©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2022; 14(12): 1411-1417
Published online Dec 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i12.1411
Published online Dec 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i12.1411
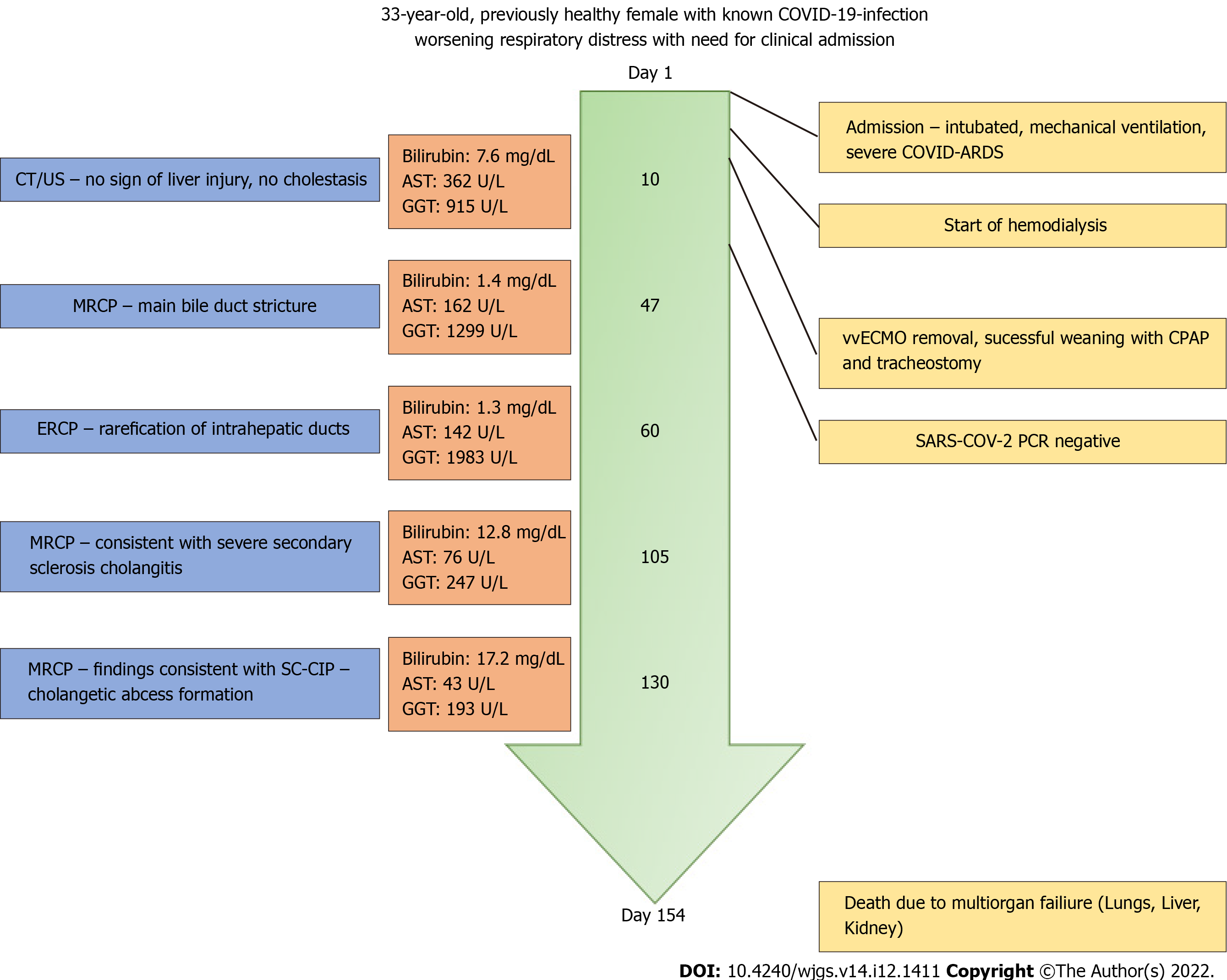
Figure 1 The chart shows the chronological timeline of patient treatment with adjacent changes in laboratory parameters and imaging as well as intensive care unit interventions.
MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
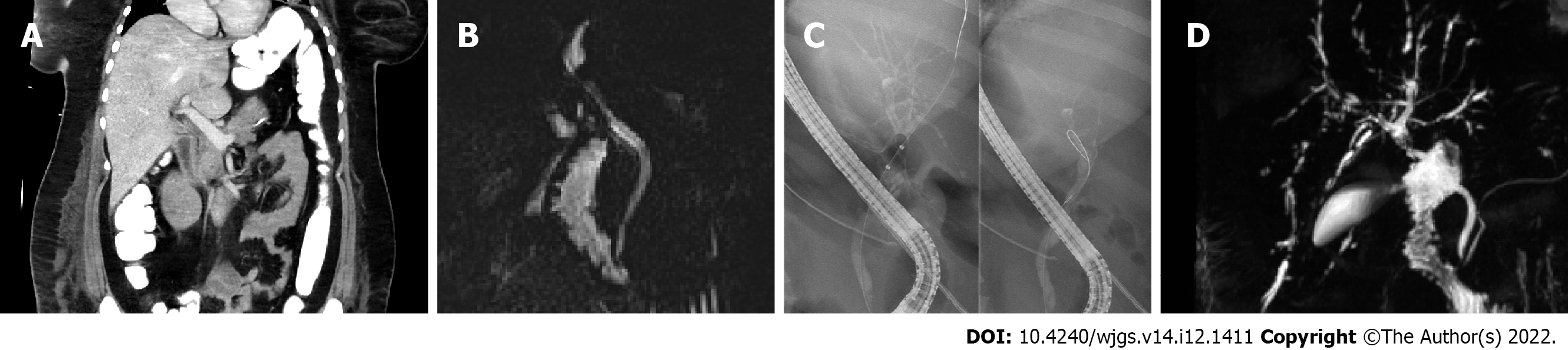
Figure 2 Imaging throughout the hospital treatment.
A: The image shows early contrast enhanced computed tomography of the upper abdomen on day 10 after admission without significant cholangetic stasis or narrowing of the common bile duct (CBD); B: A prepapillary narrowing of the CBD can be identified with at that point suspected CBD stricture (day 47); C: The image shows a rarefication of the peripheral bile ducts indicating early secondary sclerosing cholangitis on day 60; D: The image shows magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography at day 105 after admission with classical appearance of secondary sclerosing cholangitis.
- Citation: Steiner J, Kaufmann-Bühler AK, Fuchsjäger M, Schemmer P, Talakić E. Secondary sclerosing cholangitis in a young COVID-19 patient resulting in death: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(12): 1411-1417
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i12/1411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i12.1411