©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. May 27, 2024; 16(5): 1443-1448
Published online May 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i5.1443
Published online May 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i5.1443
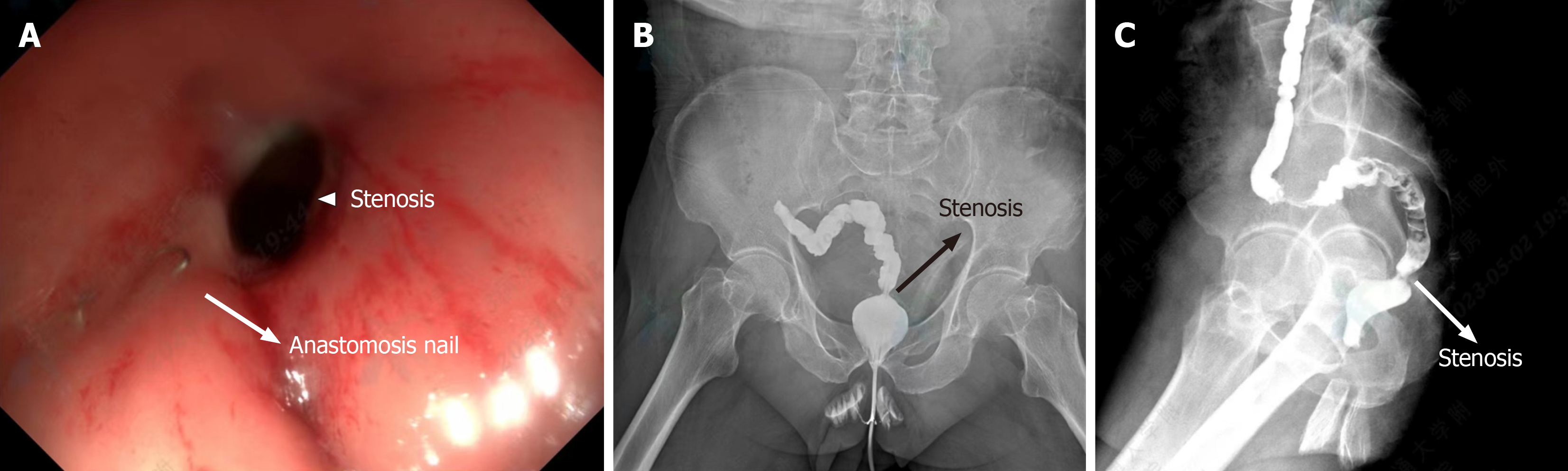
Figure 1 Preoperative examination.
A: Colonoscopy; B and C: Colonography.
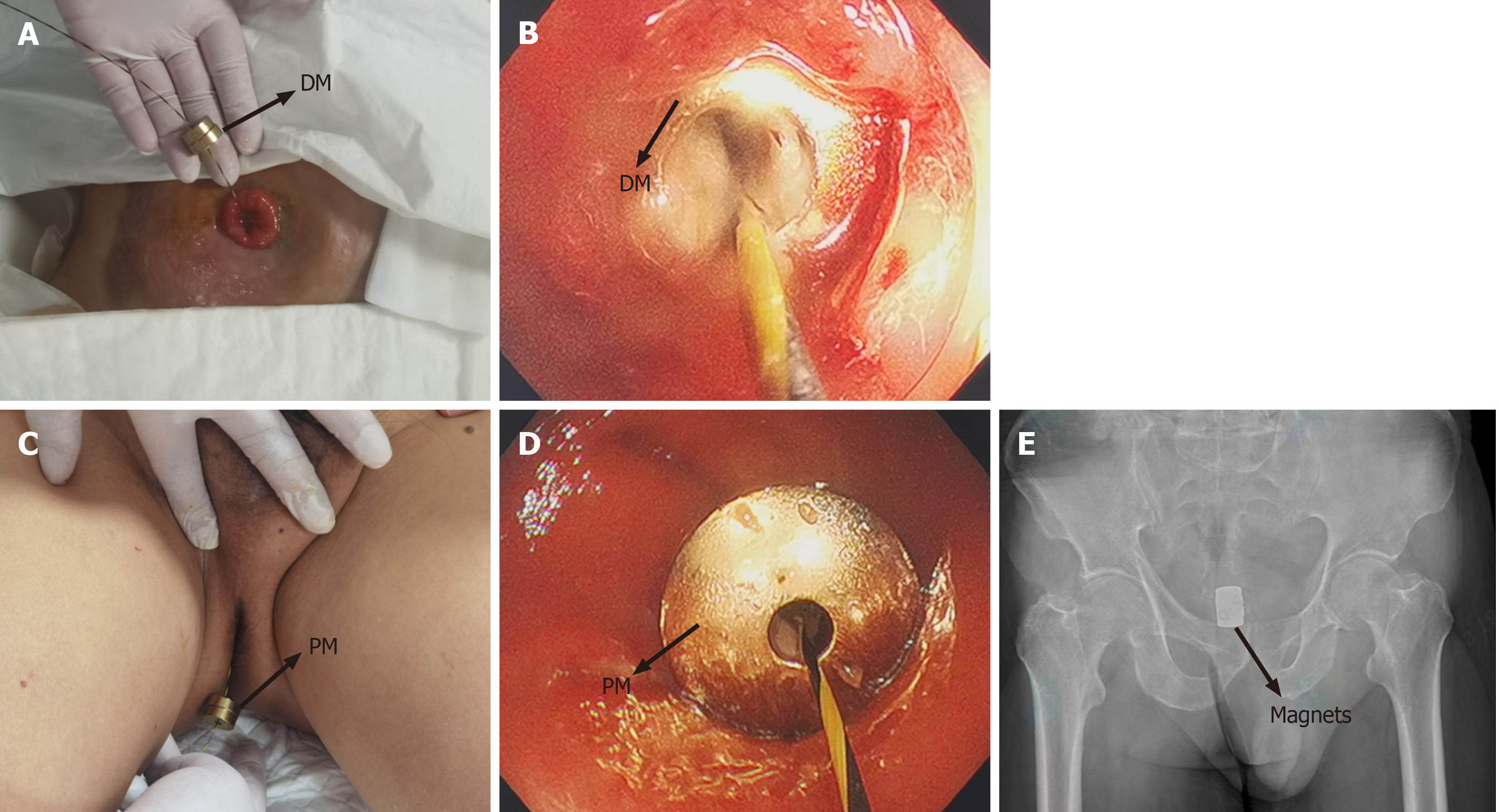
Figure 2 Magnet placement process.
A: The daughter magnet (DM) was inserted along the zebra guide wire via ileostomy; B: Colonoscopy pushed the DM to the proximal end of the rectum stenosis; C: The parent magnet (PM) was inserted through the anus along the zebra wire; D: The PM reached the distal end of the rectum stenosis; E: The X-ray indicates the apposition of the daughter magnet and the PM. DM: Daughter magnet; PM: Parent magnet.
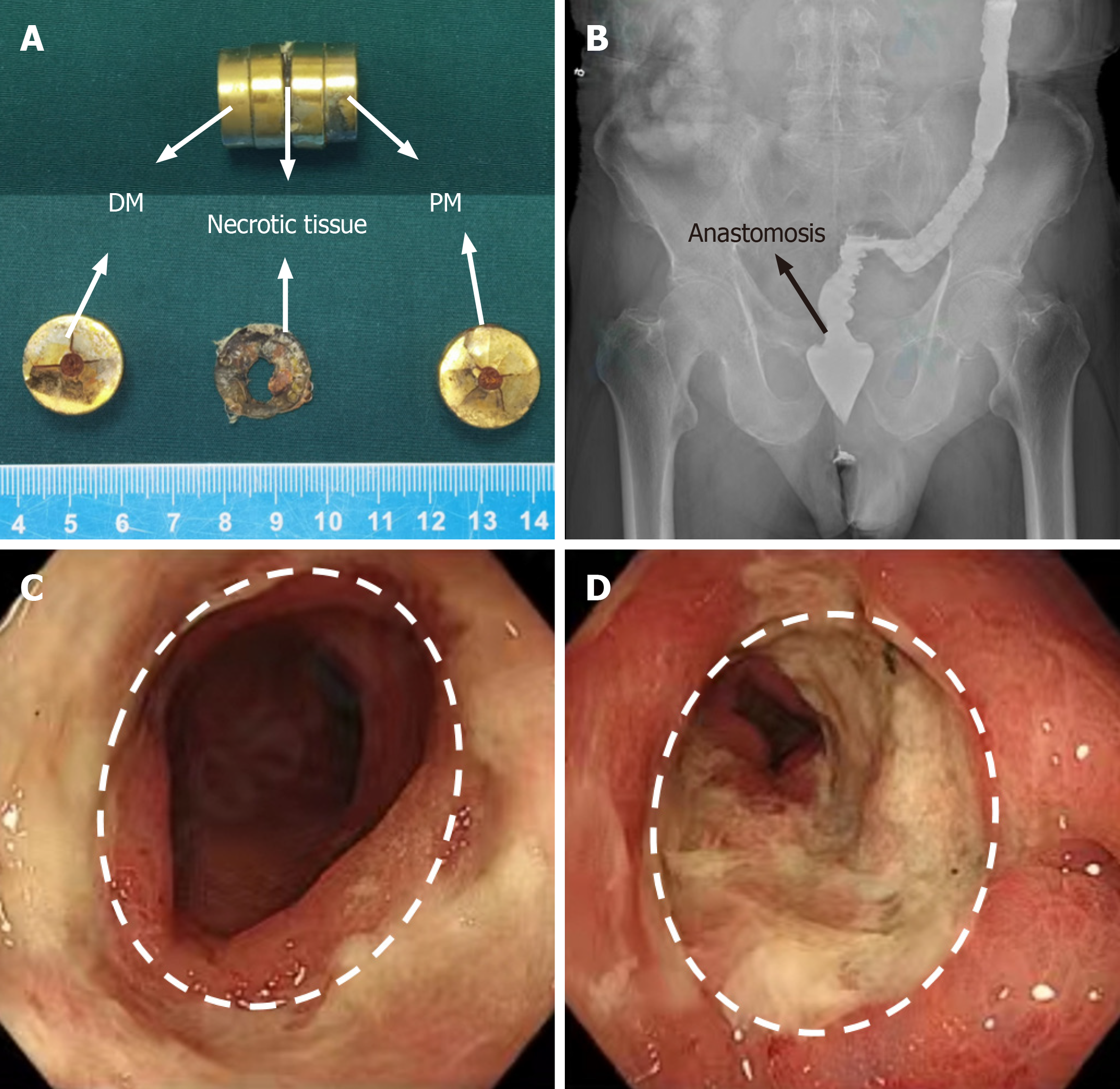
Figure 3 Postoperative examination.
A: The daughter and parent magnets were discharged on the 11th d after surgery; B: X-ray shows good rectal patency; C and D: Colonoscopic images showing good patency at the site of anastomosis. DM: Daughter magnet; PM: Parent magnet.
- Citation: Zhang MM, Sha HC, Xue HR, Qin YF, Dong FF, Zhang L, Lyu Y, Yan XP. Treatment of anastomotic stricture after rectal cancer operation by magnetic compression technique: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(5): 1443-1448
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i5/1443.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i5.1443