©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. May 27, 2024; 16(5): 1407-1419
Published online May 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i5.1407
Published online May 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i5.1407
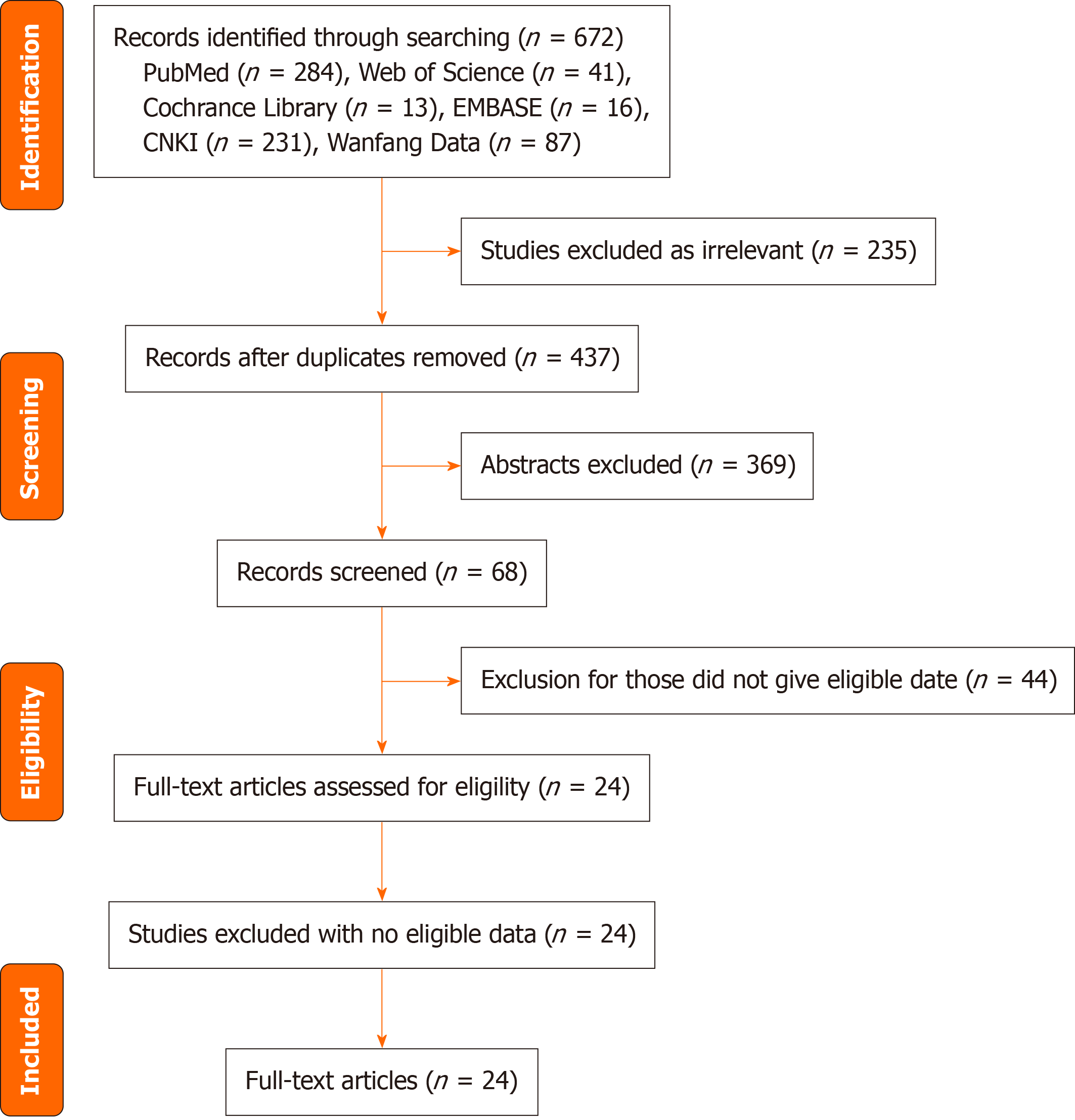
Figure 1 Flow diagram depicting the screening and inclusion process of the studies.
CNKI: China National Knowledge Infrastructure.
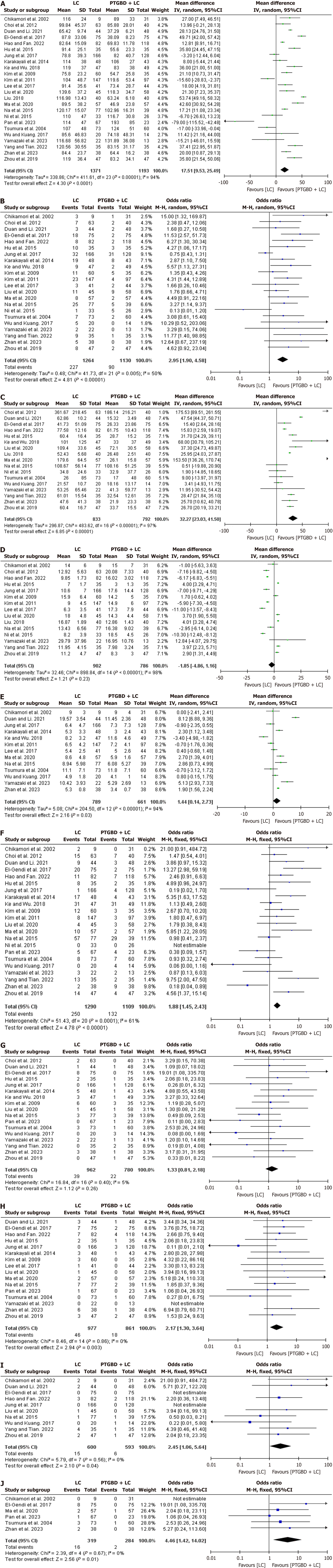
Figure 2 Forest plot depicting comparison between the percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder puncture drainage + laparoscopic cholecystectomy group and the laparoscopic cholecystectomy group.
A: Forest plot depicting the operation time comparison between the percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder puncture drainage (PTGBD) + laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) group and the LC group; B: Forest plot illustrating the comparison of the conversion rate to open surgery between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group; C: Forest plot illustrating the comparison of intraoperative bleeding between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group; D: Forest plot depicting the comparison of overall hospital stay between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group; E: Forest plot depicting the comparison of postoperative hospital stay between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group; F: Forest plot illustrating the comparison of postoperative complications between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group; G: Forest plot illustrating the comparison of bile leakage rates between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group; H: Forest plot depicting the comparison of wound infection rates between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group; I: Forest plot depicting intraperitoneal hemorrhage in the PTGBD + LC group compared to the LC group; J: Forest plot comparing bile duct injury incidence between the PTGBD + LC group and the LC group. PTGBD: Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder puncture drainage; LC: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
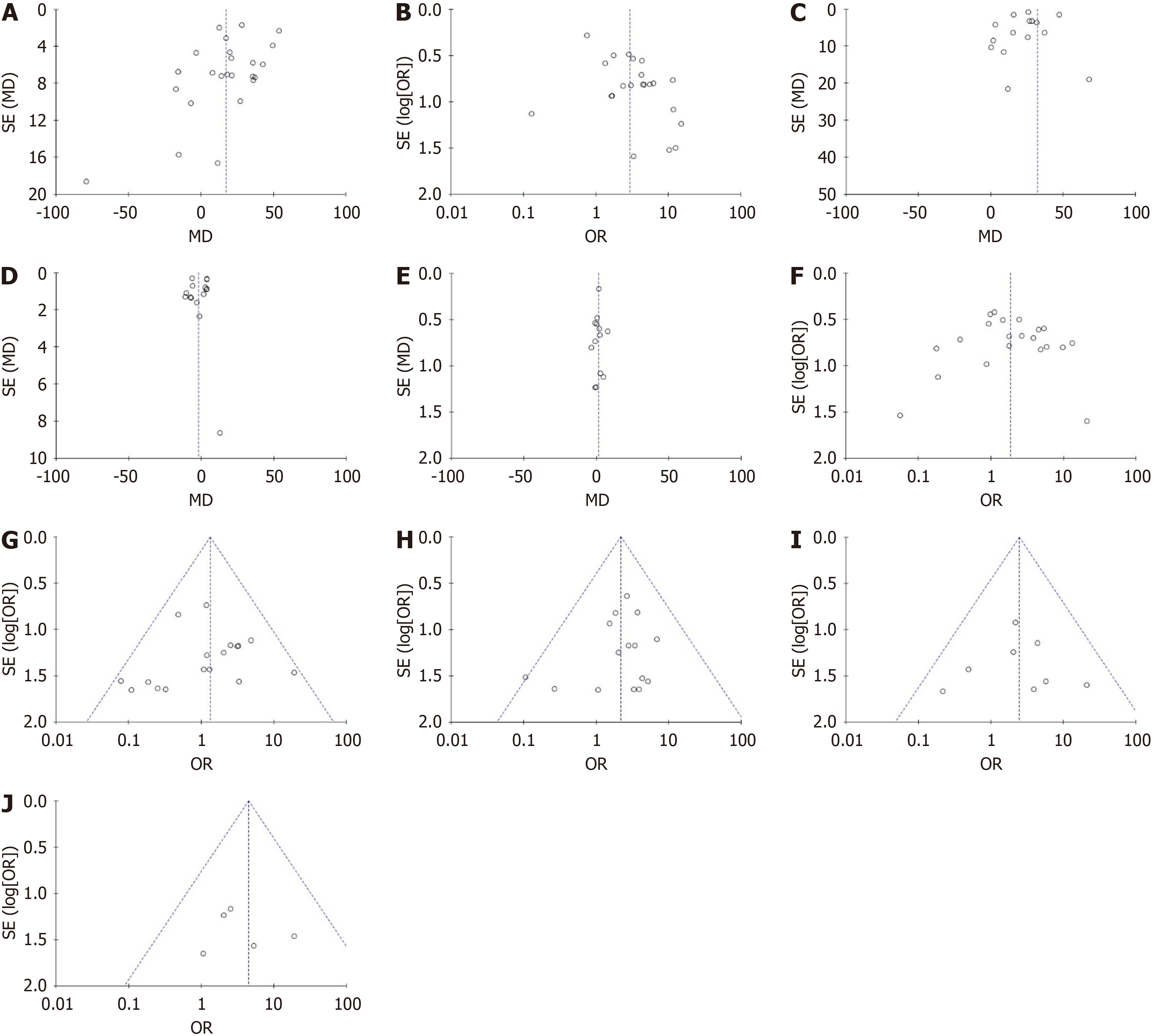
Figure 3 Funnel plots of each outcome.
A: Operative time; B: Conversion rate to open surgery; C: Intraoperative bleeding; D: Overall hospital stay; E: Postoperative hospital stay; F: Postoperative complications; G: Bile leakage; H: Wound infection; I: Intraperitoneal hemorrhage; J: Bile duct injury. MD: Mean difference; OR: Odds ratio.
- Citation: Li Y, Xiao WK, Li XJ, Dong HY. Evaluating effectiveness and safety of combined percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage and laparoscopic cholecystectomy in acute cholecystitis patients: Meta-analysis. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(5): 1407-1419
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i5/1407.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i5.1407