©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2024; 16(6): 1681-1690
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1681
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1681
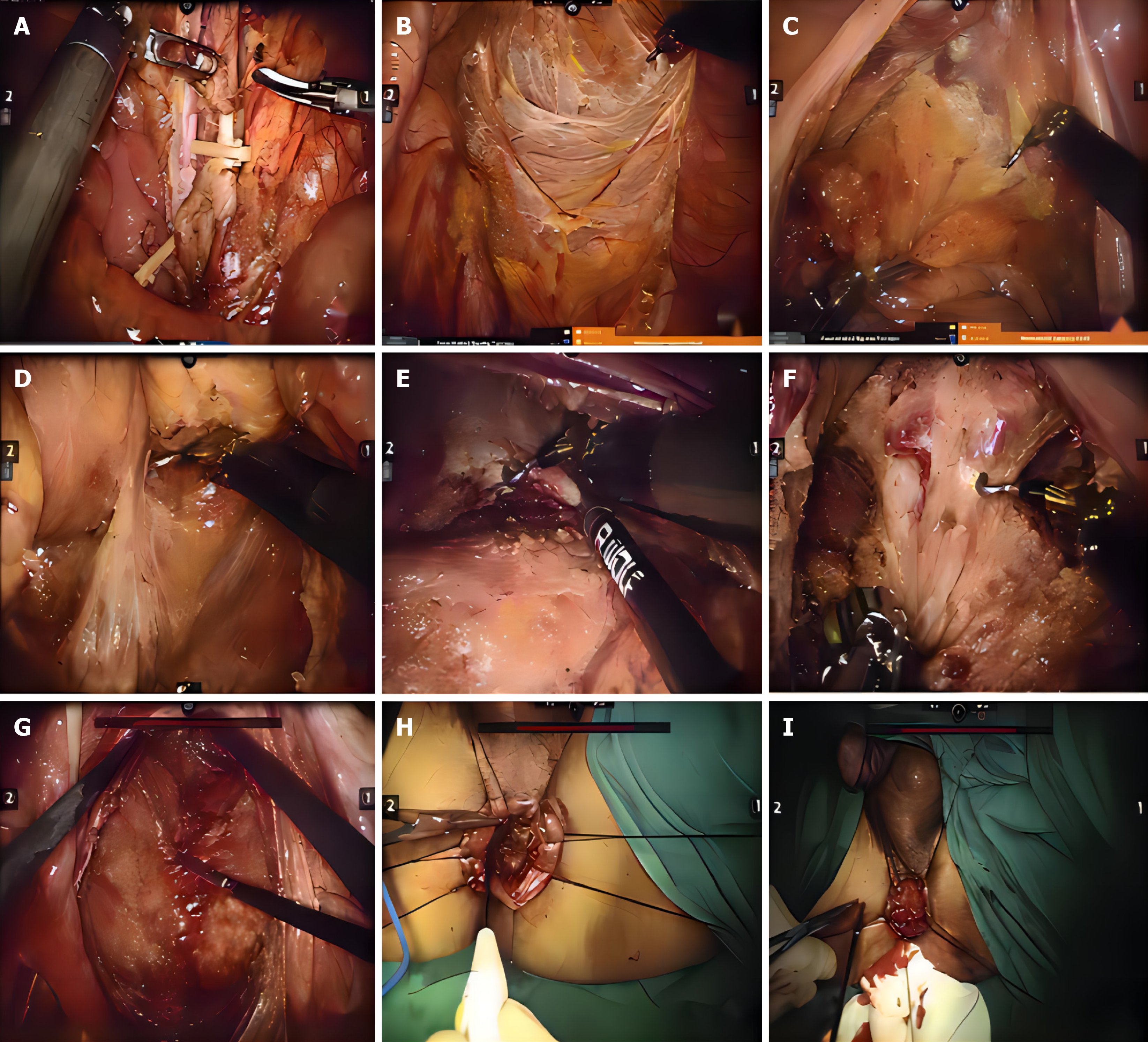
Figure 1 The surgical procedure for the Da Vinci robot diagram.
A: The left colic artery was preserved, and the lymph nodes in group 253 were dissected; B: Free retrorectal space; C: Free anterior rectal space; D: Hiatal ligament; E: The puborectal muscle was redrawn to free the sphincter space through the abdominal path; F: Anterior wall venous plexus; G: Complete abdominal path intersphincter separation; H: Free the sphincter space via the anal route; I: Colo-anal end-to-end anastomosis.
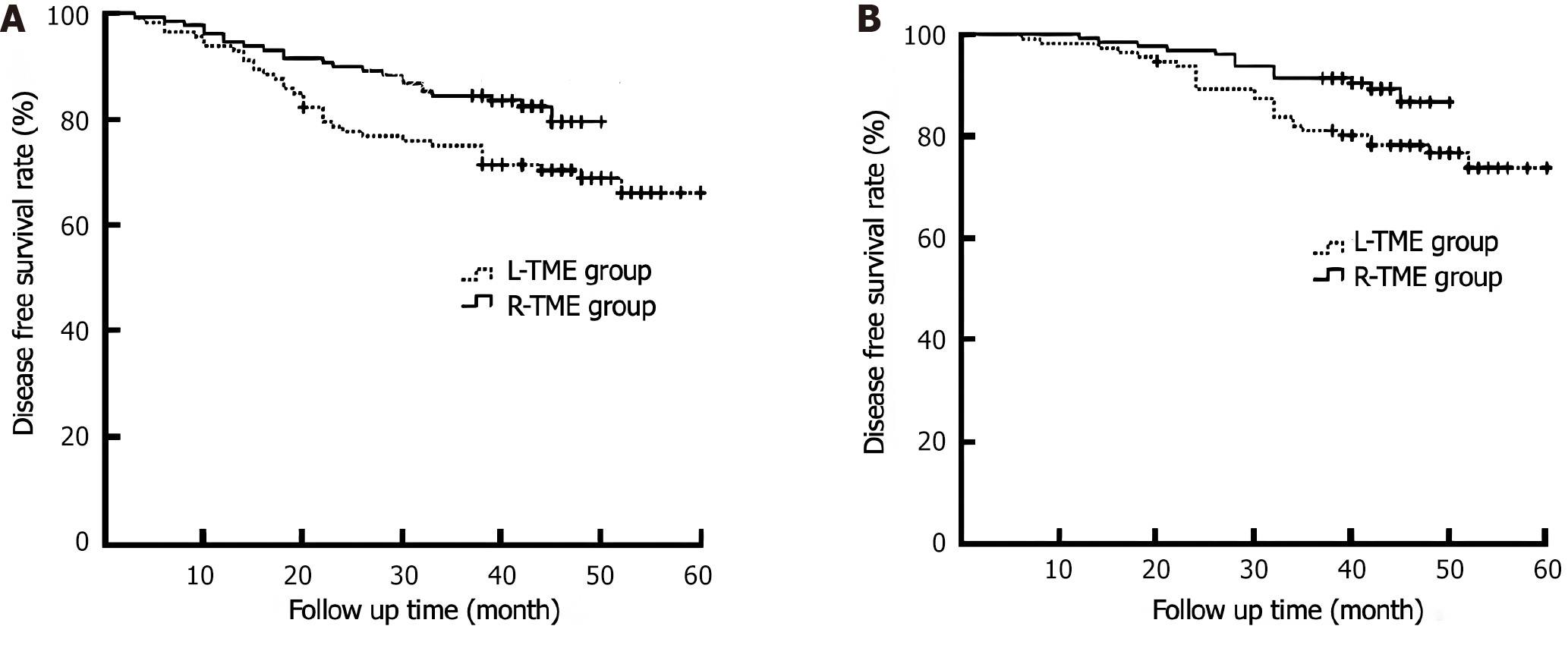
Figure 2 Comparison of the 3-year disease-free survival rate and overall survival rate between laparoscopic mesangectomy and robotic mesangectomy.
A: 3-year disease-free survival rate; B: 3-year overall survival rate. L-TME: Laparoscopic total mesorectal resection; R-TME: Robotic total mesorectal resection.
- Citation: Gao WG, Shi W, Gong XC, Li ZW, Tuoheti Y. Comparative analysis of the short and medium-term efficacy of the Da Vinci robot versus laparoscopic total mesangectomy for rectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(6): 1681-1690
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i6/1681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1681