©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Aug 27, 2023; 15(8): 1591-1599
Published online Aug 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i8.1591
Published online Aug 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i8.1591
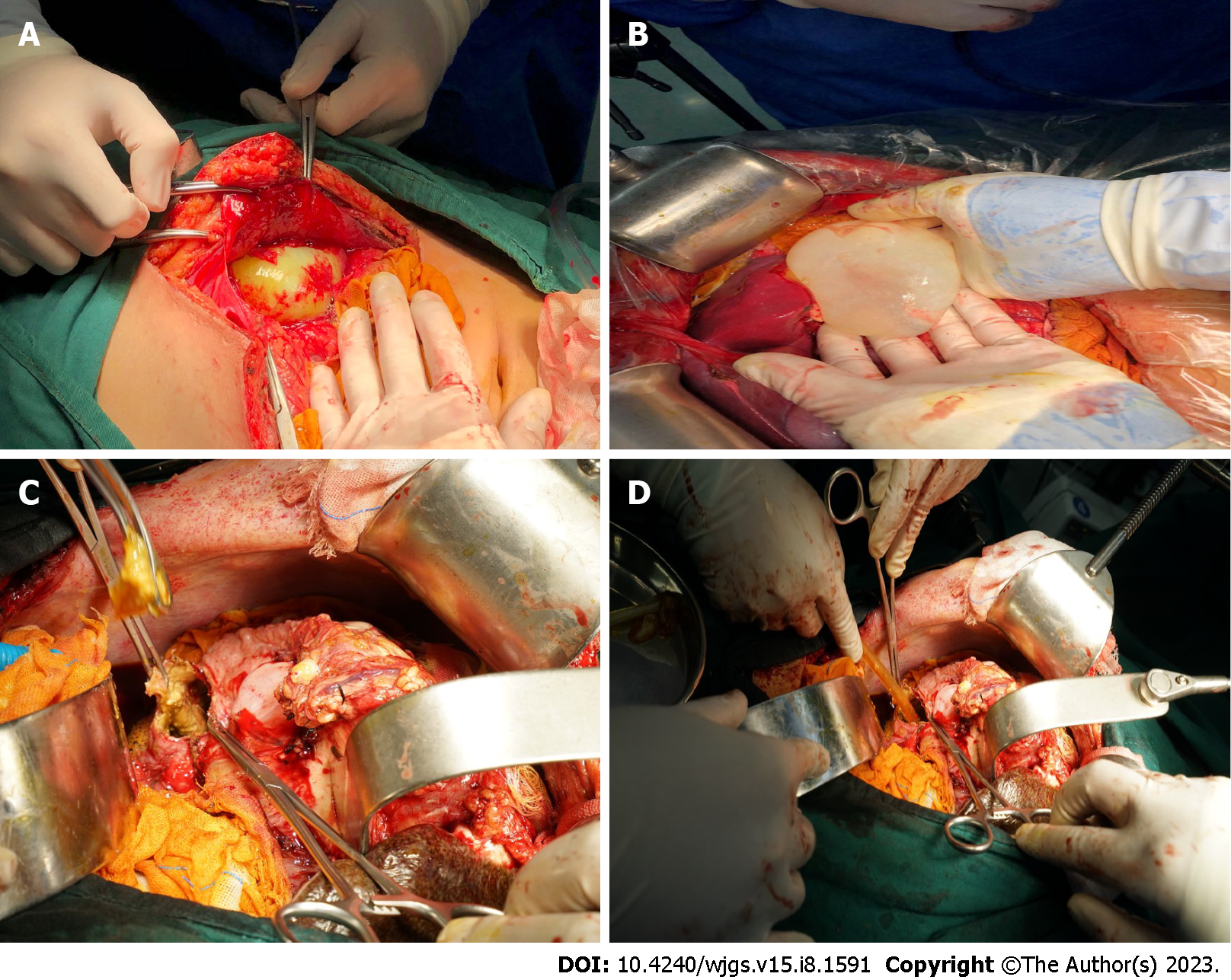
Figure 1 Excision of the internal capsule.
A: After the incision of the peritoneum, the outer capsule of cystic echinococcosis (CE) was ruptured, and the inner capsule was intact; B: The gauze soaked with iodophor was used to isolate the surrounding organs and the intact ascus was removed carefully; C: The CE cyst was large in size and dense in adhesion with the diaphragm. Therefore, we chose to perform the internal capsule enucleation and found an internal fistula in the bile duct of the hydatid cyst, and the contents of the cyst were stained with bile; D: The aspirator aspirated the contents of the capsule, the capsule was repeatedly rinsed with iodophor and wiped with gauze, and a rubber drainage tube was placed.
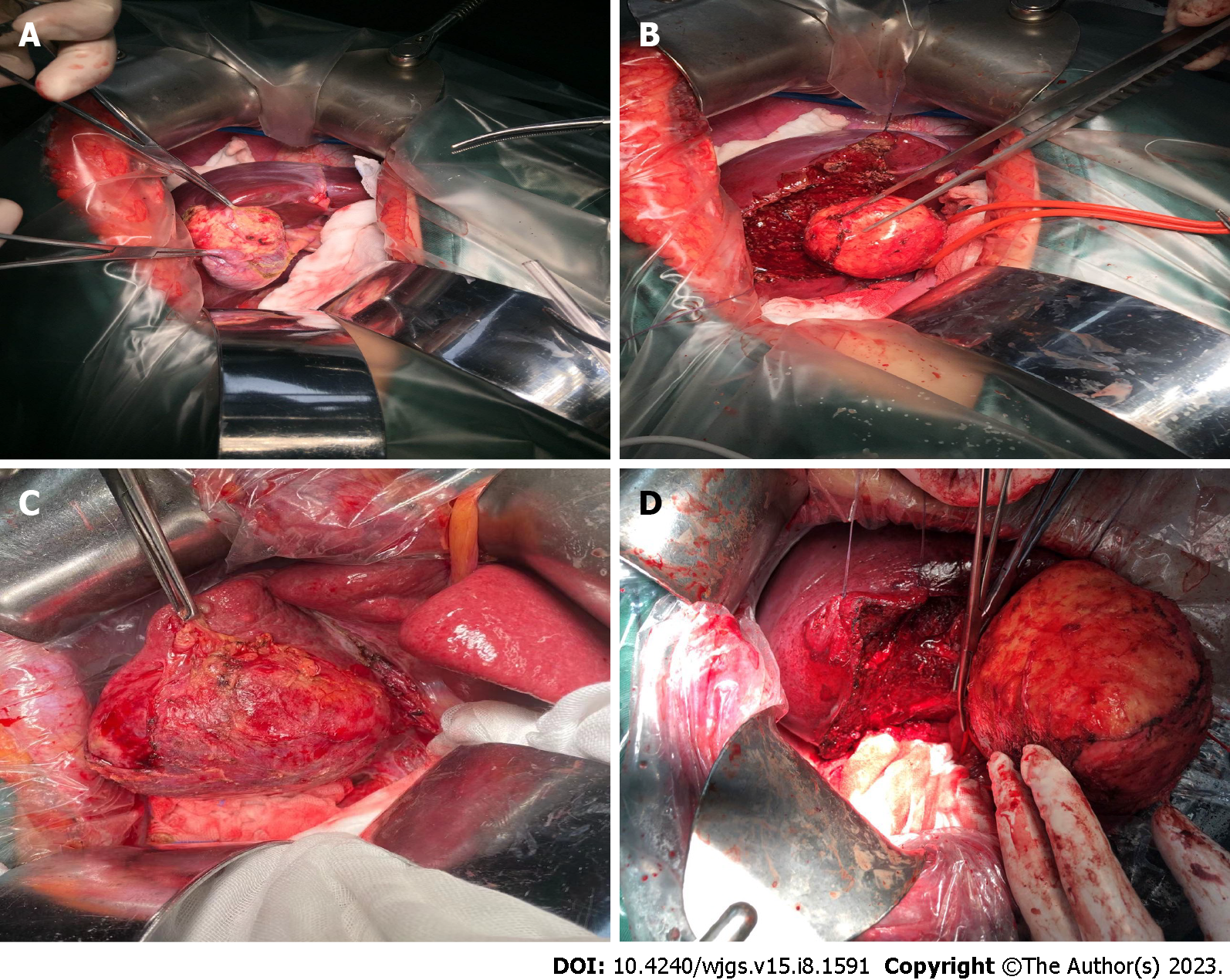
Figure 2 Total cystectomy.
A: The cystic echinococcosis (CE) cyst was located behind the gallbladder, and the lesion size was small; B: The gallbladder and CE cyst were completely removed; C: CE cyst was located in the S5 and S6 segments of the liver, with a certain distance from the first and second hilum hepatitis; D: The CE cyst was completely removed along the edge of the external capsule, and the remaining liver section was definitely hemostatic.
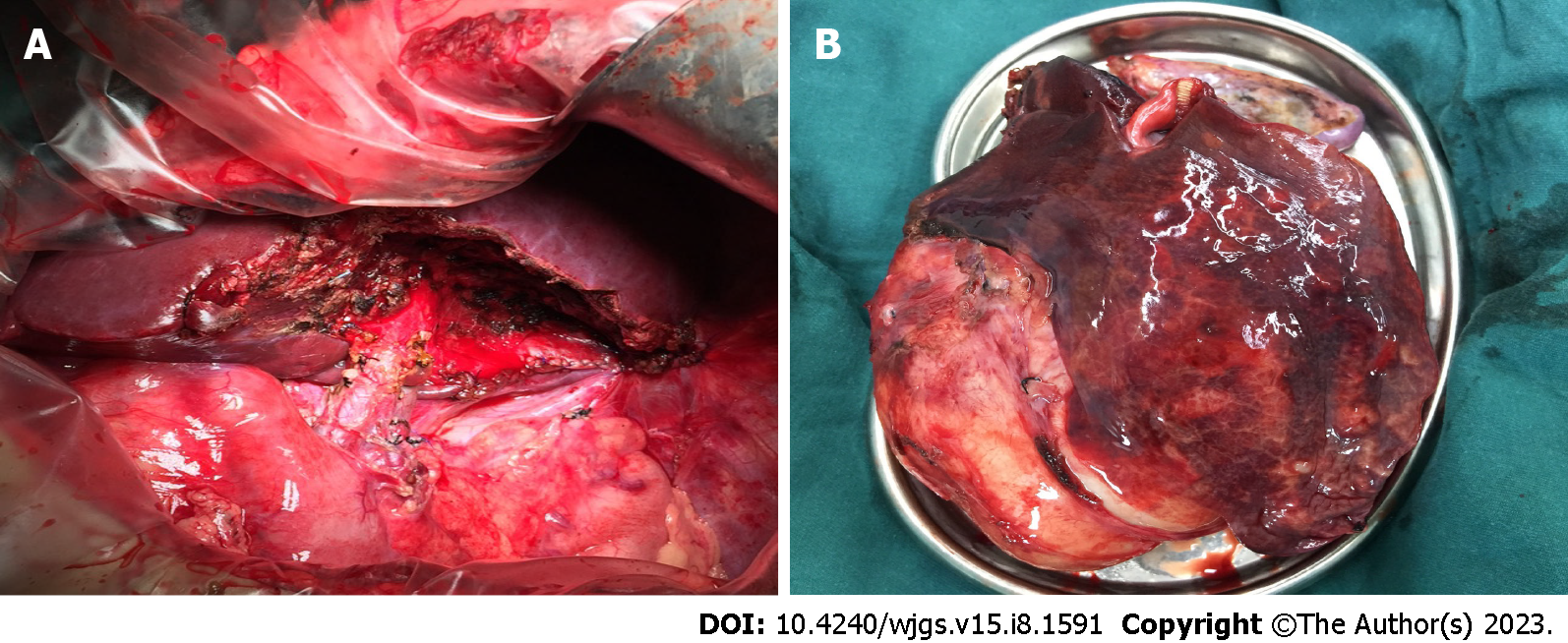
Figure 3 Partial hepatectomy.
A: Cystic echinococcosis (CE) occupied the entire S3 segment of the liver, so segmentectomy was performed; B: Some liver tissue was observed on the surface of CE.
- Citation: A JD, Chai JP, Jia SL, A XR. Historical changes in surgical strategy and complication management for hepatic cystic echinococcosis. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(8): 1591-1599
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i8/1591.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i8.1591