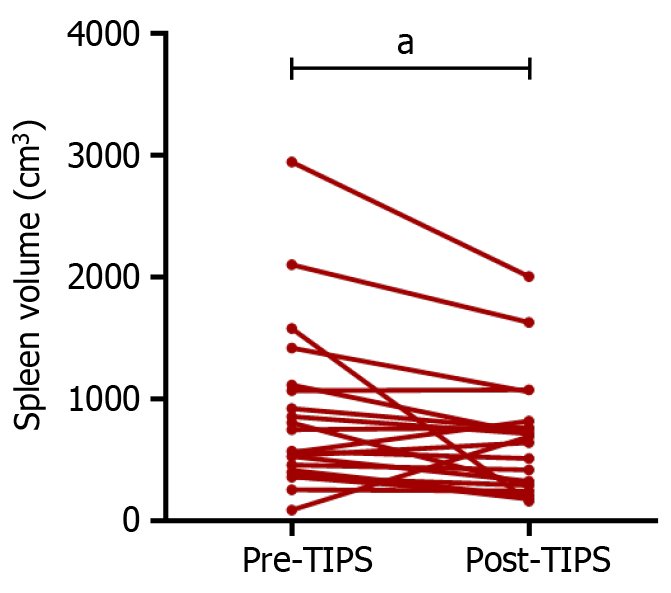
Figure 4 Comparison of spleen volumes pre- and post-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
Paired t-test, aP < 0.05. TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
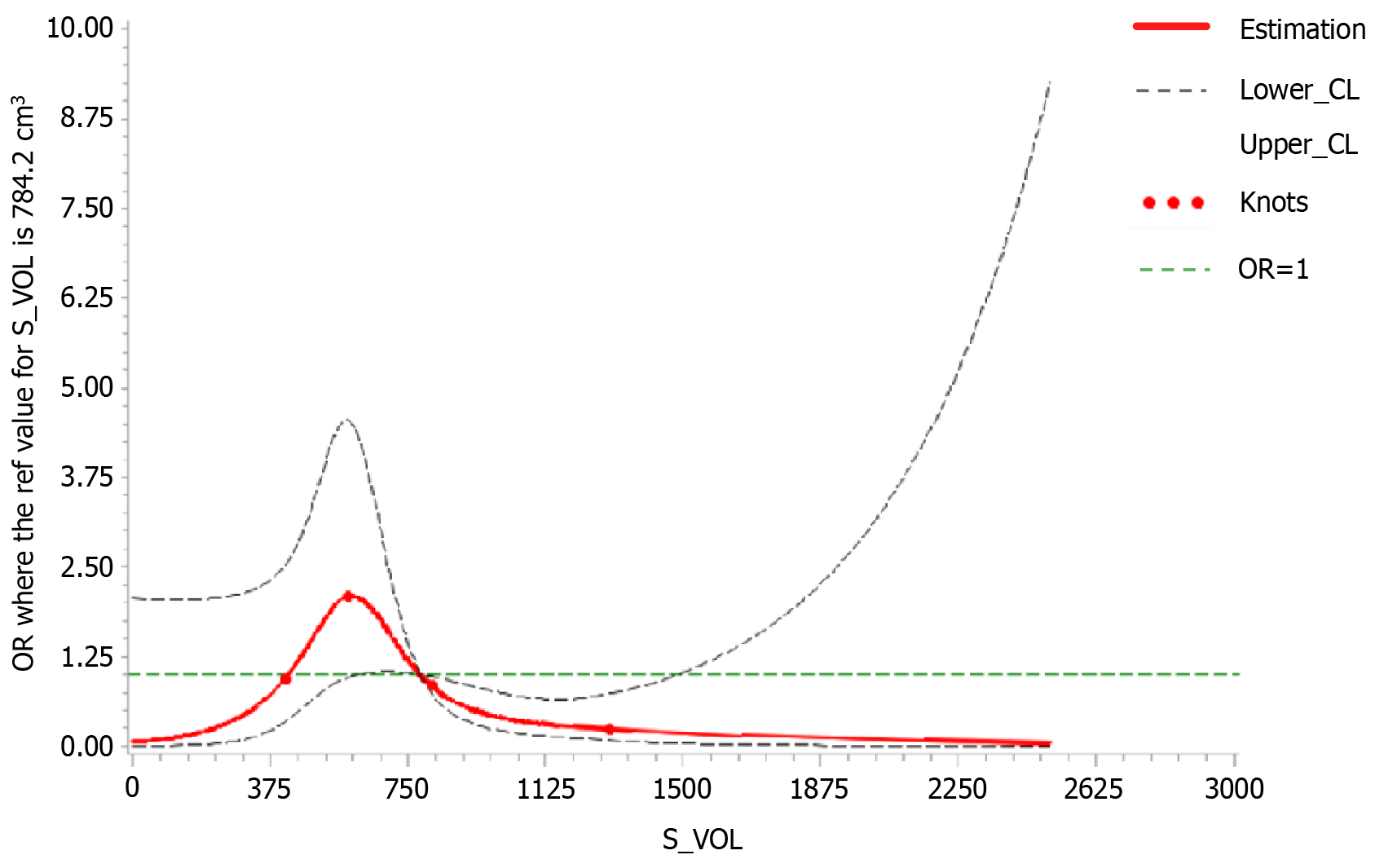
Figure 5 Correlation between spleen volume and post-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt overt hepatic encephalopathy.
A restricted cubic spline model was used to evaluate the dose-response relationship. S_VOL: Spleen volume.
- Citation: Zhao CJ, Ren C, Yuan Z, Bai GH, Li JY, Gao L, Li JH, Duan ZQ, Feng DP, Zhang H. Spleen volume is associated with overt hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with portal hypertension. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(7): 2054-2064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i7/2054.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i7.2054