©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Feb 27, 2024; 16(2): 616-621
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.616
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.616
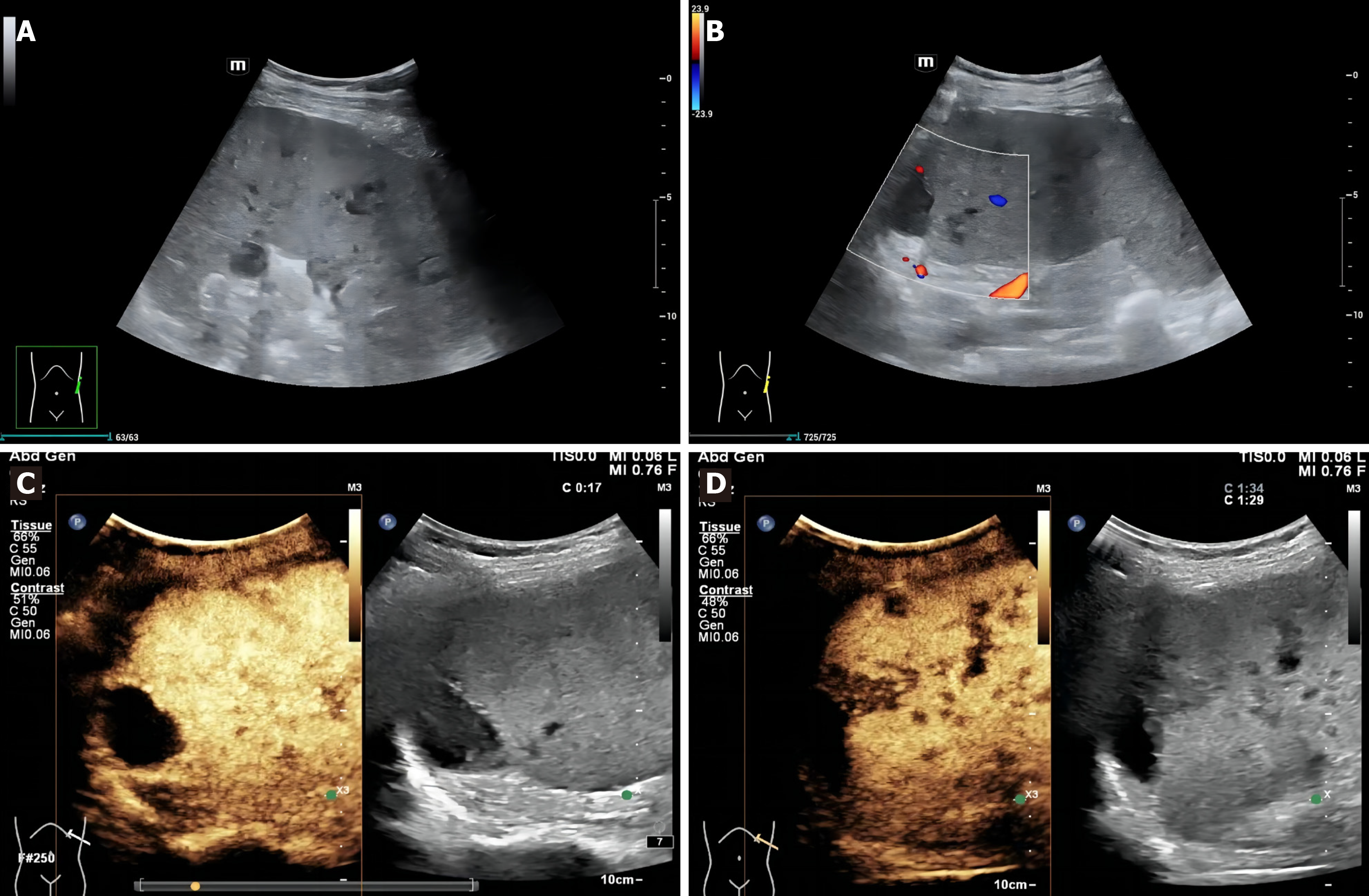
Figure 1 Ultrasonography images of the patient.
A: Conventional grayscale ultrasound (US) showed multiple hypoechoic nodules and masses in the spleen; B: There were no blood flow signals in the splenic lesions on Color Doppler US; C: Arterial phase imaging on contrast-enhanced US; D: Venous phase imaging on contrast-enhanced US.
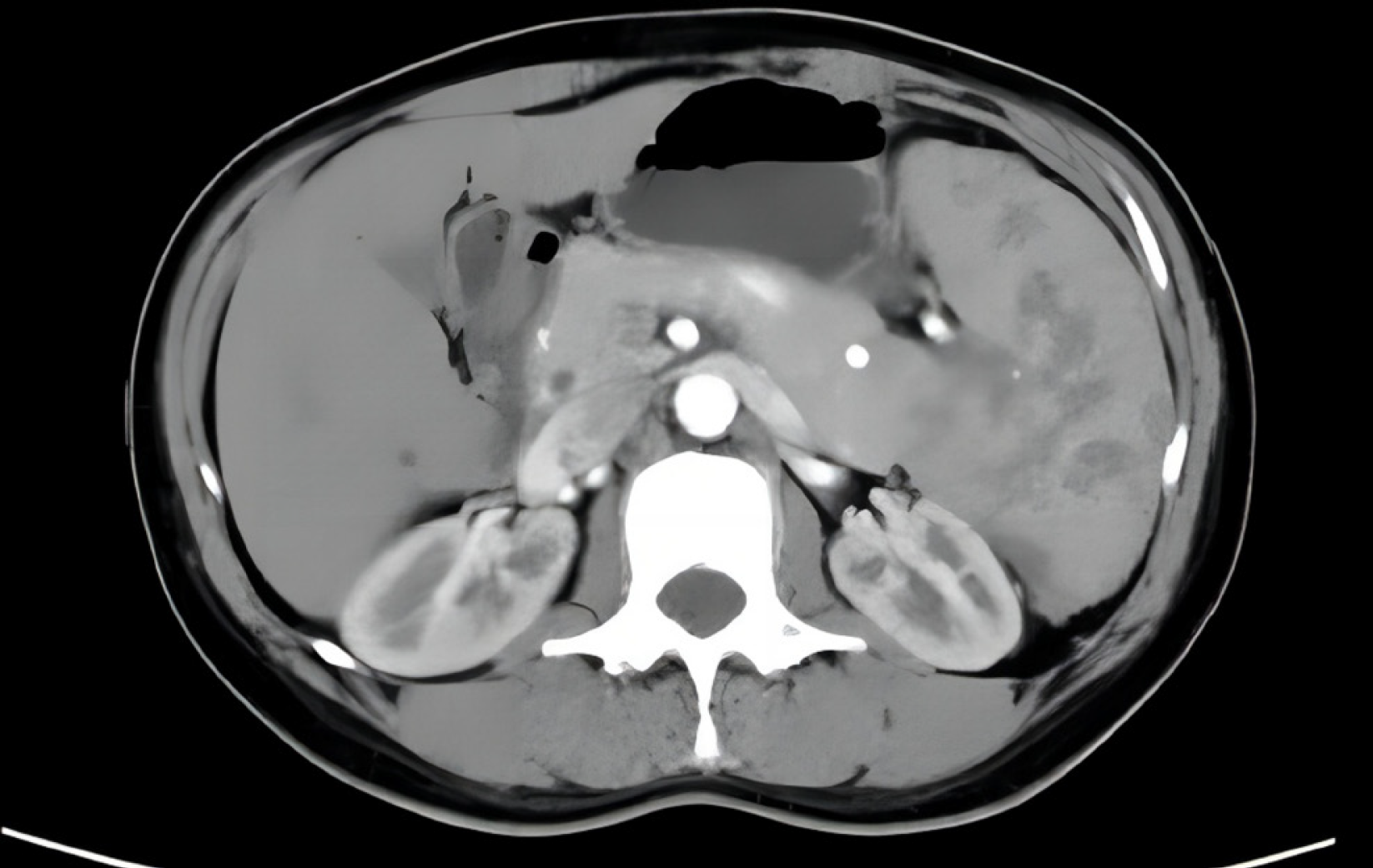
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of the patient.
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography revealed an enlarged spleen, with multiple irregular nodular and patchy low density shadows, the largest measuring approximately 1.7 cm × 1.7 cm.
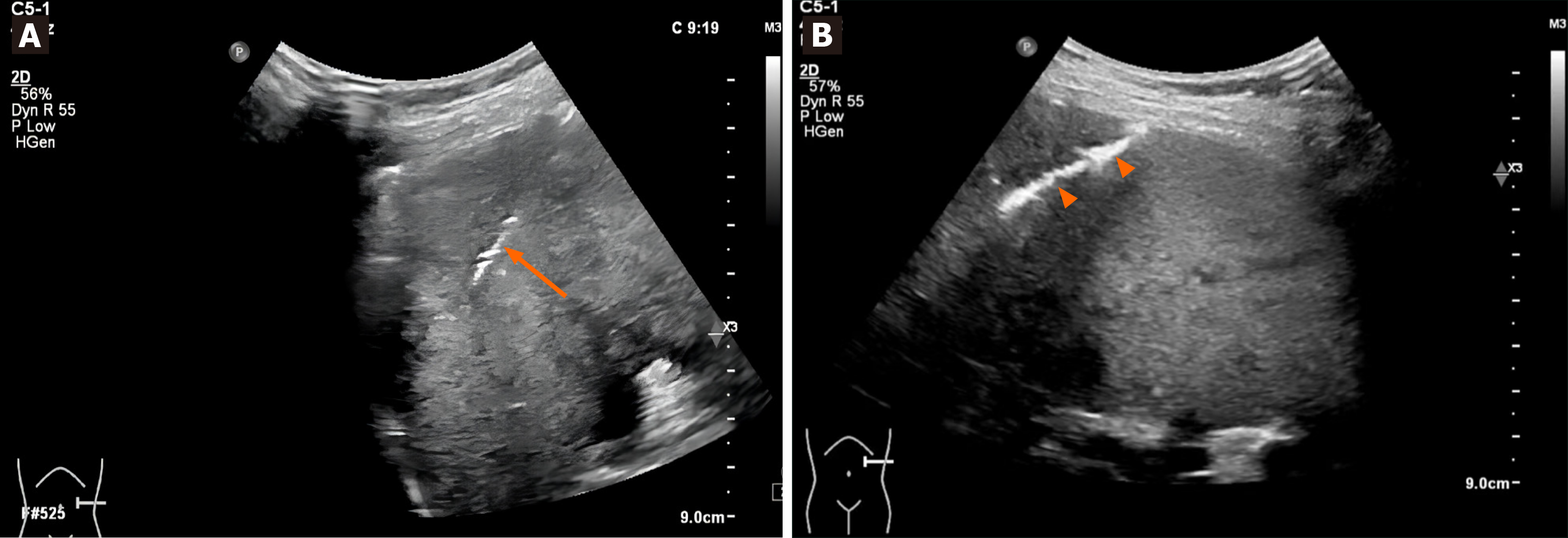
Figure 3 Images of the puncture procedure.
A: A 18G coaxial needle (arrow) was applied under real-time ultrasound guidance; B: A muddy mixture(arrowheads) of gelfoam and saline was injected into the coaxial needle sheath to prevent hemorrhage at the end of procedure.
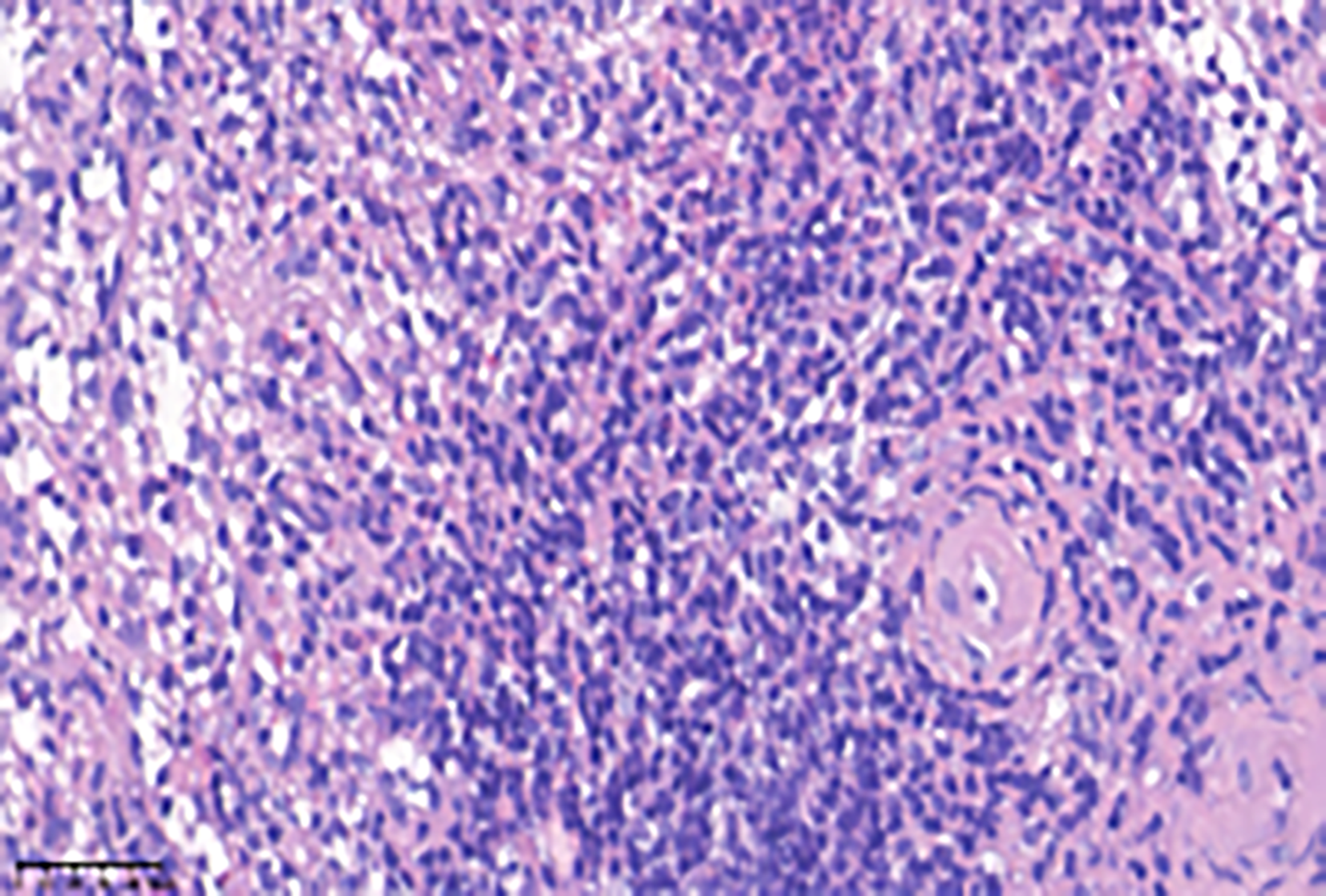
Figure 4 Histopathological findings by hematoxylin-eosin staining (40 ×).
Granulomas were noted in focal areas, accompanied by peripheral lymphoid hyperplasia involving infiltration of neutrophils, monocytes, and plasma cells.
- Citation: Pu SH, Bao WYG, Jiang ZP, Yang R, Lu Q. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided coaxial core needle biopsy for the diagnosis of multiple splenic lesions: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(2): 616-621
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i2/616.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.616