©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2019; 11(7): 303-307
Published online Jul 27, 2019. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v11.i7.303
Published online Jul 27, 2019. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v11.i7.303
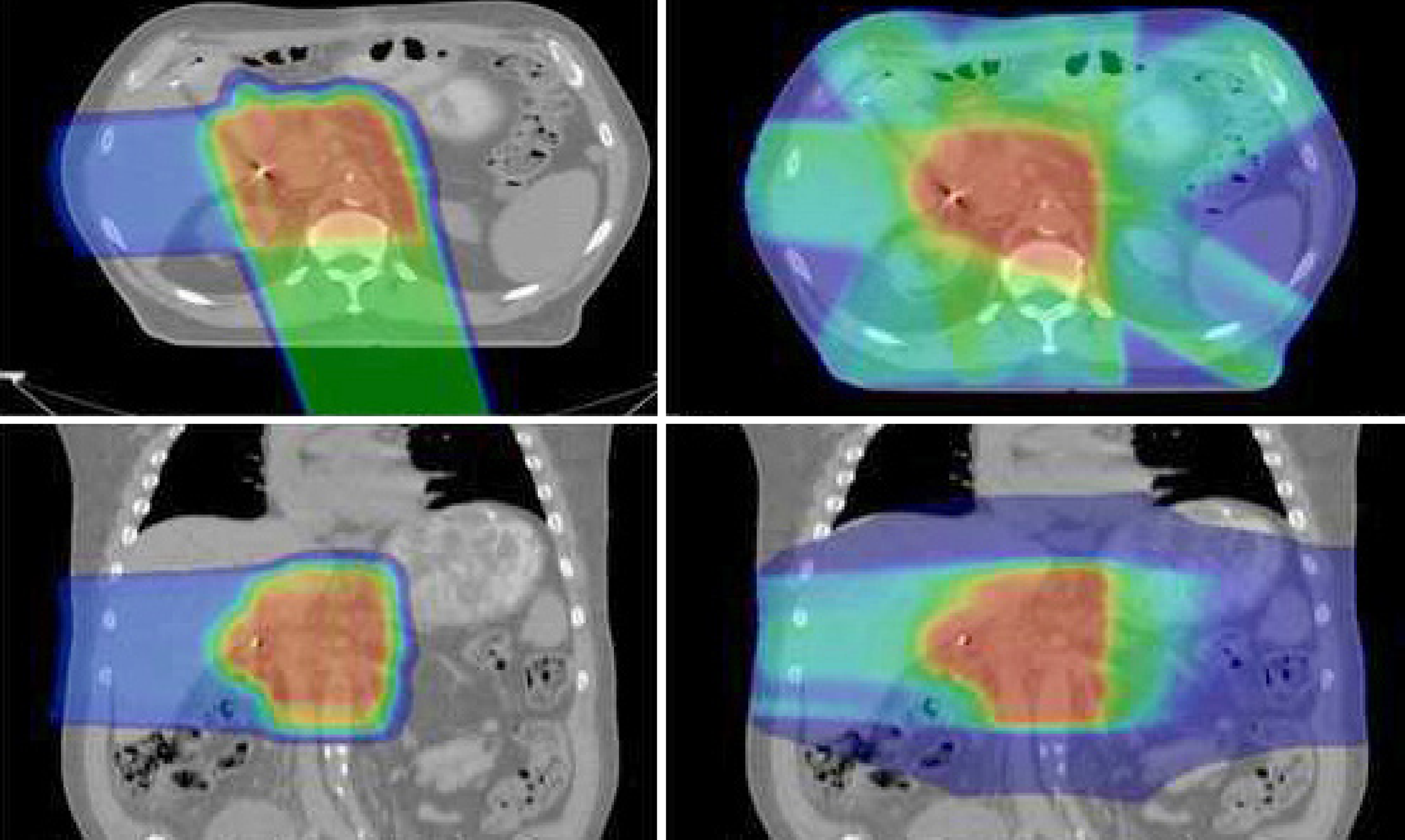
Figure 1 Images on the left side demonstrate a typical dose distribution for a patient receiving proton therapy for pancreatic cancer.
Images on the right side show corresponding dose distributions for the same patient treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT). It is evident that protons are associated with significantly less bowel and gastric exposure compared with the IMRT plan.
- Citation: Nichols RC, Rutenberg M. Optimizing neoadjuvant radiotherapy for resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer using protons. World J Gastrointest Surg 2019; 11(7): 303-307
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v11/i7/303.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v11.i7.303